* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Natural Selection and the Evidence for Evolution
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
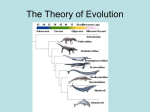
Natural Selection and the Evidence for Evolution Review Galapagos tortoises are the largest on Earth Differing from other tortoises in body size and shape The beak of this Galapagos finch Is adapted to feed on cacti Galapagos marine iguanas eat algae Fro the ocean, an unusual food source For reptiles. Large claws help them cling to slippery rocks. ~ Studying the specimens made Darwin curious about possible relationships among species. ~ His studies provided the foundation for his theory of evolution by natural selection I. Darwin Explains Natural Selection A. In nature, organisms produce more offspring than can survive. Fishes, for example, can sometimes lay millions of eggs. B. In any population, individuals have variations. Fishes, fore example, may differ in color, size, and speed. C. Individuals with certain useful variations, such as speed, survive in their environment, passing those variations to the next generation. D. Over time, offspring with certain variations make up most of the population and may look entirely different from their ancestors. ~ Natural Selection is a mechanism for change in population. ~ It occurs when organisms with favorable variations survive, reproduce, and pass their variations to the next generation. Foldable Purpose: Make the following foldable to help you analyze and critique evidence supporting the theory of evolution Indirect ~ Structural adaptations II.such Adaptations as the teeth and claws of mole-rats are often used to defend against predators. ~ Some adaptations of other organisms that keep predators from approaching include a rose’s thorns or a porcupine's quills. ~ these may take Millions of years To develop. Some adaptations are subtle. Mimicry is a structural adaptation that enables one species to resemble another species. Another subtle adaptation is camouflage, an adaptation that enable species to blend with their surroundings Structural Adaptations arise over time According to Darwin’s theory, adaptations in species develop over many generations. Dot Demonstration: Using the white paper, use the hole punch to make a minimum of 20 holes. Using the black paper, use the hole punch to make a minimum of 20 holes. (follow teacher verbal direction) • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yuUi2E3t3UY ~ Physiological adaptations can develop rapidly. ~ Physiological adaptations are changes in an organisms metabolic processes. Kudzu: plant that grows 12 inches each day. Does not take over or kill anything, competes for sunlight from other plants Antibiotics can be used So much that bacteria become Familiar with its response, Changing how it operates ~ Fossils provide a record of early life and evolutionary history. ~ Example: Fossils of whale ancestors were probably land-dwelling, doglike animals. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8cn0kf8mhS4 ~ Although the fossil record provides evidence that evolution occurred, the record is incomplete. ~ Even though they do not have all the fossils for all the animals they can understand an overall picture of how most groups evolved. ~ Looking at the anatomy of organisms, biologist can view structural similarities as evidence that organisms evolved from a common ancestor. ~ It would be unlikely for so many animals to have similar structures if each species arose separately. ~ Homologous structures are features with a common evolutionary origin. ~ Similar in arrangement, in function or in both. ~ The structural or functional similarity of body feature doesn’t always mean that two species are closely related. These are analogous structures. ~ The body parts of organisms that do not have a common evolutionary origin but are similar in function are called analogous structures. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Edcz_MzM5qc ~ Embryo is the earliest state of growth and development of both plants and animals. ~ At this stage all embryos have a tail and pharyngeal pouches. ~ In fish these pouches form into gills but in mammals, reptiles and birds they develop into ears. ~ Biochemistry provide strong evidence for evolution. ~ Nearly all organisms share DNA, ATP and many enzymes among their biochemical molecules. ~ Groups that share more similarities are interpreted as being more closely related or as sharing a closer ancestor. Interactives http://www.sciencechannel.com/games-andinteractives/charles-darwin-game/ http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/sortingfinch-species Homework questions 1. Briefly explain Darwin’s ideas of natural selection. 2. Some snakes have vestigial legs (legs during embryo but not when born). Why is this considered evidence for evolution? 3. Explain the difference between mimicry and camouflage. Now explain how it helps them to survive. 4. How do homologous structures provide evidence for evolution?