Molecular Genetics Review - Biology 12U Chapter 7: Nucleic Acids
... Chapter 7: Nucleic Acids: The Molecular Basis of Life material of heredity - components or RNA and DNA *5 people in the book who are important for DNA history : Watson and Crick; Franklin; Chargaff; Meishner; and Griffith. structure of nucleic acids organiztion of genetic material in prokaryotes a ...
... Chapter 7: Nucleic Acids: The Molecular Basis of Life material of heredity - components or RNA and DNA *5 people in the book who are important for DNA history : Watson and Crick; Franklin; Chargaff; Meishner; and Griffith. structure of nucleic acids organiztion of genetic material in prokaryotes a ...
Cloze passage 4
... n) The number of naturally occurring amino acids o) The amino acid with the abbreviation Asp p) Changes that occur spontaneously to DNA are called q) A type of radiation from the sun r) Environmental factors that induce mutations are known as ……………….. s) A type of mutation where some of the DNA is l ...
... n) The number of naturally occurring amino acids o) The amino acid with the abbreviation Asp p) Changes that occur spontaneously to DNA are called q) A type of radiation from the sun r) Environmental factors that induce mutations are known as ……………….. s) A type of mutation where some of the DNA is l ...
Reviewing Key Concepts Chapter 12 DNA and RNA Section Review 12-3
... 8. Hypothesizing How would it benefit a cell to possess a sequence of DNA that could be transcribed and then edited into several different mRNA molecules? ...
... 8. Hypothesizing How would it benefit a cell to possess a sequence of DNA that could be transcribed and then edited into several different mRNA molecules? ...
24 October - web.biosci.utexas.edu
... Please write a brief summery for the animations of Helicase and Replication posted on the course website. PRINT it out and turn it in either on your discussion sections or on next Monday's class no later than 12:00PM. Email attachments and late delivery are not acceptable. 1. What factors ensure the ...
... Please write a brief summery for the animations of Helicase and Replication posted on the course website. PRINT it out and turn it in either on your discussion sections or on next Monday's class no later than 12:00PM. Email attachments and late delivery are not acceptable. 1. What factors ensure the ...
Describe the relationship between genes, nucleic acids, amino
... Proteins function in a variety of critical ways in living things not the least of which is to serve as enzymes that catalyze numerous and necessary chemical reactions that involve very stable molecules. DNA’s structure is critical to its function. It is organized in a manner that there are 30,000 di ...
... Proteins function in a variety of critical ways in living things not the least of which is to serve as enzymes that catalyze numerous and necessary chemical reactions that involve very stable molecules. DNA’s structure is critical to its function. It is organized in a manner that there are 30,000 di ...
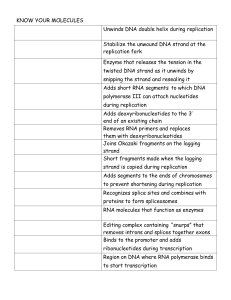
Know your molecules organizer
... Unwinds DNA double helix during replication Stabilize the unwound DNA strand at the replication fork Enzyme that releases the tension in the twisted DNA strand as it unwinds by snipping the strand and resealing it Adds short RNA segments to which DNA polymerase III can attach nucleotides during repl ...
... Unwinds DNA double helix during replication Stabilize the unwound DNA strand at the replication fork Enzyme that releases the tension in the twisted DNA strand as it unwinds by snipping the strand and resealing it Adds short RNA segments to which DNA polymerase III can attach nucleotides during repl ...
Unit 1C: Molecular Biology-1
... _____________ are biological catalyst that works by ______________ the activation energy of a chemical reaction. Proteins serve as effective buffers by combining with H+ or OH-. Nucleic Acids Nucleic Acids are a type of polymer/macromolecule composed of the basic units called ____________. Each of t ...
... _____________ are biological catalyst that works by ______________ the activation energy of a chemical reaction. Proteins serve as effective buffers by combining with H+ or OH-. Nucleic Acids Nucleic Acids are a type of polymer/macromolecule composed of the basic units called ____________. Each of t ...
August 31, 2016 - Iowa State University
... c. DNA contains an extra hydroxyl group that RNA does not have d. DNA is much less reactive than RNA ...
... c. DNA contains an extra hydroxyl group that RNA does not have d. DNA is much less reactive than RNA ...
Review for Molecular Genetics Quest
... 12. On what type of RNA molecule will you find anti-codons? ...
... 12. On what type of RNA molecule will you find anti-codons? ...
