* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Additional Study Questions for Fuel Metabolism Lectures
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacometabolomics wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
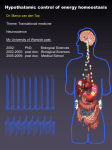
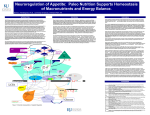
Additional Study Questions for Fuel Metabolism Lectures (1) Explain in detail why acetyl-CoA and pyruvate are at the “crossroads” of the major metabolic pathways. (2) Explain the alternative fates of glucose-6-phosphate in the liver, depending on the glucose demand. (3) Why does fasting result in an increase in liver concentrations of PEP carboxykinase and glucose-6-phosphatase. (4) Explain why the sigmoidal kinetics behavior of glucokinase helps the liver to adjust its metabolic activities to the amount of available glucose. (5) After several days of starvation, the ability of the liver to metabolize acetyl-CoA via the citric acid cycle is severely compromised. Why is this so? (6) Summarize the roles of insulin, glucagons and epinephrine in regulating mammalian fuel metabolism. (7) Explain the way that the arcuate nucleus in the hypothalamus integrates the hormonal signals presented by leptin, ghrelin, PYY3-36 and insulin. When answering this question, state from which organs the peptides originate and their specific effects on the NPY/AgRP and POMC/CART neurons. Also describe how the neuropeptides secreted by these neurons affect food intake and energy expenditure. (You do not have to consider “higher-level” interactions here, like the interneuronal connections between NPY/AgRP and POMC/CART neurons, or other neurons in the hypothalamus). (8) Explain the biochemical alterations induced by leptin that suggest its evolutionary advantage as a “thrifty gene” with regard to energy metabolism and storage. (9) Explain the biochemical changes seen in obesity. (10) Explain the biochemical changes seen in a person who is using the Atkins diet and describe how the physical symptoms that we discussed in class arise from these alterations. (11 )Explain the biochemical changes seen in a person with diabetes and describe how the physical symptoms that we discussed in class arise from these alterations. (12) Explain the proposed link between obesity and insulin resistance as described by Gerald Shulman in your text.