DNA/RNA
... 9 Must be able to replicate and must direct protein synthesis for it to play a role in inheritance ...
... 9 Must be able to replicate and must direct protein synthesis for it to play a role in inheritance ...
Review Game
... WHAT ARE THE TYPES OF RNA? (YOU HAVE TO BE SPECIFIC) Messenger, Transfer, Ribosomal ...
... WHAT ARE THE TYPES OF RNA? (YOU HAVE TO BE SPECIFIC) Messenger, Transfer, Ribosomal ...
DNA RNA Protein Hwk KEY
... and synthesize functional human protein. Instead, the protein produced is found to contain many fewer amino acids and doesn't work. What could have gone wrong? Perhaps the human gene contained one or more introns. Prokaryotes like bacteria do not have introns in their genes and do not have cutting & ...
... and synthesize functional human protein. Instead, the protein produced is found to contain many fewer amino acids and doesn't work. What could have gone wrong? Perhaps the human gene contained one or more introns. Prokaryotes like bacteria do not have introns in their genes and do not have cutting & ...
DNA and RNA Review
... What is DNA? What shape (structure) does this molecule have? Draw a sketch of DNA in the space provided. ...
... What is DNA? What shape (structure) does this molecule have? Draw a sketch of DNA in the space provided. ...
DNA and Genetic Engineering Midterm Review Chapter 12 Review
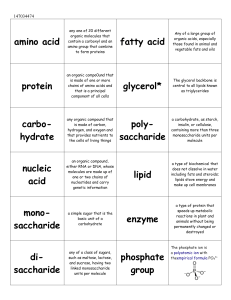
... 12. DNA is a long molecule made up of nucleotides. Each nucleotide has three parts: a 5carbon sugar called deoxyribose, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (adenine, guanine, cytosine or thymine). 13. The two strands of DNA are held together by hydrogen bonds between certain bases – A and T, a ...
... 12. DNA is a long molecule made up of nucleotides. Each nucleotide has three parts: a 5carbon sugar called deoxyribose, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (adenine, guanine, cytosine or thymine). 13. The two strands of DNA are held together by hydrogen bonds between certain bases – A and T, a ...
DNA – The Double Helix
... within the cell; which proteins are made is determined by the sequence of the DNA. Proteins are the building blocks of an organism. How you look is largely determined by the proteins that are made. ...
... within the cell; which proteins are made is determined by the sequence of the DNA. Proteins are the building blocks of an organism. How you look is largely determined by the proteins that are made. ...
DNA NOTES
... 19. In the cytoplasm, mRNA attaches to a ________________. The ________________, with its attached mRNA, is now ready to synthesize a __________________. 20. During Translation, a __________ molecule transfers an _____________________to the ribosome. Each new ______________________links with the pre ...
... 19. In the cytoplasm, mRNA attaches to a ________________. The ________________, with its attached mRNA, is now ready to synthesize a __________________. 20. During Translation, a __________ molecule transfers an _____________________to the ribosome. Each new ______________________links with the pre ...
Ecology
... does not dissolve in water including fats and steroids; lipids stove energy and make up cell membranes ...
... does not dissolve in water including fats and steroids; lipids stove energy and make up cell membranes ...
Vocabulary 7
... 1) DNA – made of subunits known as nucleotides – made of: • sugar • phosphate • base • Shape: Double Helix • Found in the nucleus; chromosomes ...
... 1) DNA – made of subunits known as nucleotides – made of: • sugar • phosphate • base • Shape: Double Helix • Found in the nucleus; chromosomes ...
AT CG - Middletown Public Schools
... DNA and Mutations DNA is made up of nucleotides that each contain a sugar, a phosphate, and a base. The four possible bases are adenine, cytosine, thymine, and guanine. Remember that adenine and thymine are complementary and form pairs, and cytosine and guanine are complementary and form pairs. 1. B ...
... DNA and Mutations DNA is made up of nucleotides that each contain a sugar, a phosphate, and a base. The four possible bases are adenine, cytosine, thymine, and guanine. Remember that adenine and thymine are complementary and form pairs, and cytosine and guanine are complementary and form pairs. 1. B ...
