* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5/e
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Oligonucleotide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
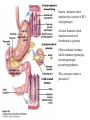
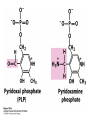
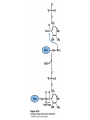
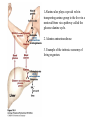
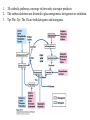
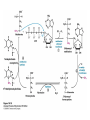
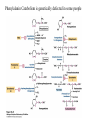
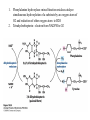
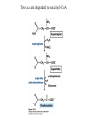
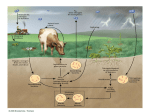
David L. Nelson and Michael M. Cox LEHNINGER PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY Fifth Edition CHAPTER 18 Amino Acid Oxidation and the Production of Urea © 2008 W. H. Freeman and Company Introduction 1. In animal, AA undergo oxidative degradation in three different metabolic circumstance - The normal degradation of cellular protein - A diet is rich in protein - When carbohydrates are either unavailable, cellular proteins are used as fuel 2.AA lose their amino groups to form a-keto acid 3.a-keto acid undergo oxidation to CO2 and H2O 4.a-kteo acid can converted by gluconeogenesis into glucose, the fuel for brain, skeletal muscle, and other tissue 5.AA acid contains an amino group and thus aa degradation include a key step in which the a-amono group is shunted into the pathways of amino group metabolism Overview of aa catabolism in mammal Amino group catabolism 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Most aa are metabolized in the liver The ammonia generated in this process is recycled and used in a variety of biosynthetic pathway The excess is either excreted directly or converted to urea or uric acid for excretion Excess ammonia generated in other tissues travels to the liver for conversion to the excretory form In cytosol of hepatocytes, amino groups are transferred to a-KG to form Glu, which enter to Mito. To form the ammonia Excess ammonia from most other tissue is converted to the amide nitrogen of Gln which pass to liver In skeletal muscle, excess amino groups are tranffered to pyruvate to form alanine Gastrin : hormone which stimulate the secretion of HCl and pepsinogen Secretin: hormone which stimulate secretion of bicarbonate by pancreas Cholecystokinin: hormone which stimulate trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen, procarbosypeptidases Why zymogens (inactive precursors)? 1.First step is removal of the a-amino groups by aminotranferase 2. In this transamination reaction, the aamino group is transferred to the a-carbon atom of a-ketoglutarate 3. The glutamate then functions as the amino group donor for biosynthetic pathways or for excretion pathway 4. Amino transferase contain the prosthetic group, pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) 5. PLP is covalently bound to lysine through aldimine (Schiff base) 6. Aminotransferases are classic example of ping-pong reaction. 1.In hepatocyte, glutamate is transported from the cytosol into mitochondria, where it undergoes oxidative deamination catalyzed by glutamate dehydrogenase. 2. Combined action of an aminotransferase and glutamate dehydregenase is referred to as transdeamination. 3. a-kg can be used in citric acid cycle. 1.Ammonia is quite toxic to animal tissue and thus much of free ammonia is converted to a nontoxic compound before export from the extrahepatic tissues into the blood. 2. The free ammonia in tissues is combined with glutamate to yield glutamine by glutamine synthetase. 3. Glutaminase 1.Alanine also plays a special role in transporting amino group to the liver in a nontoxid from via a pathway called the glucose-alanine cycle. 2. Alanine aminotransferase 3. Example of the intrinsic economy of living organism. 1.The ammonia deposited in the mitochondria of hepatocytes is converted to urea in the urea cycle 2. Urea production occurs almost exclusively in the liver . 3. The urea passes into the blood stream and thus to the kidneys and is excreted into the urine 4. Five enzymatic steps: two steps in mito. And three steps in cyto. 5. Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I 6. Orninthin transcarbamoylase 7. Arginosuccinate synthetase 8. Argrinosuccinase 9. Arginase Nitrogen-acquiring reactions in the synthesis of urea. 1. 2. 3. 4. The citric acid cycle and urea cycle are interconnected through common intermediate, fumarate. Communication depends on the transport of key intermediates between Mito. and Cyto. Fumarate from the urea cycle is transported to Mito. and can be enter the citric acid cycle. Aspartate from the citric acid cycle is transported to cytosol and can transfer amino group to citrulline Regulation of the urea cycle 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. When the dietary intake is primarily protein, the carbon skeletons of amino acid are used for fuel, producing much urea from the excess amino group During prolong starvation, when breakdown of muscle protein begins to supply much of the organism’s metabolic energy, urea production increases The activity of the urea cycle is regulated at two level: long term and short term regulation Long term by regulation of the rates of synthesis of urea cycle enzyme Short term by allosteric activation of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I by N-acetylglutamate Pathway interconnections reduce the energetic cost of urea synthesis 1. The synthesis of urea requires four high-energy phosphate groups. - Two ATP molecules are required to make carbamoyl phosphate - Two for making arginosuccinate 2. The urea cycle also causes a net conversion of oxaloacetate to fumarate (via aspartate), and the regeration of axaloacetate produces NADH . 3. Each NADH can generate up to 2.5 ATP , greatly reducing the overall energetic cost of urea synthesis. 1. People with genetic defects in any enzyme involved in urea formation cannot tolerate protein-rich diets 2. A protein-free diet is not treatment option because humans are incapable of synthesizing all a.a. and these essential a.a must be provided in the diet. 1. 2. 3. 4. Careful administration of the aromatic acids benzoate or phenylbutyrate in the diet can help lower the level of ammonia in the blood Benzate is converted to benzyolCoA, which combines with glycine to form benzoylglycine Phenylacetyl-CoA combines with glutamin to form phenyacetylglutamine. Both products are nontoxic compounds that are excreted in the urine. 1. 20 catabolic pathways converge to form only six major products 2. The carbon skeletons are diverted to gluconeogenesis, ketogenesis or oxidation 3. Trp, Phe, Tyr, Thr, Ile are both ketogenic and transgenic. 1. 2. 3. Two reactions are important for a.a catabolism Transamination: PLP One carbone transfer: Biotin (CO2), THF (intermediate oxidation state), SAM (most reduced state, methyl group) Six a.a are degraded to pyruvate Seven a.a are degraded to acetyl-CoA Phenylalanin Catabolism is genetically defected in some people 1. 2. Phenylalanine hydroxylase: mixed function oxidase catalyze simultaneous hydroxylation of a substrate by an oxygen atom of O2 and reduction of other oxygen atom to H2O Tetrahydrobiopterin : electron from NADPH to O2 Five a.a are degraded to a-ketoglutarate Four a.a are degraded to succinyl-CoA Two a.a are degraded to succinyl-CoA