* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transamination, Deamination,urea cycle
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
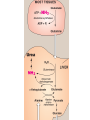
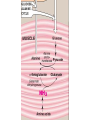
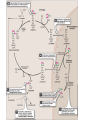
Transamination, Deamination,urea cycle 24-5-13 • Transamination & deamination reactions Transamination • α- ketoglutrate plays vital role in amino acid metabolism by accepting amino groups from most amino acids becoming glutamate • Glutamate become deaminated or used in the formation of non essential amino acids • location • exception of lysine & threonine Most important Amino Transferases • ALT: transfers amino group of alanine to alpha-ketoglutrate hence forming pyruvate & glutamate • AST: transfers amino groups from glutamate to oxaloacetate forming aspartate ( N source in urea cycle) • Plasma ALT, AST can be elevated in hepatic and non hepatic diseases i.e. Myocardial and muscle disorders • Deaminations Glutamate dehydrogenase causes the oxidative deamination of amino acids liberation free ammonia (NH3) • Glutamate ---the only amino acid that undergoes rapid oxidative deamination • NAD+ or NADP+ as a coenzyme • (GTP) is an allosteric inhibitor of glutamate dehydrogenase, whereas (ADP) is an activator • When energy levels are low in the cell, amino acid degradation by glutamate dehydrogen ase is high, facilitating energy production Urea cycle • first two reactions leading to the synthesis of urea occur in the mitochondria, whereas the remaining cycle enzymes are located in the cytosol • One nitrogen of the urea molecule is supplied by free ammonia, and the other nitrogen by aspartate Ammonia disorders • The two major causes of hyperammonemia (with its CNS effects) are liver disease and inherited deficiencies of enzymes (such as ornithine transcarbamolyase) in the urea cycle Overall stoichiometry of the urea cycle • Aspartate + NH3+ CO2+ 3 ATP + H2O → urea + fumarate + 2 ADP + AMP + 2 Pi + PP