Human Fatty Acid Transport Protein 2a/Very Long Chain Acyl
... by proteins and enzymes, which function in fatty acid uptake and metabolic trafficking. Previously it has been very difficult to distinguish these fatty acid trafficking events, but advances in mass spectrometry has provided the requisite tools to resolve these outstanding questions and to define th ...
... by proteins and enzymes, which function in fatty acid uptake and metabolic trafficking. Previously it has been very difficult to distinguish these fatty acid trafficking events, but advances in mass spectrometry has provided the requisite tools to resolve these outstanding questions and to define th ...
ATP
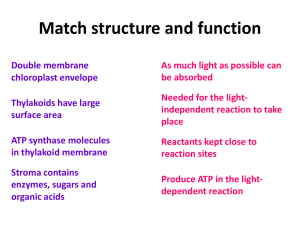
... • CO2 diffuses into the stroma • Combines with a 5C acceptor RuBP – uses enzyme • RuBP has become carboxylated – carboxyl group • Produces 2 x 3C molecule – glycerate 3-phosphate ...
... • CO2 diffuses into the stroma • Combines with a 5C acceptor RuBP – uses enzyme • RuBP has become carboxylated – carboxyl group • Produces 2 x 3C molecule – glycerate 3-phosphate ...
Digestion - WordPress.com
... When you have low blood sugar, glucagon tells the liver and muscles to convert the polysaccharide glycogen (often called ‘animal starch’) into sugar. This is called hydrolysis - which is also digestion. When the pancreatic cells cannot produce these hormones, a disease called diabetes occurs. Chitin ...
... When you have low blood sugar, glucagon tells the liver and muscles to convert the polysaccharide glycogen (often called ‘animal starch’) into sugar. This is called hydrolysis - which is also digestion. When the pancreatic cells cannot produce these hormones, a disease called diabetes occurs. Chitin ...
lecture_ch02_2014 modified
... broken by organisms. The simplest carbohydrates, including glucose, are monosaccharides or simple sugars. They contain from three to six carbon atoms. ...
... broken by organisms. The simplest carbohydrates, including glucose, are monosaccharides or simple sugars. They contain from three to six carbon atoms. ...
Ecology Review Science Department
... 20. What are the elements that make up a protein? CHON Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen ...
... 20. What are the elements that make up a protein? CHON Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen ...
Proteins – Amides from Amino Acids
... amino acid sequence. • The secondary structure of a protein describes how segments of the peptide backbone orient into a regular pattern. • The tertiary structure describes how the entire protein molecule coils into an overall threedimensional shape. • The quaternary structure describes how diffe ...
... amino acid sequence. • The secondary structure of a protein describes how segments of the peptide backbone orient into a regular pattern. • The tertiary structure describes how the entire protein molecule coils into an overall threedimensional shape. • The quaternary structure describes how diffe ...
MILK SYNTHESIS ENZYMES AND THEIR ROLES IN MILK QUALITY
... taken up by the mammary gland and inserted into milk fat. Trans11 18:1 and 18:0 can be transformed in the mammary gland into cis9,trans11 18:2 (CLA) by the enzyme ∆9 desaturase. The gene symbol for this enzyme is SCD for stearoyl-CoA desaturase. Increasing activity of this enzyme is desirable in ord ...
... taken up by the mammary gland and inserted into milk fat. Trans11 18:1 and 18:0 can be transformed in the mammary gland into cis9,trans11 18:2 (CLA) by the enzyme ∆9 desaturase. The gene symbol for this enzyme is SCD for stearoyl-CoA desaturase. Increasing activity of this enzyme is desirable in ord ...
Document
... To predict whether intracellular cholesterol synthesis will be up- or down-regulated in response to energy availability as influenced by diet, hormones and exercise. To distinguish the different mechanisms by which plasma cholesterol levels are controlled by clinically adminstrered pharmacological a ...
... To predict whether intracellular cholesterol synthesis will be up- or down-regulated in response to energy availability as influenced by diet, hormones and exercise. To distinguish the different mechanisms by which plasma cholesterol levels are controlled by clinically adminstrered pharmacological a ...
Identification of Two Mammalian Reductases
... carbons in length. Long chain fatty acids are important components of phospholipids, represent the largest energy storage reservoir in the form of triglycerides, and are the preferred fatty acids used for the esterification of cholesterol. The highest rate of de novo fatty acid synthesis occurs in t ...
... carbons in length. Long chain fatty acids are important components of phospholipids, represent the largest energy storage reservoir in the form of triglycerides, and are the preferred fatty acids used for the esterification of cholesterol. The highest rate of de novo fatty acid synthesis occurs in t ...
Lecture Power Point
... •It is also known as citric acid cycle or the Krebs cycle. •It is a series of enzyme-catalyzed chemical reactions of central importance in all living cells that use oxygen as part of cellular respiration. ...
... •It is also known as citric acid cycle or the Krebs cycle. •It is a series of enzyme-catalyzed chemical reactions of central importance in all living cells that use oxygen as part of cellular respiration. ...
Question
... a. Charging electrons to power ATP synthase b. Catalyzing the formation of acetyl-CoA c. Providing electrons and H+ to the electron ...
... a. Charging electrons to power ATP synthase b. Catalyzing the formation of acetyl-CoA c. Providing electrons and H+ to the electron ...