Cytosine – ______ Sugar
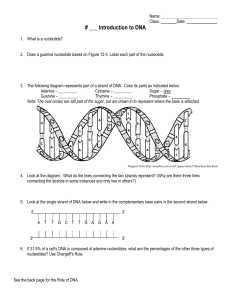
... 2. Draw a guanine nucleotide based on Figure 12-5. Label each part of the nucleotide. ...
... 2. Draw a guanine nucleotide based on Figure 12-5. Label each part of the nucleotide. ...
RNA
... ________________________ are the site of protein synthesis ________________________ are the building blocks of proteins ...
... ________________________ are the site of protein synthesis ________________________ are the building blocks of proteins ...
Genetic Information
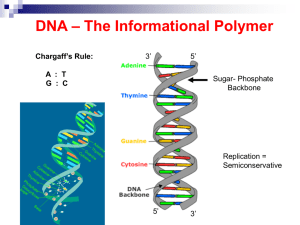
... will only bond with their complementary base like a lock and a key o adenine + thymine o guanine + cytosine if you know one strand you can figure out the other strand o CGTTAACGTA o GCAATTGCAT DNA Replication o Occurs during interphase, right before cell enters prophase (mitosis and mitosis I) ...
... will only bond with their complementary base like a lock and a key o adenine + thymine o guanine + cytosine if you know one strand you can figure out the other strand o CGTTAACGTA o GCAATTGCAT DNA Replication o Occurs during interphase, right before cell enters prophase (mitosis and mitosis I) ...
DNA Connection
... DNA is made up of 4 nitrogen bases. Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) ...
... DNA is made up of 4 nitrogen bases. Adenine (A) Thymine (T) Guanine (G) Cytosine (C) ...
Chapter 10 Section 3 Notes Answer Key
... I. DNA A. DNA- a chemical that contains information an organism needs to grow and function 1. Watson and Crick made and accurate model of DNA in 1953 2. The structure of DNA is similar to a twisted ladder. a. The sides of the ladder are made up of sugarphosphate molecules. b. The rungs of the ladder ...
... I. DNA A. DNA- a chemical that contains information an organism needs to grow and function 1. Watson and Crick made and accurate model of DNA in 1953 2. The structure of DNA is similar to a twisted ladder. a. The sides of the ladder are made up of sugarphosphate molecules. b. The rungs of the ladder ...
013368718X_CH13_193
... 2. Messenger RNA carries copies of the instructions for making proteins from DNA to other parts of the cell. 3. RNA polymerase transfers amino acids to ribosomes. 4. The process of transcription produces a complementary strand of RNA on a DNA template. 5. The enzyme that assembles a complementary st ...
... 2. Messenger RNA carries copies of the instructions for making proteins from DNA to other parts of the cell. 3. RNA polymerase transfers amino acids to ribosomes. 4. The process of transcription produces a complementary strand of RNA on a DNA template. 5. The enzyme that assembles a complementary st ...
BIO_Protein_Synthesis_Outline - Cole Camp R-1
... ▸Describe the DNA molecule as being Spiral in Shape with the BASES on the inside and the Sugar- Phosphate Groups on the outside. ...
... ▸Describe the DNA molecule as being Spiral in Shape with the BASES on the inside and the Sugar- Phosphate Groups on the outside. ...
replication (nucleus) transcription (nucleus) translation (cytoplasm
... Both occur within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, are catalyzed by large enzymes, involve unwinding of the DNA double helix, involve complementary base pairing of the DNA strand, and are highly regulated by the cell. Replication occurs only once during each round of the cell cycle and makes a doubl ...
... Both occur within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, are catalyzed by large enzymes, involve unwinding of the DNA double helix, involve complementary base pairing of the DNA strand, and are highly regulated by the cell. Replication occurs only once during each round of the cell cycle and makes a doubl ...
DNA/RNA Worksheet TACGGCACCGTTAGGATT
... 19. Using the genetic code, please indicate whether the following DNA base pair substitutions would lead to a change in the amino acid sequence by writing YES or NO. A. ...
... 19. Using the genetic code, please indicate whether the following DNA base pair substitutions would lead to a change in the amino acid sequence by writing YES or NO. A. ...
Tuesday5/10
... to 1/1 billion base pairs. Cells can repair many errors; Humans have 130 known DNA repair enzymes! ...
... to 1/1 billion base pairs. Cells can repair many errors; Humans have 130 known DNA repair enzymes! ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.