DB QS
... At first, glycogen is broken down into glucose. Only enough glycogen; however, is stored in the person's liver to last a few hours. After that period of time, blood glucose levels are maintained by the breakdown of fats and proteins. Fats are decomposed into glycerol and fatty acids. Fatty acids can ...
... At first, glycogen is broken down into glucose. Only enough glycogen; however, is stored in the person's liver to last a few hours. After that period of time, blood glucose levels are maintained by the breakdown of fats and proteins. Fats are decomposed into glycerol and fatty acids. Fatty acids can ...
Monosaccharides
... having more chiral atoms. For example, aldohexoses (С6Н12О6), that contain 4 chiral atoms, have 16 stereoisimers (N=2n) and 8 pair of enantiomers To determine the belonging of monosaccharide to L- or D-series we use the configuration at the farthest carbon atom from the carbonyl group. ...
... having more chiral atoms. For example, aldohexoses (С6Н12О6), that contain 4 chiral atoms, have 16 stereoisimers (N=2n) and 8 pair of enantiomers To determine the belonging of monosaccharide to L- or D-series we use the configuration at the farthest carbon atom from the carbonyl group. ...
Anaerobic and Aerobic Glycolysis
... energy is required in the absence of oxygen. It is vital for tissues with high energy requirements, insufficient oxygen supply or absence of oxidative enzymes. Glycolysis produces reduced forms of NAD in the energy generation phase. In an anaerobic environment, lactate dehydrogenase converts pyruvat ...
... energy is required in the absence of oxygen. It is vital for tissues with high energy requirements, insufficient oxygen supply or absence of oxidative enzymes. Glycolysis produces reduced forms of NAD in the energy generation phase. In an anaerobic environment, lactate dehydrogenase converts pyruvat ...
What is a Protein?
... protein as well as the specific folding of each determines the final function of the protein. Proteins break down or are used up continuously in living organisms. Therefore new proteins have to be created constantly. There are two main ways in which your body receives the amino acids that it needs i ...
... protein as well as the specific folding of each determines the final function of the protein. Proteins break down or are used up continuously in living organisms. Therefore new proteins have to be created constantly. There are two main ways in which your body receives the amino acids that it needs i ...
Homework1
... Identify whether each of the following covalent bonds, C-O, C-H, N-H and O-H is polar or nonpolar, and explain how these different characteristics relate to the electronegativity of each atom involved in the bond. ...
... Identify whether each of the following covalent bonds, C-O, C-H, N-H and O-H is polar or nonpolar, and explain how these different characteristics relate to the electronegativity of each atom involved in the bond. ...
Chapter 4
... Chapter 4 Cellular Metabolism 4.1 Introduction 1. Define metabolism. (p. 115) Metabolism is the sum total of chemical reactions in the cell. 2. Explain how metabolic pathways are linked and intersect. (p. 115) In many cases, products of one reaction are starting materials for the next. These reactio ...
... Chapter 4 Cellular Metabolism 4.1 Introduction 1. Define metabolism. (p. 115) Metabolism is the sum total of chemical reactions in the cell. 2. Explain how metabolic pathways are linked and intersect. (p. 115) In many cases, products of one reaction are starting materials for the next. These reactio ...
METABOLISM - Doctor Jade Main
... • during steps atoms of citric acid are rearranged producing different intermediates called keto acids • eventually turns into OAA ...
... • during steps atoms of citric acid are rearranged producing different intermediates called keto acids • eventually turns into OAA ...
Chapter 15 Study Outline
... Be able to identify and locate these parts. A __________________ sphincter controls release of food from the stomach into the small intestine. Gastric secretions and functions: ________________ glands within the mucosa of the stomach open as ______________ pits. These glands generally contain three ...
... Be able to identify and locate these parts. A __________________ sphincter controls release of food from the stomach into the small intestine. Gastric secretions and functions: ________________ glands within the mucosa of the stomach open as ______________ pits. These glands generally contain three ...
1 CHRONIC LIVER DISEASES DERANGEMENTS OF HEPATIC
... synthesis of liver intracellular proteins, plasma proteins, and special compounds, such as glutathione, glutamine, taurine, and creatine. Disruption of normal amino acid metabolism may be reflected in altered plasma amino acid concentrations. In general, levels of aromatic amino acids, normally meta ...
... synthesis of liver intracellular proteins, plasma proteins, and special compounds, such as glutathione, glutamine, taurine, and creatine. Disruption of normal amino acid metabolism may be reflected in altered plasma amino acid concentrations. In general, levels of aromatic amino acids, normally meta ...
