Phospholipid fatty acid – A bioindicator of environment
... scale has been studied at the process level, in terms of the number, respiration rates and enzyme activities4, which provide total pool sizes and gross activity measures at a broader scale. However, these are not particularly sensitive indicators5 because of redundancy of the functions and complex i ...
... scale has been studied at the process level, in terms of the number, respiration rates and enzyme activities4, which provide total pool sizes and gross activity measures at a broader scale. However, these are not particularly sensitive indicators5 because of redundancy of the functions and complex i ...
Citric Acid Cycle
... • Process in which cells consume O2 and produce CO2 • Provides more energy (ATP) from glucose than Glycolysis • Also captures energy stored in lipids and amino acids • Evolutionary origin: developed about 2.5 billion years ago • Used by animals, plants, and many microorganisms • Occurs in three majo ...
... • Process in which cells consume O2 and produce CO2 • Provides more energy (ATP) from glucose than Glycolysis • Also captures energy stored in lipids and amino acids • Evolutionary origin: developed about 2.5 billion years ago • Used by animals, plants, and many microorganisms • Occurs in three majo ...
BCAA 4:1:1 - ProAction
... molecule of succinyl-CoA and one of acetyl-CoA; and the complete catabolism of leucine produces three molecules of acetyl-CoA, and this process continues in the Krebs cycle until oxidation is complete. The principal point where BCAA catabolism is regulated is on a level with the branched-chain ketoa ...
... molecule of succinyl-CoA and one of acetyl-CoA; and the complete catabolism of leucine produces three molecules of acetyl-CoA, and this process continues in the Krebs cycle until oxidation is complete. The principal point where BCAA catabolism is regulated is on a level with the branched-chain ketoa ...
Additional Study Questions for Fuel Metabolism Lectures
... adjust its metabolic activities to the amount of available glucose. (5) After several days of starvation, the ability of the liver to metabolize acetyl-CoA via the citric acid cycle is severely compromised. Why is this so? (6) Summarize the roles of insulin, glucagons and epinephrine in regulating m ...
... adjust its metabolic activities to the amount of available glucose. (5) After several days of starvation, the ability of the liver to metabolize acetyl-CoA via the citric acid cycle is severely compromised. Why is this so? (6) Summarize the roles of insulin, glucagons and epinephrine in regulating m ...
1. overall goals a. general knowledge of microbiology b. in
... (1) simple, acellular entities consisting of DNA or RNA enclosed in a protein coat (2) obligate intracellular parasites (3) specific viruses infect bacterial, plant, animal cells 2. Microorganisms as Cells a. the cell is the fundamental unit of living matter (1) membrane = barrier (2) nucleus or nuc ...
... (1) simple, acellular entities consisting of DNA or RNA enclosed in a protein coat (2) obligate intracellular parasites (3) specific viruses infect bacterial, plant, animal cells 2. Microorganisms as Cells a. the cell is the fundamental unit of living matter (1) membrane = barrier (2) nucleus or nuc ...
Notes
... -water, ions, bilirubin (pigment derived from hemoglobin breakdown), cholesterol, & bile salts (lipids) -water & ions dilute & buffer acids -bile salts emulsify (create tiny drops) lipids that aren’t water-soluble & normally form large blobs that are difficult to breakdown -increase surface area to ...
... -water, ions, bilirubin (pigment derived from hemoglobin breakdown), cholesterol, & bile salts (lipids) -water & ions dilute & buffer acids -bile salts emulsify (create tiny drops) lipids that aren’t water-soluble & normally form large blobs that are difficult to breakdown -increase surface area to ...
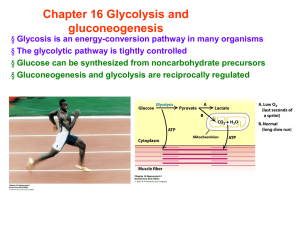
Chapter 16 Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis
... Glc + 2 Pi + 2 ADP 2 Lactate + 2 ATP + 2 H2O Magnesium lactate: a gel constituent; inhibit the production of histamine by histidine decarboxylase ...
... Glc + 2 Pi + 2 ADP 2 Lactate + 2 ATP + 2 H2O Magnesium lactate: a gel constituent; inhibit the production of histamine by histidine decarboxylase ...
Four Amino Acids Are Converted to Succinyl
... • Valine: undergoes transamination and decarboxylation, then a series of oxidation reactions that convert the remaining four carbons to propionyl-CoA. • Threonine: is also converted in two steps to propionylCoA. (This is the primary pathway for threonine degradation in humans) ...
... • Valine: undergoes transamination and decarboxylation, then a series of oxidation reactions that convert the remaining four carbons to propionyl-CoA. • Threonine: is also converted in two steps to propionylCoA. (This is the primary pathway for threonine degradation in humans) ...
