* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mock Exam 2 BY 123 - Cusic Supplemental Instruction
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium in biology wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
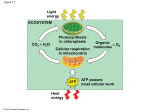
Mock Exam 2 BY 123 - Cusic Supplemental Instruction 1. Which of the following are in accordance with the laws of thermodynamics? a. Energy can’t be create be destroyed. b. Things in nature move toward increasing Entropy. c. Entropy of a system may increase as long as the total entropy of the universe increases. d. Both A and B e. All of the above 1. Conservation of Energy - Energy cannot be created or destroyed. 2. Free energy is declining. Things in nature go towards disorder or randomness or an increase in Entropy. If the entropy of a system increases then the total entropy of the universe must decrease 2. Spontaneous reactions require _________ and __________. a. energy input/ the stability of the system increases b. no energy input/ the stability of the system decreases. c. no energy input/ the stability of the system increases. d. energy input/ the stability of the system decreases. Exergonic – Spontaneous or favored reaction, delta G less that 0… energy released/ no energy added stability increases Endergonic – Nonspontaneous, delta G greater than 0…. had to add energy/ stability decreases 3. Changes in free energy are directly proportional to _________ and inversely proportional to ________. a. Entropy/ Enthalpy b. Disorder/ Heat c. Enthalpy/ Entropy d. None of the above As H increases so does delta G…. as S increases delta G decreases 4. If an enzyme in solution is saturated with substrate, the most effective way to obtain a faster yield of products is to _________. a. heat the solution to 90 C b. add more substrate c. add a non competitive inhibitor d. add an allosteric inhibitor f. add more of the enzyme. The only way to turn more substrates into products is by adding more enzymes so the substrates can bind to the active sites and be converted into products 5. Enzymes are known as biological catalyst and _____________. a. Increase delta G b. Decrease delta G. c. Increase activation energy d. Decrease activation energy. Catalysts only have kinetic properties… they don’t mess with themodynamics 6. Enzymes can turn __________. a. Monosaccharaides into disaccharides b. Disaccharides into monosaccharaides. c. ADP into ATP. d. ATP into ADP. e. A and B only f. All of the above 7. Enzymes can be affected by ___________. a. Salt concentration b. pH c. Increase in temperature d. Decrease in temperature e. Only A B and C f. All of the above Temperature – denaturing of protein pH – pepsin, trypsin Salt Concentration – ions can alter the activity of enzymes 8. A molecule is added to a reaction containing enzymes and substrates. The molecule binds away from the active site and changes the shape of the enzyme’s active site. This molecule is an example of a _____________. a. Competitive inhibitor. b. Non-competitive inhibitor. c. Additional enzyme d. A cofactor Noncompetitive inhibitors do not bind to the active sit but to somewhere else that ultimately changes the s of the active site which in turn does not allow the substrate to fit in the active site 9. How many ATP’s are made from substrate level phosphorylation in glycolysis? a. 2 b. 4 c. 1 d. 3 2 1,3 Bisphosphoglycerates to 3 phosphoglycerate ………….. 