* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Werkstuk Biologie The Tongue <strong style="line
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of human intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
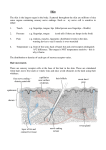
Werkstuk Biologie The Tongue <div> <strong style="line-height: 1.5em;">Taste buds: </strong>The taste buds are nerve endings on the tongue that are stimulated by substances in food. The nerves send this information to the brain. The brain takes this information up and translate it as a taste perception. </div> Your taste buds can distinct five flavours: <ol> <li>Sweet </li> <li>Bitter</li> <li>Salty</li> <li>Umami</li> <li>Sour</li> </ol> <strong style="line-height: 1.5em;">In the middle of the tongue you can’t savour good because there are less taste buds than on the other sides.</strong> Taste buds contain the receptors for taste. They are located around the small structures on the upper surface of the tongue, soft palate, upper esophagus, the cheek, epiglottis, which are called papillae. This structures can taste five elements. (see the picture left under) The receptors send signals to the brain through the sensory neurons to the interneurons and get the response from the motorneurons. <strong style="line-height: 1.5em;">The tongue of the giraffe in comparing with the tongue of a human.</strong> Did you ever thought about the length of your tongue? And did you know that the color of the tongue of a giraffe is grey/blue? The human tongue is longer than you see, the tongue of an average human is about 4.28 centimeter long. An funny fact is that the longest tongue is of Stephen Taylor, his tongue is 9,8 centimeter long! But in comparing with the tongue of a giraffe It’s just about 45-50 centimeter! That’s about ten times as much as the tongue of Stephen Taylor! And about eleven times as much as an average humans tongue! By humans the digestion of food is not the only task of the tongue, it also helps a lot by the articulation of making sounds and words, by a giraffe of course not. Another funny thing is the color of the tongue, by humans is the tongue pink or red, but by a giraffe its grey/blue! on the picture below you see the tongue of a giraffe, his tongue is very long en grey/blue. <strong style="line-height: 1.5em;">Conclusion:</strong> It looks simple how you can taste but if you really knows how your body works it looks more difficult. You get a stimulus that goes to your sensory receptors (taste buds). In the taste buds the taste receptors picks up the signal and send through the sensory neurons to the brain (to the interneurons). The interneurons send another signal back through the motorneurons to the effectors, the effectors gives the response (by de tongue is that you can taste what you are eating)