* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cell energy test review
Magnesium in biology wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
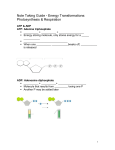
CELL ENERGY TEST REVIEW BIO 11 MULTIPLE CHOICE: Select the lettered choice that best fits each question or statement. In each case, there is only one correct choice. 1 Which statement about photosynthesis is correct? a. occurs only in the dark b. will not occur if respiration is taking place c. some stages are interrupted by darkness d. requires no coenzyme similar to NADP in respiration 2. What happens during the dark reactions of photosynthesis? a. oxidation of water b. formation of ATP c. reduction of oxygen d. conversion of carbon dioxide into an organic molecule 3. Leaves appear to be green because they a. absorb only green wavelengths of light b. reflect green light while absorbing other wavelengths c. reradiate green light as heat d. reflect all wavelengths of light 4. In addition to chlorophyll, what other pigments do leaves contain? a. phototrophs c. carotenes and xanthophylls b. green proteins d. no other pigments 5. What is the yellow pigment that captures the light energy not absorbed by chlorophyll during photosynthesis? a. chlorophyll a b. Type II chlorophyll c. carotene d. xanthophyll Questions 6—8 refer to the figure below. 6. The reactions shown above comprise the a. light reaction b. Calvin cycle c. Krebs cycle 7. The energy to drive the reactions is provided by a. 2 and 3 b. 3 and 4 c. 6 and 8 d. glycolysis d. 7 and 9 8. Which of the following represent PGAL and glucose, respectively? a. 1 and 5 b. 4 and 5 c. 8 and 6 d. 2 and 7 9. The two reactions used in photosynthesis are known as the a. Calvin and Krebs cycles c. light reactions and Calvin cycle b. glycolysis and Calvin cycle d. glycolysis and Krebs cycle 10. In photosynthesis, when light is absorbed by Type I chlorophyll, high energy electrons are produced and a. transferred to Type II chlorophyll c. carried directly to the Calvin cycle b. used to make water from oxygen and hydrogen d. used to make carbon dioxide 11. When Type II chlorophyll absorbs photons a. excited electrons are transferred to Type I chlorophyll b. excited electrons are transferred to NADP to help make NADPH2 c. ADP is broken down d. water is formed 12. In the light reactions, when excited electrons are transferred between the carrier molecules a. Type II chlorophyll breaks down c. NADP is produced from NADPH2 b. PGAL is used d. ATP is synthesized from ADP and phosphate 13. The foods most commonly broken down for energy are a. carbohydrates b. proteins c. lipids d. nucleic acids 14. Respiration a. can occur without enzymes b. is the transport of substances from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration c. only occurs in heterotrophs d. releases energy from fuel molecules 15. The final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain is a. NAD b. FAD c. cytochrome d. oxygen 16. An end product formed during fermentation in yeast is a. FAD b. hydrogen c. water d. alcohol 17. Which of the following sequences is correct for cellular respiration? a. C6H1206 → 2C compound → pyruvic acid b. 2C compound → pyruvic acid → C6H12O6 c. C6H1206 → pyruvic acid → 2C compound d. pyruvic acid → C6H1206 → 2C compound 18. When ADP changes to ATP a. there is an increase in the number of high energy bonds in the molecule b. there is an increase in the number of phosphate groups in the molecule c. phosphorylation has taken place d. all of the above occur 19. Respiration occurs in a. animal cells b. yeast cells c. plant cells d. all of the above 20. Approximately what percent of the total ATP yield of one glucose molecule is produced anaerobically? a. 5% c. 45% b. 25% d. 65% 21. Which of the following is true of carbohydrates? a. They are an end product of photosynthesis and a fuel in respiration. b. They are a fuel of photosynthesis and an end product in respiration. c. They are fuel for both reactions. d. The carry electrons in both reactions. 22. Electron transport occurs in a. mitochondria b. the nucleus c. ribosomes d. the cytoplasm 23. In the process of respiration, the oxidation of glucose occurs when glucose a. is directly oxidized by oxygen c. loses hydrogen atoms b. gains electrons d. is converted to PGAL MATCHING QUESTIONS From the list below, select the term that best fits each description. Each term may be used more than once, but there is only one correct answer for each description. Questions 1—5 refer to the following: a. electron transport b. glycolysis c. Krebs cycle _____ 1. For each 2-carbon compound 1 ATP molecule and 2 CO2 molecules are produced. _____ 2. For each glucose molecule 2 ATP molecules are produced. _____ 3. For each glucose molecule 32 ATP molecules are produced. _____ 4. produces the same number of ATP molecules as fermentation _____ 5. the process by which energy is obtained in anaerobic organisms Write the answers to the following questions on a separate sheet of paper. 1. Write the complete balanced chemical equation for photosynthesis. Design an experiment that shows oxygen as a product of photosynthesis. 2. How does ADP form ATP? Why isn’t the energy in a glucose molecule released in one single burst? 3. In human cells, what are two possible fates for pyruvic acid in cellular respiration? 4. Explain why runners feel burning sensations in their leg muscles after strenuous exercise. Why do their legs feel better after resting for a short period? 5. What is the first product of glycolysis? 6. How is a molecule of PGAL formed? 7. How many ATP molecules are used in the conversion of glucose to ATP? 8. How many ATP molecules are gained from the conversion of PGAL to pyruvic acid? What is the net gain? 9. Why is glycolysis not considered an aerobic process? 10. In what part of the cell do the process of glycolysis and fermentation take place? 11. Define respiration. 12. In the process of converting pyruvic acid to acetic acid, what molecule is lost as waste? 13. Where do the Kreb’s cycle and the electron transport system take place? 14 What happens to the H+ produced in the citric acid cycle? 15. In what part of aerobic respiration are the most ATP produced? 16. How are the equations for photosynthesis and aerobic respiration related?