Protein Synthesis 1 - Transcription Translation
... 4) First, the DNA (genetic code) gets transcribed into mRNA. 5) Why do we need to make a coded copy of DNA? __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ ...
... 4) First, the DNA (genetic code) gets transcribed into mRNA. 5) Why do we need to make a coded copy of DNA? __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ ...
Section 4.3 – DNA
... Code contained in hereditary material Stored in cells that have a nucleus 1952 – Rosalind Franklin discovered that DNA is 2 chains in a spiral -‐ 1953 – Watson and Crick made a DNA model o ...
... Code contained in hereditary material Stored in cells that have a nucleus 1952 – Rosalind Franklin discovered that DNA is 2 chains in a spiral -‐ 1953 – Watson and Crick made a DNA model o ...
DNA-notes
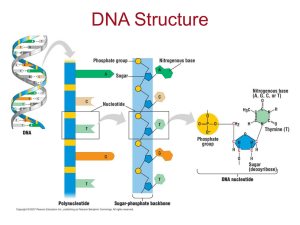
... repeating units. *Nucleotides: repeating units of DNA *Nucleotides are composed of a sugar molecule, a phosphorus containing molecule, (called the backbone) and a nitrogen containing molecule called a base. *Four types of bases: adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine. *Bases pair A to T and ...
... repeating units. *Nucleotides: repeating units of DNA *Nucleotides are composed of a sugar molecule, a phosphorus containing molecule, (called the backbone) and a nitrogen containing molecule called a base. *Four types of bases: adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine. *Bases pair A to T and ...
2.5.4. DNA Revision Qs
... (a) freckles _____________________________________ (b) the production of an enzyme _____________________________________ (c) the ability to play a musical instrument _____________________________________ (d) the ability to form a blood clot _____________________________________ (e) the ability to re ...
... (a) freckles _____________________________________ (b) the production of an enzyme _____________________________________ (c) the ability to play a musical instrument _____________________________________ (d) the ability to form a blood clot _____________________________________ (e) the ability to re ...
Lect2 Genetics
... DNA polymerases can make mistakes -> mutations DNA repair mechanisms Recombination can occur –cutting out and insertion of pieces of DNA These can all leads to changes in genetic material and thus changes in phenotype! ...
... DNA polymerases can make mistakes -> mutations DNA repair mechanisms Recombination can occur –cutting out and insertion of pieces of DNA These can all leads to changes in genetic material and thus changes in phenotype! ...
259071_DNAStructureStudyGuide
... to the back of this sheet. You can find all of the answers by clicking on the link labeled “DNA – Structure basics” 1. Write a simplified version of the idea that is known as “The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology”. (What I’m looking for here is the three word ...
... to the back of this sheet. You can find all of the answers by clicking on the link labeled “DNA – Structure basics” 1. Write a simplified version of the idea that is known as “The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology”. (What I’m looking for here is the three word ...
Biology Study Guide CH 12 Part I DNA-RNA
... 5. Define NUCLEOTIDE…be sure to know the 3 parts of the DNA nucleotide! 6. How would the amount of purines & pyrimidines found in the DNA molecule compare? *Remember that purines are: Adenine & Guaine; Pyrimidines are: Thymine & Cytosine; 7. DNA is copied during a process called __________________. ...
... 5. Define NUCLEOTIDE…be sure to know the 3 parts of the DNA nucleotide! 6. How would the amount of purines & pyrimidines found in the DNA molecule compare? *Remember that purines are: Adenine & Guaine; Pyrimidines are: Thymine & Cytosine; 7. DNA is copied during a process called __________________. ...
Vocabulary Quiz Key Terms
... An enzyme that breaks the hydrogen bonds holding the base pairs together as it unwinds and unzips the double helix, allowing new nucleotides to bind to the 2 single strands by base pairing. An enzyme that adds complementary nucleotides to the template strand of the unzipped double helix until the en ...
... An enzyme that breaks the hydrogen bonds holding the base pairs together as it unwinds and unzips the double helix, allowing new nucleotides to bind to the 2 single strands by base pairing. An enzyme that adds complementary nucleotides to the template strand of the unzipped double helix until the en ...
Chapter 10 Structure and Function of DNA
... Lagging Strand How is DNA replication related to S- Phase? Primase Okazaki Fragments What is significant about the 3’-OH Why do chromosomes get shorter and shorter every round of replication? What are telomeres? What is telomerase? What happens if there is a mistake? What is the role of single-stra ...
... Lagging Strand How is DNA replication related to S- Phase? Primase Okazaki Fragments What is significant about the 3’-OH Why do chromosomes get shorter and shorter every round of replication? What are telomeres? What is telomerase? What happens if there is a mistake? What is the role of single-stra ...
What is RNA? - Manhasset Schools
... DNA is too ________________ to leave the nucleus, so a smaller molecule called __________ is made to carry the _______________________ out of the _________________ so ____________________ can be made. * This is completed through the process of _________________________________ * ...
... DNA is too ________________ to leave the nucleus, so a smaller molecule called __________ is made to carry the _______________________ out of the _________________ so ____________________ can be made. * This is completed through the process of _________________________________ * ...
DNA Practice problems
... If you were to replicate the above strand of DNA in this direction ----, from left to right, which of the parent stands is used to build the leading strand of DNA? The lagging strand??? Here is a model for the above DNA strands: ...