Document
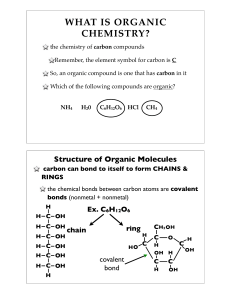
... all have the same chemical formula: C12H22O11 they are ISOMERS of each other they can only be absorbed into the intestine & blood stream when they are broken down into their monomers (monosaccharides) by enzymes Examples ...
... all have the same chemical formula: C12H22O11 they are ISOMERS of each other they can only be absorbed into the intestine & blood stream when they are broken down into their monomers (monosaccharides) by enzymes Examples ...
chapter-02
... a) The primary structure is the sequence of amino acids that make up the polypeptide chain. b) The secondary structure, which can take the form of an alpha-helix or a beta-pleated sheet, is maintained by hydrogen bonds between amino acids in different regions of the original polypeptide strand. c) T ...
... a) The primary structure is the sequence of amino acids that make up the polypeptide chain. b) The secondary structure, which can take the form of an alpha-helix or a beta-pleated sheet, is maintained by hydrogen bonds between amino acids in different regions of the original polypeptide strand. c) T ...
Glycolysis I
... a large free energy change and the reaction is irreversible. This makes it a reaction that is possible to control by controlling hexokinase. This reaction step is one of the good places in the pathway to have regulation because entry of glucose into the catabolic pathway should closely match the ene ...
... a large free energy change and the reaction is irreversible. This makes it a reaction that is possible to control by controlling hexokinase. This reaction step is one of the good places in the pathway to have regulation because entry of glucose into the catabolic pathway should closely match the ene ...
PHOTOSYNTHESIS & RESPIRATION
... Use of ATP & NADPH from Light reactions ATP for energy to power chemical reactions NADPH – hydrogen source to add to CO2 to make ...
... Use of ATP & NADPH from Light reactions ATP for energy to power chemical reactions NADPH – hydrogen source to add to CO2 to make ...
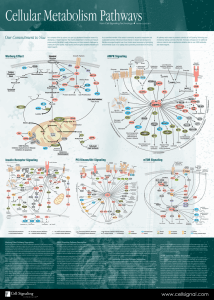
Cellular Metabolism Pathways
... Cancer cells frequently use glutamine as a secondary fuel source, which enters the mitochondria and can be used to replenish Krebs Cycle intermediates or can be used to produce more pyruvate through the action of malic enzyme. Highly proliferative cells need to produce excess lipid, nucleotide, and ...
... Cancer cells frequently use glutamine as a secondary fuel source, which enters the mitochondria and can be used to replenish Krebs Cycle intermediates or can be used to produce more pyruvate through the action of malic enzyme. Highly proliferative cells need to produce excess lipid, nucleotide, and ...
Digestion & Absorption
... • Absorbed nutrients enter either the: 1. Vascular system – water-soluble nutrients (monosaccharides, amino acids, water-soluble vitamins, minerals, water) enter the blood via the portal vein for transport to the liver ...
... • Absorbed nutrients enter either the: 1. Vascular system – water-soluble nutrients (monosaccharides, amino acids, water-soluble vitamins, minerals, water) enter the blood via the portal vein for transport to the liver ...
Insulin
... ◊ G6PO4 does not fit onto the transporter ◊ Liver alone has an enzyme to reverse the reaction, allowing liver to release glucose to blood if blood glucose is low. ◘ This occurs under the action of the hormone glucagon, which is produced by pancreatic beta cells ...
... ◊ G6PO4 does not fit onto the transporter ◊ Liver alone has an enzyme to reverse the reaction, allowing liver to release glucose to blood if blood glucose is low. ◘ This occurs under the action of the hormone glucagon, which is produced by pancreatic beta cells ...
Photosynthesis - Crestwood Local Schools
... The remaining 2C fragment (called an acetyl group) is attached to a coenzyme (coenzyme A) and forms acetyl-CoA. The acetyl-CoA gets either used in fat synthesis if there is enough ATP or it goes to be used in the Krebs Cycle to make more ATP. The Krebs Cycle: This is a repeating series of rxns that ...
... The remaining 2C fragment (called an acetyl group) is attached to a coenzyme (coenzyme A) and forms acetyl-CoA. The acetyl-CoA gets either used in fat synthesis if there is enough ATP or it goes to be used in the Krebs Cycle to make more ATP. The Krebs Cycle: This is a repeating series of rxns that ...
Chapter 6
... 21.What happens to the functionality of a protein if the amino acid sequence is altered, for example, by a mutation to a gene? 22.Explain several roles of proteins 23.Why can a protein deficiency cause edema? 24.What types of people are (at least should be) in positive nitrogen balance? Why is that? ...
... 21.What happens to the functionality of a protein if the amino acid sequence is altered, for example, by a mutation to a gene? 22.Explain several roles of proteins 23.Why can a protein deficiency cause edema? 24.What types of people are (at least should be) in positive nitrogen balance? Why is that? ...
Topic 3.7 and Opt C Cell Respiration
... Explain aerobic cellular respiration, including the link reaction, the Krebs cycle, the electron transport chain ...
... Explain aerobic cellular respiration, including the link reaction, the Krebs cycle, the electron transport chain ...