Unit 4 Review Sheet Genetics and Biotechnology Vocabulary
... - Do you know how to use the codon chart? - Why is the sequence of amino acids important to the shape and function of a protein? *You do NOT need to know the names of the enzymes involved in this process. Mutations - What is a mutation? - What kind of mutations can happen to DNA (i.e. a nucleotide i ...
... - Do you know how to use the codon chart? - Why is the sequence of amino acids important to the shape and function of a protein? *You do NOT need to know the names of the enzymes involved in this process. Mutations - What is a mutation? - What kind of mutations can happen to DNA (i.e. a nucleotide i ...
Reading Study Guide B
... Describe the DNA transcription process by completing each sentence. During transcription, DNA is used to make _______________________________________. Only _________________________________________________________ are transcribed. Many copies of RNA can be made from _________________________________ ...
... Describe the DNA transcription process by completing each sentence. During transcription, DNA is used to make _______________________________________. Only _________________________________________________________ are transcribed. Many copies of RNA can be made from _________________________________ ...
week2
... Proteins do all the work on cellular level They act catalysts called Enzymes They make everything work Different cells do different things. In each cell is the genetic blue print to do everything But only a small part of the blue print is used by an individual cell. ...
... Proteins do all the work on cellular level They act catalysts called Enzymes They make everything work Different cells do different things. In each cell is the genetic blue print to do everything But only a small part of the blue print is used by an individual cell. ...
Central Dogma.pptx
... Uses original (parent strand) as a template to create to new daughter strands (semi-conservative replication). ...
... Uses original (parent strand) as a template to create to new daughter strands (semi-conservative replication). ...
Last Name - JhaveriChemBioWiki
... 3. Using the central dogma, explain why RNA is important for making protein. ...
... 3. Using the central dogma, explain why RNA is important for making protein. ...
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
... 1. In addition to cells, in which genetic information is always stored in the form of double-stranded DNA, numerous viruses exist, in which genetic information can be in the form of single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) or single- or double-stranded RNA (ssRNA or dsRNA), as well as in the form of duplex DNA ( ...
... 1. In addition to cells, in which genetic information is always stored in the form of double-stranded DNA, numerous viruses exist, in which genetic information can be in the form of single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) or single- or double-stranded RNA (ssRNA or dsRNA), as well as in the form of duplex DNA ( ...
Biology Pre-Learning Check
... LS-C5. Illustrate the relationship of the structure and function of DNA to protein synthesis and the characteristics of an organism. ...
... LS-C5. Illustrate the relationship of the structure and function of DNA to protein synthesis and the characteristics of an organism. ...
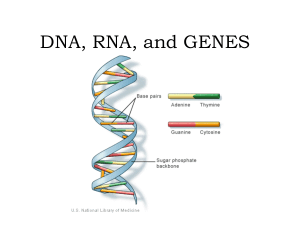
DNA, RNA, and GENES
... • Chargaff discovered the pattern found in the nitrogen bases. • Rosalind Franklin discovered shape of DNA. ...
... • Chargaff discovered the pattern found in the nitrogen bases. • Rosalind Franklin discovered shape of DNA. ...
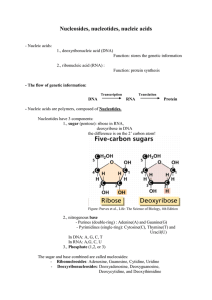
Nucleosides, nucleotides, nucleic acids
... protein synthesis. Single stranded. - ribosomal RNA = rRNA : components of the ribosome, which is the site of protein synthesis (translation). rRNA forms self-complementary double-stranded regions (in RNA there is Uracil instead of Thymine as a base, it forms double hydrogen bonds with Adenine). - t ...
... protein synthesis. Single stranded. - ribosomal RNA = rRNA : components of the ribosome, which is the site of protein synthesis (translation). rRNA forms self-complementary double-stranded regions (in RNA there is Uracil instead of Thymine as a base, it forms double hydrogen bonds with Adenine). - t ...
Protein Synthesis Review Concepts • Protein synthesis occurs in two
... Protein Synthesis Review Concepts • Protein synthesis occurs in two stages: transcription and translation • Transcription is the process in which information is copied from DNA to RNA • Translation is the process in which information from RNA codes for amino acids • Cells with the same DNA can speci ...
... Protein Synthesis Review Concepts • Protein synthesis occurs in two stages: transcription and translation • Transcription is the process in which information is copied from DNA to RNA • Translation is the process in which information from RNA codes for amino acids • Cells with the same DNA can speci ...