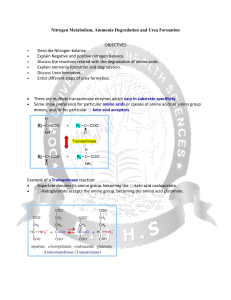
Nitrogen Metabolism, Ammonia Degradation and Urea Formation
... Urea is the major disposal form of amino groups derived from amino acids. 90% of the nitrogen containing components of urine are urea. The carbon and oxygen of urea are derived from CO2. Urea is produced by the liver, transported in the blood to the kidneys for excretion. ...
... Urea is the major disposal form of amino groups derived from amino acids. 90% of the nitrogen containing components of urine are urea. The carbon and oxygen of urea are derived from CO2. Urea is produced by the liver, transported in the blood to the kidneys for excretion. ...
DIGESTION
... sugars, amino acids or nucleotides. They were also used to build triglycerides (fats). During digestion, water is added to these molecules to reverse the condensation reactions. This process is called hydrolysis. So, digestion is the hydrolysis of large bulk nutrient molecules to produce their compo ...
... sugars, amino acids or nucleotides. They were also used to build triglycerides (fats). During digestion, water is added to these molecules to reverse the condensation reactions. This process is called hydrolysis. So, digestion is the hydrolysis of large bulk nutrient molecules to produce their compo ...
1) Which of the following is (are) true for anabolic
... 19) During glycolysis, when glucose is catabolized to pyruvate, most of the energy of glucose is A) retained in the pyruvate. B) transferred to ADP, forming ATP. C) transferred directly to ATP. D) used to phosphorylate fructose to form fructose-6-phosphate. E) stored in the NADH produced. 20) A mol ...
... 19) During glycolysis, when glucose is catabolized to pyruvate, most of the energy of glucose is A) retained in the pyruvate. B) transferred to ADP, forming ATP. C) transferred directly to ATP. D) used to phosphorylate fructose to form fructose-6-phosphate. E) stored in the NADH produced. 20) A mol ...
cell energy test review
... 13. Where do the Kreb’s cycle and the electron transport system take place? 14 What happens to the H+ produced in the citric acid cycle? 15. In what part of aerobic respiration are the most ATP produced? 16. How are the equations for photosynthesis and aerobic respiration related? ...
... 13. Where do the Kreb’s cycle and the electron transport system take place? 14 What happens to the H+ produced in the citric acid cycle? 15. In what part of aerobic respiration are the most ATP produced? 16. How are the equations for photosynthesis and aerobic respiration related? ...
document
... – Tetany (Sustained uncontrolled muscle contraction) » Muscle contraction controlled mainly by Na in neuron and Ca in muscle ...
... – Tetany (Sustained uncontrolled muscle contraction) » Muscle contraction controlled mainly by Na in neuron and Ca in muscle ...
Accelerated Analysis of Amino Acids in Physiological
... (35ml/h) and pressure. Calibration was performed using Amino Acid Standards Acidic/Neutral and Basics (Sigma Aldrich) spiked with Saccharopine, Alloisoleucine and ASA (Sigma Aldrich) at a concentration of 250µM. 20µL of this calibration solution were injected. The separation of all amino acids was a ...
... (35ml/h) and pressure. Calibration was performed using Amino Acid Standards Acidic/Neutral and Basics (Sigma Aldrich) spiked with Saccharopine, Alloisoleucine and ASA (Sigma Aldrich) at a concentration of 250µM. 20µL of this calibration solution were injected. The separation of all amino acids was a ...
Chapter 7 Review Name: Date: Question Answer Process that
... pathway; occurs in your muscles; used by bacteria ...
... pathway; occurs in your muscles; used by bacteria ...
3070 Lecture
... • Water content of margarine also affects its texture and “melting” point. A wide variety of margarine products with different water contents are available in today’s market place. • Corn oil is a highly unsaturated liquid at room temperature and is the main source of oil for ...
... • Water content of margarine also affects its texture and “melting” point. A wide variety of margarine products with different water contents are available in today’s market place. • Corn oil is a highly unsaturated liquid at room temperature and is the main source of oil for ...
Cell Respiration notes
... – Typically, cell will use most of the amino acids to make its own proteins, but enzymes will convert excess a.a. to intermediates of glycolysis or the Kreb’s cycle, and their energy is harvested by cell respiration. – Amino groups unused are disposed in urine. ...
... – Typically, cell will use most of the amino acids to make its own proteins, but enzymes will convert excess a.a. to intermediates of glycolysis or the Kreb’s cycle, and their energy is harvested by cell respiration. – Amino groups unused are disposed in urine. ...