Chemistry 2000 Lecture 20: Organic bases
... Other than the conjugate bases of organic acids we have already talked about, the only significant group of organic bases are compounds containing nitrogen atoms, mainly amines, although some others (e.g. imines, compounds that contain a carbon-nitrogen double bond) can also be reasonably strong bas ...
... Other than the conjugate bases of organic acids we have already talked about, the only significant group of organic bases are compounds containing nitrogen atoms, mainly amines, although some others (e.g. imines, compounds that contain a carbon-nitrogen double bond) can also be reasonably strong bas ...
Cellular Respiration PowerPoint review
... The cell can use Fermentation instead!! Occurs in the Cytoplasm Just like glycolysis!! Fermentation A series of reactions that convert NADH (from glycolysis) back into NAD allowing glycolysis to keep producing a small amount of ATP ...
... The cell can use Fermentation instead!! Occurs in the Cytoplasm Just like glycolysis!! Fermentation A series of reactions that convert NADH (from glycolysis) back into NAD allowing glycolysis to keep producing a small amount of ATP ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best
... A. His mitochondria lack the transport protein that moves pyruvate across the outer mitochondrial membrane. B. His cells have a defective electron transport chain, so glucose goes to lactate instead of to acetyl CoA. C. His cells contain something that inhibits oxygen use in his mitochondria. D. His ...
... A. His mitochondria lack the transport protein that moves pyruvate across the outer mitochondrial membrane. B. His cells have a defective electron transport chain, so glucose goes to lactate instead of to acetyl CoA. C. His cells contain something that inhibits oxygen use in his mitochondria. D. His ...
melgarejo richard
... method in my everyday life. I mean when I feel there is something wrong with one of my daily routines, I go and try to find out if there is a problem. Then I inspect the problem and then finally form a good hypothesis of why I am having that problem. Finally, I test ways on how to solve my problem a ...
... method in my everyday life. I mean when I feel there is something wrong with one of my daily routines, I go and try to find out if there is a problem. Then I inspect the problem and then finally form a good hypothesis of why I am having that problem. Finally, I test ways on how to solve my problem a ...
Lecture Suggestions and Guidelines
... Answer: See textbook—Inorganic Substances Common in Cells. Critical Thinking Issue(s) 1. Although most carbon dioxide is transported in plasma, small amounts of carbon dioxide are carried bound to the hemoglobin inside of red blood cells. How is this possible, since red blood cells seek to transport ...
... Answer: See textbook—Inorganic Substances Common in Cells. Critical Thinking Issue(s) 1. Although most carbon dioxide is transported in plasma, small amounts of carbon dioxide are carried bound to the hemoglobin inside of red blood cells. How is this possible, since red blood cells seek to transport ...
protein lesson
... biological value proteins and can list food examples of each. I understand two lows make a high. ...
... biological value proteins and can list food examples of each. I understand two lows make a high. ...
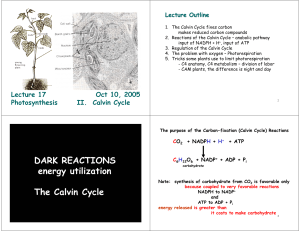
DARK REACTIONS energy utilization The Calvin Cycle
... ATP and reducing potential NADPH + H+ 2. Dark reactions use ATP and reducing potential to synthesize carbohydrates - powers reduction of 3-carbon acid to 3-carbon aldehyde ...
... ATP and reducing potential NADPH + H+ 2. Dark reactions use ATP and reducing potential to synthesize carbohydrates - powers reduction of 3-carbon acid to 3-carbon aldehyde ...
Basic Equine Nutrition
... Difference between Fat & Water Soluble? Fat soluble are stored in body can be toxic if overfed Water soluble can be fed daily excess is excreted ...
... Difference between Fat & Water Soluble? Fat soluble are stored in body can be toxic if overfed Water soluble can be fed daily excess is excreted ...
Answers - U of L Class Index
... Fats can be stored in unlimited amounts in adipose tissue compared to the limited storage of carbohydrates as glycogen. ...
... Fats can be stored in unlimited amounts in adipose tissue compared to the limited storage of carbohydrates as glycogen. ...
Untitled
... A stomachful of digestive juice laced with strong acid breaks apart the cells in our food, kills bacteria, and begins the digestion of proteins. At the same time, these chemicals, acidic enough to dissolve iron nails, can be harmful. The opening between the esophagus and the stomach is usually clos ...
... A stomachful of digestive juice laced with strong acid breaks apart the cells in our food, kills bacteria, and begins the digestion of proteins. At the same time, these chemicals, acidic enough to dissolve iron nails, can be harmful. The opening between the esophagus and the stomach is usually clos ...