* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit-2-vocab-2015
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
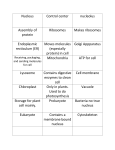
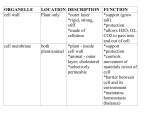
Name_________________________Date_____________________Bell__________ Unit Two: Cells Vocabulary ______1. Active transport (pg 59) ______2. Cell (pg 19) ______3. Cell membrane (pg 35) ______4. Cell Theory (pg 30) ______5. Cell wall (pg 35) ______6. Chloroplast (pg 40) ______7. Cytoplasm (pg 37) ______8. Diffusion (pg 57) ______9. Endoplasmic Reticulum (pg 40) ______10. Eukaryote (pg 41) ______11. Lysosome (pg 41) ______12. Mitochondrion (pg 37) ______13. Multicellular Organism (pg 19) ______14. Nuclear membrane (pg 36) ______15. Nucleus (pg 36) ______16. Organ (pg 311) ______17. Organ system (pg 475) ______18. Organelle (pg 35) ______19. Osmosis (pg 28) ______20. Passive transport (pg 59) ______21. Prokaryote (pg 41) ______22. Ribosome (pg 40) ______23. Selectively Permeable (pg 56) ______24. Tissue (pg 252) ______25. Unicellular Organism (pg 19) ______26. Vacuole (pg 41) A. Allows the movement of substances, especially oxygen, water, food molecules, carbon dioxide, and waste products, into or out of the cell B. Commonly found in animal cells, small, round, with a membrane, breaks down larger food molecules into smaller molecules, digests old cell parts C. Consists of three main parts: Cells are the basic units of life, all organisms are made from cells, all cells come from other cells D. Diffusion of water through a membrane. E. Found in both plant and animal cells, bean-shaped with inner membranes, breaks down sugar molecules into energy F. Found in both plant and animal cells, clear, thick, jellylike material and organelles found inside cell membrane, supports /protects cell organelles G. Found in both plant and animal cells, large oval shape, controls cell activities H. Found in both plant and animal cells, network of tubes or membranes, carries materials through cell I. Found in both plant and animal cells, selectively permeable, support, protection, controls movement of materials in/out of cell, barrier between cell and its environment, maintains homeostasis J. Found in both plant and animal cells, small bodies free or attached to the E.R., produce proteins K. Found in both plant and animal cells, surrounds nucleus, selectively permeable, controls movement of materials in/out of nucleus L. Found in few/large plant cells and small animal cells, fluid-filled sacs, store food, water, waste (plants need to store large amounts of food) M. Found in plant cells, not animal, outer layer, rigid, strong, stiff, made of cellulose, support (grow tall), protection, allows H2O, O2, CO2 to pass into and out of cell N. Found in plant, not animal cells, green, oval usually containing chlorophyll (green pigment), uses energy from sun to make food for the plant (photosynthesis) O. Made up of cells that are similar in structure and function and which work together to perform a specific activity. P. Made up of organs that are similar in structure and function and which work together to perform a specific activity. Q. Made up of tissues that work are similar in structure and function and which together to perform a specific activity. R. Movement of molecules from a less crowded to a more crowded area WITH the use of energy. Molecules are "carried" into or out of the cell using some of the cell's energy. S. Movement of molecules from a more crowded to a less crowded area WITHOUT the use of energy T. Movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. U. Organism whose cells do contain a nucleus V. Organism whose cells do not contain a nucleus W. Organisms made of many cells (example sponge) X. Organisms made of one cell (example amoeba) Y. The most basic or primary level of cellular organization Z. Tiny cell structure that carries out a specific function within the cell