* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plasma Membrane
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
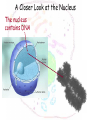
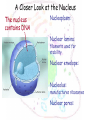
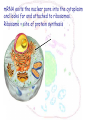
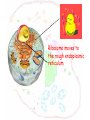
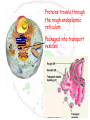
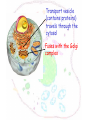
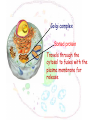
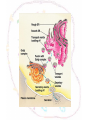
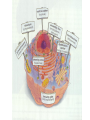
The cell Chapter 4 Pgs 69-71; 74-82 Two Categories of Cells Prokaryotic cells: bacteria and archaea Eukaryotic cells: plants, animals, fungi Eukaryotic Prokaryotic Common Features of All Cells Structural components - Plasma Membrane: phospholipids - Cytoplasm: fluid & organelles Molecular Components - DNA & RNA - Biological Molecules Metabolism Parts of a Eukaryotic Cell 1.Nucleus: membrane that surrounds DNA 2.Organelles: highly organized structures in the cells that serve a special function 3.Cytosol: jelly-like liquid that suspends the organelles Cytoplasm = fluid + organelles 4.Cytoskeleton: protein fibers for cell structure (shape and organization), transport and movement 5.Plasma membrane: outer lining of a cell The Nucleus Where is the nucleus? A Closer Look at the Nucleus The nucleus contains DNA A Closer Look at the Nucleus The nucleus contains DNA Nucleoplasm: Nuclear lamina: filaments used for stability Nuclear envelope: Nucleolus: manufactures ribosomes Nuclear pores: mRNA exits the nuclear pore into the cytoplasm and looks for and attached to ribosomes. Ribosome = site of protein synthesis Ribosome Reads the mRNA message and starts to add the code for proteins mRNA Ribosome moves to the rough endoplasmic reticulum Endoplasmic Reticulum Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Site where ribosomes “dock” Processes the immature protein Folds into a protein as it travels through the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Proteins travels through the rough endoplasmic reticulum Packaged into transport vesicles Transport vesicle (contains proteins) travels through the cytosol Fuses with the Golgi complex Stack of membranes The Golgi complex sorts and packages proteins into transport vesicles Proteins are then squeezed off into the little blebs which drift off into the cytoplasm Golgi complex Sorted protein Travels through the cytosol to fuses with the plasma membrane for release 1. mRNA copies instructions from DNA 2. mRNA exist through nuclear pores and moves to ribosomes 3. Ribosomes move to the endoplasmic reticulum 4. Drops amino acid chain into the endoplasmic reticulum for folding 5. Packaged into transport vesicles 6. Moves to the Golgi complex for processing, sorting and shipping 7. Proteins bud off and are released 8. Fuses with the plasma membrane 9. Release of a functional protein Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum No ribosomes attached Network of membranes Synthesis of lipids, fats, steroids Site of detoxification Ex. Alcohol smooth endoplasmic reticulum of liver cells Mitochrondia Protein production, ribosome production, etc.. requires energy!!!! Site of energy conversion Take food and converts it into energy that a cell can use Energy molecule = ATP adenosine triphosphate Ex. Coal is converted to electricity Lysosome Cytoskeleton Plasma Membrane