TSTH Cleanse Foods to Consume
... Nettle Leaf – has a great number of amino acids, panthotenic acid, folic acid, chlorophyll. It also contains vitamins C, B2 and K, beta-carotene, Calcium, Magnesium, and Iron. Because of these compounds, the plant has anti-anemic, anti-diabetic, haemostatic and diuretic properties Milk Thistle – ant ...
... Nettle Leaf – has a great number of amino acids, panthotenic acid, folic acid, chlorophyll. It also contains vitamins C, B2 and K, beta-carotene, Calcium, Magnesium, and Iron. Because of these compounds, the plant has anti-anemic, anti-diabetic, haemostatic and diuretic properties Milk Thistle – ant ...
1 Introduction and History Introduction to the course (syllabus
... (1) simple, acellular entities consisting of DNA or RNA enclosed in a protein coat (2) obligate intracellular parasites (3) specific viruses infect bacterial, plant, animal cells 2. Microorganisms as Cells a. the cell is the fundamental unit of living matter (1) membrane = barrier (2) nucleus or nuc ...
... (1) simple, acellular entities consisting of DNA or RNA enclosed in a protein coat (2) obligate intracellular parasites (3) specific viruses infect bacterial, plant, animal cells 2. Microorganisms as Cells a. the cell is the fundamental unit of living matter (1) membrane = barrier (2) nucleus or nuc ...
24.9 Synthesis of Amino Acids
... Overview, Metabolism Catabolic pathways • degrade large molecules. • form small molecules that enter the citric acid cycle and electron transport to produce energy. Anabolic pathways • use small molecules and energy. • synthesize larger molecules in the cell. In the overall view of metabolism, ther ...
... Overview, Metabolism Catabolic pathways • degrade large molecules. • form small molecules that enter the citric acid cycle and electron transport to produce energy. Anabolic pathways • use small molecules and energy. • synthesize larger molecules in the cell. In the overall view of metabolism, ther ...
Exam Review 2 10/2/16
... A. Adenosine triphosphate B. Adenine triphosphate C. Adenosine transphosphate D. Adenine transphosphate 40. What word refers to a reaction that releases energy? A. Exergonic B. Endergonic C. Intergonic D. Intragonic 41. What type of fermentation occurs in animal cells is the absence of oxygen? A. La ...
... A. Adenosine triphosphate B. Adenine triphosphate C. Adenosine transphosphate D. Adenine transphosphate 40. What word refers to a reaction that releases energy? A. Exergonic B. Endergonic C. Intergonic D. Intragonic 41. What type of fermentation occurs in animal cells is the absence of oxygen? A. La ...
Activated B Complex
... vital the B group vitamins are as cofactors for the function of this pathway. If the body is deficient in any of these integral nutrients due to poor supply, reduced absorption or increased demand, it is clear how energy production and well-being may be compromised. Thiamine serves as a cofactor for ...
... vital the B group vitamins are as cofactors for the function of this pathway. If the body is deficient in any of these integral nutrients due to poor supply, reduced absorption or increased demand, it is clear how energy production and well-being may be compromised. Thiamine serves as a cofactor for ...
Lect 8 hormones 4
... • Stimulus for secretion is high blood glucose • Secreted by β cells • Leads to glucose uptake and storage in liver, muscle and fat tissue. • Effect is to ↓ blood glucose ...
... • Stimulus for secretion is high blood glucose • Secreted by β cells • Leads to glucose uptake and storage in liver, muscle and fat tissue. • Effect is to ↓ blood glucose ...
Worksheet – Proteins Proteins are polymers of amino acids, joined
... interact via LDF. These are also called hydrophobic interactions, since these groups can not interact with water. For this reason, they are usually buried in the interior of proteins, away from water. They can be disrupted by the addition of detergent. The polar side chains interact via H bonding si ...
... interact via LDF. These are also called hydrophobic interactions, since these groups can not interact with water. For this reason, they are usually buried in the interior of proteins, away from water. They can be disrupted by the addition of detergent. The polar side chains interact via H bonding si ...
Sorting the Fatty Acid Chaff from the Toxin Wheat, or is it All
... Success in identifying genes and enzymes that are involved in the biosynthesis of toxins by dinoflagellates has been limited thus far, despite considerable efforts by many groups. The chemical structures of dinoflagellate polyketides suggest that they are produced by modular type I PKS enzymes in so ...
... Success in identifying genes and enzymes that are involved in the biosynthesis of toxins by dinoflagellates has been limited thus far, despite considerable efforts by many groups. The chemical structures of dinoflagellate polyketides suggest that they are produced by modular type I PKS enzymes in so ...