... If you were to replicate the above strand of DNA in this direction ----, from left to right, which of the parent stands is used to build the leading strand of DNA? The lagging strand??? Here is a model for the above DNA strands: ...
Unit 7 Study Guide ANSWERS 2014
... 16. Give an example of a mutagen? UV light, radiation 17. Define gene. A segment of DNA that contains the information necessary to produce a protein 18. Where are genes located? Chromosomes 19 Where is DNA located in the cell? Nucleus 20. What cell organelle is responsible for assembling proteins? R ...
... 16. Give an example of a mutagen? UV light, radiation 17. Define gene. A segment of DNA that contains the information necessary to produce a protein 18. Where are genes located? Chromosomes 19 Where is DNA located in the cell? Nucleus 20. What cell organelle is responsible for assembling proteins? R ...
Book 11.5 HB Questions
... 5. The process of joining exons together to form an mRNA molecule is called _________________________. 6. During transcription, the _________________________ between base pairs are broken. 7. A mutation will cause the cell to make an incomplete polypeptide if the mutation results in a(an) __________ ...
... 5. The process of joining exons together to form an mRNA molecule is called _________________________. 6. During transcription, the _________________________ between base pairs are broken. 7. A mutation will cause the cell to make an incomplete polypeptide if the mutation results in a(an) __________ ...
Name:
... of DNA. Why do you think this is so, instead of simply starting at one end and working towards the other? 7. Why does the information encoded in DNA need to be copied onto RNA? ...
... of DNA. Why do you think this is so, instead of simply starting at one end and working towards the other? 7. Why does the information encoded in DNA need to be copied onto RNA? ...
Nucleic acid review sheet
... What is the material in each cell that contains a set of instructions that controls all genetic traits? ...
... What is the material in each cell that contains a set of instructions that controls all genetic traits? ...
How are protein made in our cells?
... • What are 3 differences between DNA and RNA? What are 3 types of RNA? • What is transcription? What are the steps in this process? • What is translation? What are the steps in this process? • Protein is made up of smaller building blocks called ______ ______. • What is the mRNA sequence for the fol ...
... • What are 3 differences between DNA and RNA? What are 3 types of RNA? • What is transcription? What are the steps in this process? • What is translation? What are the steps in this process? • Protein is made up of smaller building blocks called ______ ______. • What is the mRNA sequence for the fol ...
doc14873 - Mrothery.co.uk
... What word is used to describe the fact that several codon codes are used for the same amino acid? ...
... What word is used to describe the fact that several codon codes are used for the same amino acid? ...
the nucleic acids - This is MySchool
... isolated what he called nuclein from the nuclei of pus cells Nuclein was shown to have acidic properties, hence it became called nucleic acid ...
... isolated what he called nuclein from the nuclei of pus cells Nuclein was shown to have acidic properties, hence it became called nucleic acid ...
DNA Workshop - Lapeer High School
... Follow the directions and answer the questions as you go along. First click the button in the upper left that says “DNA Replication.” Follow the prompts and go through the animation. You can repeat if necessary. a. What kind of protein unzips the DNA to start the process? b. Which bases always pair ...
... Follow the directions and answer the questions as you go along. First click the button in the upper left that says “DNA Replication.” Follow the prompts and go through the animation. You can repeat if necessary. a. What kind of protein unzips the DNA to start the process? b. Which bases always pair ...
Genetic Engineering - Duplin County Schools
... Applications of Genetic Engineering • Transgenic Organisms – Contain genes from other organisms – Usually bacteria because they reproduce rapidly and are easy to grow. ...
... Applications of Genetic Engineering • Transgenic Organisms – Contain genes from other organisms – Usually bacteria because they reproduce rapidly and are easy to grow. ...
Ch 16-17 Practice Quiz
... 6. The Amino Acids are matched with the correct codon of the mRNA at a _________=(rRNA) and the A.A’s are delivered by ___RNA. 7. This step of making proteins (polypeptides) is called ________________. 8. If the 6th letter on the DNA were deleted (mutation) how would that affect the outcome of the p ...
... 6. The Amino Acids are matched with the correct codon of the mRNA at a _________=(rRNA) and the A.A’s are delivered by ___RNA. 7. This step of making proteins (polypeptides) is called ________________. 8. If the 6th letter on the DNA were deleted (mutation) how would that affect the outcome of the p ...
Nucleic Acids and DNA Replication
... one nucleotide and the phosphate of the next • New nucleotides can only be added to the 3’ end where there is an exposed hydroxyl group (from the sugar) • This is why we say that DNA is built in a 5’ to 3’ direction • Directionality in the structure of the DNA molecule influences how it functions ...
... one nucleotide and the phosphate of the next • New nucleotides can only be added to the 3’ end where there is an exposed hydroxyl group (from the sugar) • This is why we say that DNA is built in a 5’ to 3’ direction • Directionality in the structure of the DNA molecule influences how it functions ...
Unit 1 - Glen Rose FFA
... exists as a single, circular chromosome of double stranded DNA. Also contain smaller circular ...
... exists as a single, circular chromosome of double stranded DNA. Also contain smaller circular ...
RNA base pairing Worksheet
... 2. The complementary RNA bases are added to one template strand. 3. The new RNA strand released. ...
... 2. The complementary RNA bases are added to one template strand. 3. The new RNA strand released. ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.