2 PEPs to Pyruvate Direct coupling of a step in a catabolic reaction to make ATP by enzymatic transfer of the phosphate to ATP. Take phosphate from a substrate and puts it on an ADP making it an ATP. 10. What is the reducing agent in the following reaction? Pyruvate +NADH + H+ Lactate + NAD+ a. Oxygen b. NADH c. NAD+ d. Lactate e. Pyruvate Reducing agents get oxidized 11. Which metabolic pathway is common to both fermentation and cellular respiration of a glucose molecule? a. the citric acid cycle b. the electron transport chain c. glycolyis d. synthesis of acytyl COA from pyruvate e. reduction of pyruvate to lactate Glycolysis occurs weather oxygen is present of not 12. True or false Glycolysis can occur only in the presence of oxygen? False Glycolysis can occur in the presence or absence of oxygen (fermentation) 13. The process of glycolysis takes place in the _______ of the cell and results in the creation of 2 ________ carbon molecules of ___________. a. Mitochondria, 3 ,G3Ps b. Cytosol, 2, Pyruvates c. Mitochondria, 3, Pyruvates d. Cytosol, 3, Pyruvates 14. The first 3 reactions of Glycolysis involve what kind of enzymes (from first to last)? a. Isomerase, kinase, kinase (PFK) b. Kinase, kinase, Isomerase c. Isomerase, kinase, Isomerase d. Kinase, Isomerase, Kinase (PFK) 15. A ________ enzyme is used to convert a molecule of _________ into G3P in glycolysis in order to enter the energy payoff phase of Glycolysis. a. Dehydrogenase, Pyruvate b. Kinase, Glucose c. Isomerase, PEP d. Isomerase, Dehydroxy acetone phosphate 16. As a result of glycolysis how many NADH’s, gross ATP ‘s, and net ATP’s are made per G3P molecule? a. 2/2/4 b. 1/2/1 c. 2/1/2 d.1/2/1 2 NADH/ 4 gross ATP/ 2 NET ATP 17. The movement of Pyruvate into the Mitochondria is a(n) _________ form of transport? a. Passive b. Active c. Cytosolic d. Cooperative Pyruvate is a charged molecule so in eukaryotic cells it must enter the mitochondrion via active transport by way of a transport protein 18. ____________ connects coenzyme A onto pyruvate making it very reactive? a. Oxygen b. ATP c. Carbon dioxide d. Sulfur 19. How many electron carriers are produced by the oxidation of 4 pyruvate molecules? a. 2 NAD+ b. 4 NAD+ c. 4 NADHs d. 8 NADHs 20. Acteyl- COA meets with __________ to become _________ in the Krebb’s Cycle a. Isocitrate, Citrate b. Oxaloacetate, Succinyl- Coa c. Isocitrate, Succinyl-Coa d. Oxaloacetate, Citrate 21. How many FADH2s are generated if 7 Acetly COA’s were added to the mitochondria of a cell? a. 14 b. 7 c. 21 d. 28 22. The complete oxidation of 8 glucose molecules would take _____ turns of the Krebb’s Cycle? a. 8 b. 24 c. 12 d. 16 23. What class of enzyme is responsible for moving phosphate groups? a. Kinase b. Isomerase c. Dehydrogenase d. None of the above 24. What class of enzyme is responsible for the movement of electrons? a. Kinase b. Isomerase c. Dehydrogenase d. None of the above 25. What is reduced in the photosynthesis reaction? 6CO2 + 6H20 C6H12O6 + 602 a. CO2 b. H20 c. C6H12O6 d. 02 26. In humans the process of fermentation results in the creation of __________ from ___________. a. NADH / lactate b. ethanol / pyruvate c. lactate /pyruvate d. ATP / lactate Bateria make ethanol 27. A soft drink provides 5 molecules of Citric acid, how many ATP’s are made from substrate level phosphorylation? a. 8 b. 10 c. 5 d. 7 1 ATP is made from each turn of the Krebb’s cycle 28. How many CO2 molecules enter per turn of the Calvin cycle? a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 6 29. The color _____________ contains the _____________ energy and the ___________ wavelength. a. Indigo/ highest/ shortest b. Red/ lowest/ longest c. Violet/ highest/ longest d. Green/ lowest/ highest ROYGBIV Violet = Highest energy… and shortest WL 30. The ___________ ring is found in the _________ of a cell and contains _____________ as an important component? a. Polyphorin/ cuticle/ chitin b. polyphorin/ chlorophyll/ magnesium c. Polyphorin/ cuticle/ magnesium d. polyphorin/ chlorophyll / the stomata 31. Electrons found in photosystem 1 are replenished by _____________, those found in photosystem 2 are replenished by _____________. a. the electron transport chain #1/ the splitting of water b. the splitting of water/ the electron transport chain #1 c. the splitting of Water/ the electron transport chain #2 d. the electron transport chain #2/ the splitting of