DNA and Its Proccesses
... • Unzip DNA double strand • Add in new base pairs to each half • Base-pairing rules: ...
... • Unzip DNA double strand • Add in new base pairs to each half • Base-pairing rules: ...
SBI4U: Molecular Genetics Unit Review
... 3. What is the difference between the 5’ end of nucleic acids and the 3’ end? Draw a diagram to show this. 4. When new DNA or RNA is synthesized, in which direction does it grow? 5. What are two different kinds of bonds that hold nucleic acids together? 6. Write the complementary DNA strand: 5’- A A ...
... 3. What is the difference between the 5’ end of nucleic acids and the 3’ end? Draw a diagram to show this. 4. When new DNA or RNA is synthesized, in which direction does it grow? 5. What are two different kinds of bonds that hold nucleic acids together? 6. Write the complementary DNA strand: 5’- A A ...
Answers to the Study Guide for C12 Molecular Genetics Labeled
... 3. Two double stranded DNA each having a parental strand and a new complimentary strand. 4. A nucleotide is the repeating monomer in a nucleic acid chain. DNA : deoxyribose, phosphate group; nitrogenous bases; adenine, thymine; cytosine & guanine. RNA: ribose, phosphate group, nitrogenous bases; ade ...
... 3. Two double stranded DNA each having a parental strand and a new complimentary strand. 4. A nucleotide is the repeating monomer in a nucleic acid chain. DNA : deoxyribose, phosphate group; nitrogenous bases; adenine, thymine; cytosine & guanine. RNA: ribose, phosphate group, nitrogenous bases; ade ...
DNA Structure and Function
... form a large complex • Complex anchors to nuclear matrix • DNA moves through enzymes ...
... form a large complex • Complex anchors to nuclear matrix • DNA moves through enzymes ...
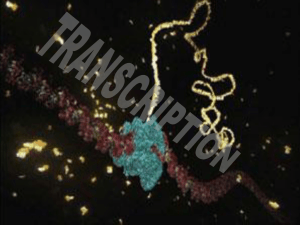
Protein Synthesis: Part I: Transcription
... p mRNA copies DNA p mRNA leaves the nucleus and travels through the cytoplasm to the ribosome p mRNA complements known as codons ...
... p mRNA copies DNA p mRNA leaves the nucleus and travels through the cytoplasm to the ribosome p mRNA complements known as codons ...
Slide 1
... sugar and phosphate groups make up the uprights of the ladder and the rungs are nitrogen bases hydrogen bonded together (recall hydrogen bonds are weak bonds and can come apart easily). The rungs are always one purine bonded to one pyrimidine…A always to T and C always to G. ...
... sugar and phosphate groups make up the uprights of the ladder and the rungs are nitrogen bases hydrogen bonded together (recall hydrogen bonds are weak bonds and can come apart easily). The rungs are always one purine bonded to one pyrimidine…A always to T and C always to G. ...
Daily Trivia - James B. Conant High School
... RNA is single stranded : DNA is double stranded RNA is made of the sugar Ribose – DNA is made of deoxyribose RNA has Uracil instead of Thymine – Both DNA and RNA have four nitrogen bases the difference is U vs T ...
... RNA is single stranded : DNA is double stranded RNA is made of the sugar Ribose – DNA is made of deoxyribose RNA has Uracil instead of Thymine – Both DNA and RNA have four nitrogen bases the difference is U vs T ...
Microbiology Unit 3 Study Guide
... 3. What are the DNA base pair rules? 4. How would you transcribe the following DNA sequence? ATA CGT CAT AAG 5. Which enzyme makes RNA by reading a strand of DNA? 6. Which enzymes cut DNA in specific locations? 7. What occurs during transcription? 8. What are the steps to obtaining DNA fragments for ...
... 3. What are the DNA base pair rules? 4. How would you transcribe the following DNA sequence? ATA CGT CAT AAG 5. Which enzyme makes RNA by reading a strand of DNA? 6. Which enzymes cut DNA in specific locations? 7. What occurs during transcription? 8. What are the steps to obtaining DNA fragments for ...
What Processes Produce RNA from DNA and Protein from mRNA
... b. For what sequence of amino acids does this mRNA code? (Assume it does not contain introns.) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________ ...
... b. For what sequence of amino acids does this mRNA code? (Assume it does not contain introns.) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________ ...
DNA to Protein - Duplin County Schools
... http://www.classzone.com/cz/books/bio_07/resources/htmls/interactive_review/bio_intrev.html ...
... http://www.classzone.com/cz/books/bio_07/resources/htmls/interactive_review/bio_intrev.html ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.