* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Carbohydrate Fans
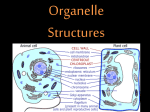
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Carbohydrate Cheerleaders What atoms are they made of? In what ratio? What are common single-ring sugars? Where is each one found in nature? What are the common two-ring sugars? Where is each one found? What are the common large carbohydrates? Where? How and where are carbohydrates broken down (metabolized)? Why are sugars fast energy? Which sugars are the fastest? Explain the difference between fruit/candy/bread in terms of athletic performance. What type of athlete would choose each? What is fiber? How does it help us? What happens to sugars not used immediately (think plants and animals)? Find some information about low-carb diets. Good idea? How many calories per gram are in carbohydrates? Carbohydrate Cheerleaders What atoms are they made of? In what ratio? What are common single-ring sugars? Where is each one found in nature? What are the common two-ring sugars? Where is each one found? What are the common large carbohydrates? Where? How and where are carbohydrates broken down (metabolized)? Why are sugars fast energy? Which sugars are the fastest? Explain the difference between fruit/candy/bread in terms of athletic performance. What type of athlete would choose each? What is fiber? How does it help us? What happens to sugars not used immediately (think plants and animals)? Find some information about low-carb diets. Good idea? How many calories per gram are in carbohydrates? Protein Promoters What are proteins? What elements (atoms) are present? What forms to proteins take? What are their functions? What is the monomer (building block) of proteins? Where do we get them? Why are some amino acids essential or nonessential? How does this relate to vegetarianism/veganism? What determines a protein’s function? How can it be lost? Explain denaturation Explain the three (or four) levels of protein structure. What are the max/min size of proteins? How do proteins affect athletic performance? Find some information about high-protein diets. Good idea?? How many calories per gram are in protein? Protein Promoters What are proteins? What elements (atoms) are present? What forms to proteins take? What are their functions? What is the monomer (building block) of proteins? Where do we get them? Why are some amino acids essential or nonessential? How does this relate to vegetarianism/veganism? What determines a protein’s function? How can it be lost? Explain denaturation Explain the three (or four) levels of protein structure. What are the max/min size of proteins? How do proteins affect athletic performance? Find some information about high-protein diets. Good idea?? How many calories per gram are in protein? Lipid Lovers What is a lipid? What forms do they come in? What elements (atoms) are present? What are the unique properties of lipids? Why are they so high in energy? How do fats and oils differ? Why do they differ? Where do we find saturated fats? Why are they solid? Where do we find unsaturated fats? Why are they liquid? Explain mono- vs. poly- unsaturated fats. Which are healthier? Why?? What is hydrogenation? Explain margarine. (see above) Why (and how) do we store fat? How do we digest it? Why are tropical oils bad for you? Which oils are best for you? How many calories per gram are in fats? What are some reasons that a high-fat diet is a bad idea? Why are Omega-3 fatty acids good for you? Where do we find them here in Alaska? Lipid Lovers What is a lipid? What forms do they come in? What elements (atoms) are present? What are the unique properties of lipids? Why are they so high in energy? How do fats and oils differ? Why do they differ? Where do we find saturated fats? Why are they solid? Where do we find unsaturated fats? Why are they liquid? Explain mono- vs. poly- unsaturated fats. Which are healthier? Why?? What is hydrogenation? Explain margarine. (see above) Why (and how) do we store fat? How do we digest it? Why are tropical oils bad for you? Which oils are best for you? How many calories per gram are in fats? What are some reasons that a high-fat diet is a bad idea? Why are Omega-3 fatty acids good for you? Where do we find them here in Alaska?