Guanine – Cytosine
... the rungs of the DNA molecule. Adenine - Thymine (A-T) AND Guanine – Cytosine (G-C) • --This specific matching up of the nitrogenous bases is called complementary base pairing. ...
... the rungs of the DNA molecule. Adenine - Thymine (A-T) AND Guanine – Cytosine (G-C) • --This specific matching up of the nitrogenous bases is called complementary base pairing. ...
Write True if the statement is true
... 10. How genetic information is put into action in a living cell E. anticodon 11. Having extra sets of chromosomes F. gene expression 12. Decoding an mRNA message into protein. G. mutation 13. A heritable change in genetic information 14. A chain of amino acids H. mutagen 15. 3 consecutive bases that ...
... 10. How genetic information is put into action in a living cell E. anticodon 11. Having extra sets of chromosomes F. gene expression 12. Decoding an mRNA message into protein. G. mutation 13. A heritable change in genetic information 14. A chain of amino acids H. mutagen 15. 3 consecutive bases that ...
Name - OnCourse
... 3. The “backbones” of the DNA molecule is made up of two components, what are these? c. _______________________________ d. _______________________________ 5. There are four different bases that make up the “rungs.” What are the names of those bases? a. _______________________________ b. ____________ ...
... 3. The “backbones” of the DNA molecule is made up of two components, what are these? c. _______________________________ d. _______________________________ 5. There are four different bases that make up the “rungs.” What are the names of those bases? a. _______________________________ b. ____________ ...
Mentor: James A. MacKay Students: Amanda Williams, Holly Sofka
... Project Description: Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is believed to be an important molecule in the evolution of life and has functionally taken on many important biological roles. Given the many functions of RNA, molecular recognition of RNA represents an attractive goal for practical applications in biotec ...
... Project Description: Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is believed to be an important molecule in the evolution of life and has functionally taken on many important biological roles. Given the many functions of RNA, molecular recognition of RNA represents an attractive goal for practical applications in biotec ...
Modern Genetics Outline
... Modern Genetics Outline Chemical Basis for Genetics In the 1940’s and 1950’s experiments showed that ______ are made up of the chemical compound ______, or ________________________. ______ is a large complex molecule found in the __________ of the cell. ______ is responsible for passing ______ ...
... Modern Genetics Outline Chemical Basis for Genetics In the 1940’s and 1950’s experiments showed that ______ are made up of the chemical compound ______, or ________________________. ______ is a large complex molecule found in the __________ of the cell. ______ is responsible for passing ______ ...
NAME Period___________ Modern Genetics Outline
... Modern Genetics Outline Chemical Basis for Genetics In the 1940’s and 1950’s experiments showed that ______ are made up of the chemical compound ______, or ________________________. ______ is a large complex molecule found in the __________ of the cell. ______ is responsible for passing ______ ...
... Modern Genetics Outline Chemical Basis for Genetics In the 1940’s and 1950’s experiments showed that ______ are made up of the chemical compound ______, or ________________________. ______ is a large complex molecule found in the __________ of the cell. ______ is responsible for passing ______ ...
Microbial Genetics
... half from the “parent” half newly synthesized. It’s initiated at a replication fork; DNA must be unwound and unbound into two single strands. ...
... half from the “parent” half newly synthesized. It’s initiated at a replication fork; DNA must be unwound and unbound into two single strands. ...
DNA notes File
... Mutations in the _____________ may not be as serious Mutations in _____________ mean that the mutation is permanent. Mutations bring ___________ to a species. Mutations can be ________________ and _____________ ...
... Mutations in the _____________ may not be as serious Mutations in _____________ mean that the mutation is permanent. Mutations bring ___________ to a species. Mutations can be ________________ and _____________ ...
Gel Electrophoresis
... * Technique used to separate samples of DNA, RNA, and protein according to charge and/or size ...
... * Technique used to separate samples of DNA, RNA, and protein according to charge and/or size ...
Webquests_files/Genes and DNA SWQ
... The four nucleotides Difference between dominant and recessive alleles ...
... The four nucleotides Difference between dominant and recessive alleles ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.