* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Honors Anatomy, Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Part 1: Cells Anatomy
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
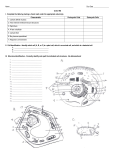
Honors Anatomy, Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Part 1: Cells Anatomy of a Generalized cell Intro 1. Draw a cell diagram including and labeling the three major cell regions (nucleus, cytoplasm, and plasma membrane). The Nucleus Intro 2. Describe the functions of the three parts of the cell nucleus. Nuclear Membrane _______________________________ protects DNA Large ___________allow RNA and proteins to leave Nucleoli Distinct grains Where _______________________________________ Chromatin ________________ form of DNA with attached _____________ Carries genes being ____________________________________ 3. Distinguish chromatin and chromosome. _________________ Fuzzy, spread out DNA ______________ during interphase ____________________ ______________________ DNA Packed in rods for ______________________________ The Plasma Membrane Intro 4. How is the structure of the plasma membrane suited to its functions. Lipid bilayer Made of ______________________________________ Separates solutions inside and outside Cytoplasm inside ________________________ between the cells Embedded proteins __________________ Allow some substances to pass _________________________ for chemical signals ________ cells together in ___________________ Specializations of the Plasma Membrane Ch. 3 Pt. 1 -1 5. Identify functions of the major specializations of the plasma membrane in relation to their structures. _____________________ Finger-like projections Provide more __________________ for transport Membrane junctions _________________________ Heavily reinforced with fibers Resist ______________________ forces Tight junctions _________________ connections between cells Prevent _______________ from going between _______________________ Tubes that connect adjacent cytoplasms Allow ____________________________ to pass The Cytoplasm Intro 6. Describe functions of the cytoplasm. Bathes organelles, allows _______________________ between Site of __________________________ Food molecules broken down Proteins assembled on _________________________ _____________________: inclusions as crystals or droplets Cytoplasmic Organelles Intro 7. Distinguish the structures and functions of the common cytoplasmic organelles. Ribosomes Grains made of __________________________________ Hold __________, line up amino acids, make peptide bonds Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Membrane system Transports; makes __________________ and proteins; storage Golgi Apparatus Stacks of membranes Accepts membranes and contents from ER; ________________; __________________________________ Lysosomes Sacs containing ________________________________ Breaks down food in food vacuoles; _________ cell components Peroxisomes Sacs with ____________________ enzymes Dispose of highly reactive substances Mitochondria Double membrane Transfer ____________ stored in food molecules to _______ Cytoskeleton ___________ microtubules and _____________ microfilaments Ch. 3 Pt. 1 -2 ______________ the cell, allows it to move and change shape Centrioles Pairs of _____________________ Helps organize the cytoskeleton, especially during cytokinesis Comparing Cells 8. What do all cells have in common? Plasma membrane to keep thins in and out and allow transport _____________________ for reaction medium and metabolism DNA to carry ___________________________ to make proteins Ribosomes to make ___________________ 9. How do animals cells specialize? Use a lot of ______________ more ________________________ _________________________ more ___________________ Generate more ______________ more ___________________ fibers _________________ a lot of proteins more ER and ____________ ________________ a lot more _____________________ Cell Physiology Membrane Transport Intro 10. Distinguish passive and active transport. _____________________ Movement from ____________________ concentration Movement by the _____________ motion of molecules _______________________ use cellular energy Examples: glucose, osmosis, O2, CO2, H+ in mitochondria Active Movement from ___________ to greater concentration Use _____________________________, often from ATP Examples: Na+, K+, phagocytosis Passive Transport Processes: Diffusion and Filtration Intro 11. How do cells change size in solutions of different concentrations? Low concentration = ___________________ solution More water outside Cell _____________________ High concentration = ____________________ Less water outside Water diffuses out, cell ____________________ Equal concentrations inside and outside = ___________ Water equal Cell _______________________________ 12. Distinguish filtration from diffusion. Diffusion ___________________ move by their random motion Ex.: ____ moving from the ________________________ Filtration Fluids and solutes ___________________ by pressure Ch. 3 Pt. 1 -3 Ex. from blood to tubule in the kidney Active Transport Processes Intro 13. How does solute pumping differ from bulk transport? Solute Pumping Active transport through a _______________________ Uses a transport protein or solute pump Bulk Transport Transport into or out of a cytoplasmic __________ Examples ____________________: out of the cell; wastes Endocytosis: into the cell; food molecules Cell Division Intro 14. What happens during the most important stages of the cell cycle? _____________________: growth and metabolism DNA replication In the middle of interphase _______ of the DNA are produced for the daughter cells Cell division __________________: division of the _______________ __________________: division of the cytoplasm Preparations: DNA Replication 15. Describe DNA structure. Two _________________ strands twisted into a ____________ Sides (backbone) held together by alternating ____________________________________________________ In opposite orientation = _______________________ AT and GC pairs fit in the ________________ ___________________ held together by hydrogen bonds 16. Predict the sequence of a complementary strand of DNA. First strand: GTGACTGAAC Opposite strand: _______________ 17. How do cells precisely copy their DNA? Complementary DNA strands __________________ Nucleotide ______________ line up Adenine (A) pairs with ____________________ (T) __________________ (G) pairs with cytosine (C) DNA _______________________ attaches nucleotides together Events of Cell Division Intro 13. Describe the major events of cell division. Mitosis ____________________ Chromosomes _____________________ Nuclear membrane is disassembled _____________________ Chromosomes _________________ across the cell Ch. 3 Pt. 1 -4 = two sister chromatids attached by the centromere Anaphase _____________________ split Sister chromatids _______________ to opposite poles _____________________: new ________________ form Cytokinesis Cleavage furrow ________________ cytoplasm in half Protein Synthesis Genes: The Blueprint for Protein Structure 19. Define gene. DNA segment carrying the instructions to make a ____________ 20. How do genes determine traits? ______________ proteins are major building blocks of cells Globular proteins serve as __________________ and receptors 21. How does DNA carry the information? Order of __________ determines order of ________________ Each 3 bases signifies an amino acid = the genetic code Each 3-base code word is a _______________ The Role of RNA 22. How is RNA used to express the information stored in DNA? __________ = messenger; copy of a gene tRNA = ___________________ Carries a specific _________________ on one end Has a specific 3-base ______________ at the other end rRNA = ribosomal; most of the ribosome structure 23. Order the steps of making a protein in an animal cell. mRNA is made on a DNA template = ______________________ _______ leaves the nucleus and attaches to a ribosome tRNA anticodon “recognizes” complementary mRNA codon tRNA-attached amino acid added to the growing chain tRNA into cytoplasm; recharged with another amino a. Ribosome _________________ mRNA adding more amino acids Cancer 24. Provide a general definition of cancer. Uncontrolled _______________________ that may spread throughout the body 25. Differentiate benign and malignant tumors. Benign A __________________, encapsulated, ________-growing mass Rarely kill unless they compress organs Malignant _________-growing, non-encapsulated mass Cells _____________________, travel in bloodstream = metastasis 26. Rate the causes of cancer. _____________________ 30-35% ______________________ 25-30% _____________________ 15-20% ______________________ 10% ______________________ 5-10% Ch. 3 Pt. 1 -5