* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution by Natural Selection
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary landscape wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary mismatch wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
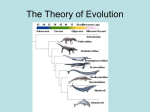
Evolution by Natural Selection Scientific Theory An explanation of natural phenomenon supported by a large body of scientific evidence obtained from many different investigations and observations Evolution A gradual change in a species (populations) through adaptations over time Charles Darwin “Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection” Proposed that new species could develop by a process of natural selection. Charles Darwin • Natural selection: When better adapted organisms survive to produce a greater number of viable offspring. • This has the effect of increasing their proportion in the population so they become more common Darwin’s studies • Studied animal species in the Galapagos Islands and found they each had unique adaptations – Galapagos finches demonstrate different adaptations to eat different foods – Galapagos turtles are the largest on earth Natural Selection • A mechanism for change in a population • Natural Selection (N.S.) is responsible for most evolutionary change by selectively changing genetic variation through differentiated survival and reproduction • Goal – To be fit “enough” to survive and reproduce How does natural selection produce change in a population? 3 types of natural selection 1. Stabilizing Selection • Favors average individuals in a population • Those individuals have a “selective advantage” • Reduces variation in a population 2. Directional Selection • Favors one of the extreme variations of a trait • Can lead to rapid evolution of a population 3. Disruptive Selection • Favors both extreme variations of a trait • Leads to evolution of two new species Speciation • A process of producing two individual species from one – Members of the 2 species no longer interbreed within their natural environment Evidence for Evolution 1. Structural Adaptations • Methods of protection • • • Teeth, claws, thorns Mimicry Camouflage 2. Physiological Adaptations: • Changes in an organism’s metabolic processes • Resistance to antibiotics or chemicals 3. Fossils: • Provide a record of early life and evolutionary history 4. Anatomy: • • • Structural features with a common evolutionary origin are called homologous structures. The body parts of organisms that do not have common evolutionary origins but are similar in function are called analogous structures. A vestigial structure does not have current function but may have been useful to an ancestor 5. Embryology: • Similarities among the young embryos suggest evolution from a distant, common ancestor 6. Biochemistry: • Comparing DNA and RNA How do we know what happened when? 1. Radiometric dating relies on half-life decay of radioactive elements to allow scientists to date rocks and materials directly. 2. Stratigraphy provides a sequence of events from which relative dates can be extrapolated. 3. Molecular clocks allow scientists to use the amount of genetic divergence between organisms to extrapolate backwards to estimate dates. What’s important from all these notes? V I S T = variation = inheritance = selection = time