* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endocrinology 3
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
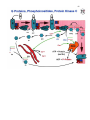
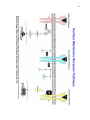
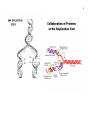
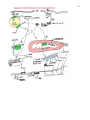
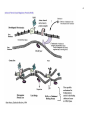
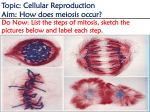
45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 Oncogenesis - Chemical Signalling and Cancer Tumor Benign (self contained) Malignant (migratory, prone to seeding tumors at other sites) Hypertrophy - hypertrophic cells; hyperplastic tissue Neoplasia - new, often irregular, growth or tissue Protooncogenes = Normal gene precursors of oncogenes I V Mutational Agents I V Oncogenes = Gene associated with abnormal cell growth Oncogene Product = Expressed protein coded by an oncogene Mutagens Radiation, Chemical - tend to be small changes, insertions, deletions, or base changes Chromosome Rearrangements (in meiosis) - can be large changes, deletions, inversions Viral Rearrangement - viruses can become lysogenic and excise and carry genes or foreign promoter DNA to subsequent cellular hosts where these insert into nonhomologous sites and are expressed in a non-regulated or inappropriately regulated fashion, often leading to oncogenesis via disruption of the normal events of the cell cycle or cell cycle regulatory points. 54 55 56 57 58 59 106) Steroid Hormones of the Reproductive System ~ http://users.rcn.com/jkimball.ma.ultranet/BiologyPages/S/SexHormones.html 60 61 62 63 64 65 Reproduction Meiosis Spermatogenesis, testicular anatomy and function Oogenesis, ovarian anatomy and function Process of fertilization, implantation, gestation, lactation 113) Images from Veterinary Reproductive Endocrinology http://www.ansci.cornell.edu/courses/as300/images300.htm Cell Division Mitosis 2n -----> 2 x 2n Replicative, simple cell division Interphase 2n Prophase DNA synthesis, nuclear envelope breakdown, centrioles replicate and move to poles, beginning of spindle formation Metaphase 4n Alignment of all chromosomes on metaphase plate Anaphase Telophase Separation and cytokinesis Meiosis I 2n Replication Division Interphase DNA synthesis and crossing-over Prophase Metaphase 66 Anaphase Telophase 2 x 2n II Reductive Division Prophase No DNA replication Metaphase Anaphase Telophase 4 x 1n 67 68 118) Gametogenesis Outline http://www.rci.rutgers.edu/%7Euzwiak/HumanSexuality/HSSpringLect4.html