water 32. _____________ is used in to create ATP by the high H+ concentration in the __________ and the low H+ concentration in _____________ in animal cells. ____________ Is used in to create ATP by the high H+ concentration in the __________ and the low H+ concentration in _____________ in plant cells. a. ATP synthase/ matrix/ intermembrane space/ ATP synthase/ Stroma/ Thylakoid memebrane b. Proton Pump/ intermembrane space/ matrix/ ATP synthase/ intermemebrane space/ stroma c. Proton pump / cytosol/ matrix/ Proton Pump/ outer membrane space/ thylakoid memebrane d. ATP synthase/ intermemebrane space/ matrix/ ATP Synthase/ thylaloid space/ stroma 33. in order to make 5- 6 carbon molecules you would use _________ in the Calvin Cycle? a. 30 CO2/ 90 ATP/ 60 NADH b. 20 CO2/ 75 ATP/ 50 NADH c. 30 CO2/ 90 ATP/ 60 NADPH d. 32 CO2/ 90 ATP/ 55 NADPH 6 C02 per Glucose *5 = 30 9 ATP per 3 C02 *10 turns = 90 ATP, 6 *10 = 60 NADPH 34. How is photosynthesis similar in C4 and CAM plants? a. in both cases, only photosystem 1 is used b. Both types of plants make sugar without the Calvin Cycle c. In both cases, rubisco is not used to fix carbon initially d. Both types of plants make most of their sugar in the dark e. In both cases, thylakoids are not involved in Photosynthesis 35. Both cylcin concentration and MPF activity are highest during __________. a. S b. G2 c. G1 d. M 36. The drug cytochalasin B blocks the function of actin. Which of the following aspects of the cell cycle would be most disrupted? a. DNA Synthesis b. Spindle formation c. Spindle attatchment d. Cleavage furrow formation e. Cell elongation during anaphase 37. An animal has 2n = 64. How many chromosomes are lined up at the metaphase plate in mitosis. How many sister chromatids are present? a. 32/ 64 b. 16/ 32 c. 64/ 128 d. 72/ 144 38. Meiosis I is the ____________ and Meiosis 2 is the ________________. a. separation of chromatids/ separation of homologous chromosomes b. Separation of homologous chromosomes/ separation of chromatids c. crossing over of sister chromatids/ separation of chromosomes d. separation of chromosomes/ crossing over of sister chromatids 39. During telophase I and cytokinesis _____________. a. Homologous chromosomes separate b. Cells become haploid instead of diploid c. Human cells go to 2n = 23 d. Both A and B e. All of the above c. should be n =23 which is diploid 40. A cell that is 2n = 6 results in __________ cells with __________ chromosomes at the end of meiosis II? a. 2/4 b. 4/3 c. 4/4 d. 2/3 41. When does crossing over occur in meiosis? a. Prophase II b. metaphase I c. metaphase II d. Prophase I 42. Which meiotic process is most similar to mitosis? a. M1 b. M2 c. Crossing Over d. Both B and C Separation of Sister Chromatids 43. When in meiosis does a cells number go from diploid to haploid? a. After M1 Cytokinesis b. After M2 Cytokinesis c. Cytokinesis of Mitosis d. None of the above 44. What kind of metabolic poison would most directly interfere with glycolysis? a. an agent that binds to pyruvate and inactivates it b. an agent that reacts with NADH and oxidizes it to NAD+ c. an agent that closely mimics the structure of glucose but is not metabolized d. an agent that reacts with oxygen and depletes its concentration in the cell 45. One function of both alcohol fermentation and lactic acid fermentation is to _________. a. reduce FADH2 to FAD+ b. oxidize NADH to NAD+ c. reduce FAD+ to FADH2 d. Reduce NAD+ to NADH 46. When comparing prophase I of meiosis with prophase of mitosis, which of the following occurs only in meiosis? a. The chromosomes condense. b. Tetrads form. c. The nuclear envelope disassembles. d. A spindle forms. e. Each chromosome is composed of two chromatids. 47. Which of the following occurs in meiosis but not in mitosis? a. chromosome replication b. synapsis c. production of daughter cells d. alignment of tetrads at metaphase plate e. both B and D