DNA Structure and Function Vocabulary
... attached oxygen atoms, which bonds to deoxyribose sugar in DNA. ...
... attached oxygen atoms, which bonds to deoxyribose sugar in DNA. ...
DNA versus RNA Notes File
... • Finally, both DNA and RNA can contain four nitrogenous bases, BUT RNA does not have Thymine. • Thymine is replaced by a similar base called uracil (U). ...
... • Finally, both DNA and RNA can contain four nitrogenous bases, BUT RNA does not have Thymine. • Thymine is replaced by a similar base called uracil (U). ...
Greatest Discoveries with Bill Nye: Genetics
... 24. In 1997, Fire and Mellow were injecting RNA into the cells of a _______________. ...
... 24. In 1997, Fire and Mellow were injecting RNA into the cells of a _______________. ...
NAME CH. 8 HONORS STUDY GUIDE SCIENTISTS: Hershey
... 1. Explain how information flows in the Central Dogma. 2. Where does DNA replication take place for eukaryotic organisms? 3. During what part of the cell cycle will replication take place & how many times? 4. After replication, explain how the new & old strands of DNA are arranged. 5. What is the fu ...
... 1. Explain how information flows in the Central Dogma. 2. Where does DNA replication take place for eukaryotic organisms? 3. During what part of the cell cycle will replication take place & how many times? 4. After replication, explain how the new & old strands of DNA are arranged. 5. What is the fu ...
Greatest Discoveries with Bill Nye: Genetics
... 24. In 1997, Fire and Mellow were injecting RNA into the cells of a _______________. ...
... 24. In 1997, Fire and Mellow were injecting RNA into the cells of a _______________. ...
Unit1-KA4-Revision
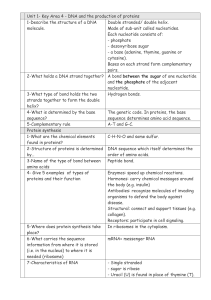
... - a base (adenine, thymine, guanine or cytosine). Bases on each strand form complementary pairs. 2-What holds a DNA strand together? A bond between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of the adjacent nucleotide. 3-What type of bond holds the two Hydrogen bonds. strands together to form the ...
... - a base (adenine, thymine, guanine or cytosine). Bases on each strand form complementary pairs. 2-What holds a DNA strand together? A bond between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of the adjacent nucleotide. 3-What type of bond holds the two Hydrogen bonds. strands together to form the ...
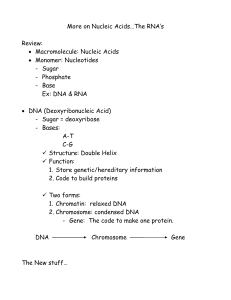
Notes: More on Nucleic Acids
... o A – U (uracil) [There is no T (thymine)] 3 types of RNA: 1. rRNA: [“r” = ribosomal] - structure: ball-like structure with specific “grooves” on the surface, for… - function: synthesize amino acids in to a protein 2. mRNA: [“m” = messenger] - structure: single straight chain of nucleotides - func ...
... o A – U (uracil) [There is no T (thymine)] 3 types of RNA: 1. rRNA: [“r” = ribosomal] - structure: ball-like structure with specific “grooves” on the surface, for… - function: synthesize amino acids in to a protein 2. mRNA: [“m” = messenger] - structure: single straight chain of nucleotides - func ...
DNA Personal Ads
... sequence is really dull, and I’m ready to move on to more exciting things. I’m looking for my true love, mRNA. (transcription) ...
... sequence is really dull, and I’m ready to move on to more exciting things. I’m looking for my true love, mRNA. (transcription) ...
Objectives 2
... 1) List the types and principal functions of the nucleic acids. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is found in the cell nucleus and in the mitochondria and functions to store genetic information used for the synthesis of proteins and enzymes. Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is found in the nucleus, in the cytosol, ...
... 1) List the types and principal functions of the nucleic acids. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is found in the cell nucleus and in the mitochondria and functions to store genetic information used for the synthesis of proteins and enzymes. Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is found in the nucleus, in the cytosol, ...
What Controls the Synthesis of Proteins
... Total number of possible 2-nucleotide strands = ___________________ Okay, now back to the original question. How many 10-nucleotide DNA strands could be made, then? How would you calculate the answer? ...
... Total number of possible 2-nucleotide strands = ___________________ Okay, now back to the original question. How many 10-nucleotide DNA strands could be made, then? How would you calculate the answer? ...
Code DNA!
... This is the process of copying DNA to RNA. The process of nuclear division in cells that produces daughter cells that are genetically identical to each other and to the parent cell. ...
... This is the process of copying DNA to RNA. The process of nuclear division in cells that produces daughter cells that are genetically identical to each other and to the parent cell. ...
Name:
... 5. What is different about how the bases pair together when making RNA? 6. After mRNA (messenger RNA) is made, what happens to it? 7. Our next step is translation. What happens during translation and where does this occur? 8. Match the amino acid anticodons with the mRNA codons. (Mr. Mason will ...
... 5. What is different about how the bases pair together when making RNA? 6. After mRNA (messenger RNA) is made, what happens to it? 7. Our next step is translation. What happens during translation and where does this occur? 8. Match the amino acid anticodons with the mRNA codons. (Mr. Mason will ...
Name Ch 12 Study Guide
... 10) Assume that the two parent strands of DNA have been separated and that the base sequence on one parent strand is A-T-T-C-G-C; the base sequence that will complement that parent strand is __________________________________________ 11) Who was Rosalind Franklin? 12) What was her contribution to th ...
... 10) Assume that the two parent strands of DNA have been separated and that the base sequence on one parent strand is A-T-T-C-G-C; the base sequence that will complement that parent strand is __________________________________________ 11) Who was Rosalind Franklin? 12) What was her contribution to th ...
Biology Packet 7: DNA & RNA
... Summarize the relationship between genes and DNA. Describe the overall structure of the DNA molecule. Describe the three components of a nucleotide. Explain the base pairing rules. Relate the role of the base pairing rules to the structure of DNA. Summarize the events of DNA replication. Describe ho ...
... Summarize the relationship between genes and DNA. Describe the overall structure of the DNA molecule. Describe the three components of a nucleotide. Explain the base pairing rules. Relate the role of the base pairing rules to the structure of DNA. Summarize the events of DNA replication. Describe ho ...
DNA and Chromosomes
... What is the relationship between DNA, chromosomes, and any organism? Drag and drop the descriptive phrase to the correct column, thereby helping us to describe the relationships between these important components of inheritance. ...
... What is the relationship between DNA, chromosomes, and any organism? Drag and drop the descriptive phrase to the correct column, thereby helping us to describe the relationships between these important components of inheritance. ...
The Story of DNA vs. RNA
... did we find out that DNA was the molecule responsible for inheritance? ...
... did we find out that DNA was the molecule responsible for inheritance? ...
DO NOW
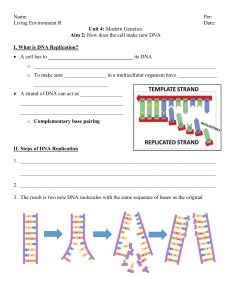
... remained intact as it served as the template for the synthesis of a complementary strand. • This mode of replication is described as semiconservative: one-half of each new molecule of DNA is old; one-half new. ...
... remained intact as it served as the template for the synthesis of a complementary strand. • This mode of replication is described as semiconservative: one-half of each new molecule of DNA is old; one-half new. ...
Study_Guide
... State that ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polynucleotide, usually single-stranded, made up of nucleotides containing the bases adenine (A), uracil (U), cytosine (C) and guanine (G). Describe, with the aid of diagrams, how hydrogen bonding between complementary base pairs (A to T, G to C) on two ant ...
... State that ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polynucleotide, usually single-stranded, made up of nucleotides containing the bases adenine (A), uracil (U), cytosine (C) and guanine (G). Describe, with the aid of diagrams, how hydrogen bonding between complementary base pairs (A to T, G to C) on two ant ...
Protein Synth Notes GO New
... A protein and its function is determined by: What’s another word for phenotype? Which macromolecule does the phenotype describe? Which macromolecule does the genotype describe? Which macromolecule does variation describe? ...
... A protein and its function is determined by: What’s another word for phenotype? Which macromolecule does the phenotype describe? Which macromolecule does the genotype describe? Which macromolecule does variation describe? ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.