Protein Synthesis
... tRNA (transfer RNA) carries amino acids to the ribosomes where they join together to form proteins rRNA (ribosomal RNA) is part of the structure of ribosomes mRNA is used to make tRNA then codes for ...
... tRNA (transfer RNA) carries amino acids to the ribosomes where they join together to form proteins rRNA (ribosomal RNA) is part of the structure of ribosomes mRNA is used to make tRNA then codes for ...
suggested essay-type questions for next exam
... bromide, a planar molecule, “intercalates” itself between the stacked DNA base pairs, thereby unwinding the supercoils. However, the linking number of the DNA is not changed! Explain the physical basis for the ability of ethidium bromide to “unwind” these supercoils. (You will have to look at the de ...
... bromide, a planar molecule, “intercalates” itself between the stacked DNA base pairs, thereby unwinding the supercoils. However, the linking number of the DNA is not changed! Explain the physical basis for the ability of ethidium bromide to “unwind” these supercoils. (You will have to look at the de ...
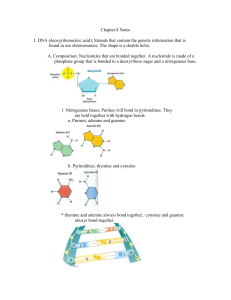
Chapter 11 Notes
... 2. Another enzyme, DNA polymerase attaches free nucleotides to their complementary base pair by hydrogen bonding. 3. Because this is directional, the pairing of bases must occur in a 5’ to 3’ direction. ...
... 2. Another enzyme, DNA polymerase attaches free nucleotides to their complementary base pair by hydrogen bonding. 3. Because this is directional, the pairing of bases must occur in a 5’ to 3’ direction. ...
DNA
... • There is a different code for each protein (which amino acids are used and in what order) • Proteins determine traits like eye color or shape of ear ...
... • There is a different code for each protein (which amino acids are used and in what order) • Proteins determine traits like eye color or shape of ear ...
Who am I?
... What is cloning? Clones are identical copies of living things. Humans have cloned a lot of things already. ...
... What is cloning? Clones are identical copies of living things. Humans have cloned a lot of things already. ...
Chapter 12
... 1. What the window look like on a P-20 if you dialed in 6.3 µL? 2. What the window look like on a P-20 if you dialed in 11.7 µL? 3. What the window look like on a P-20 if you dialed in 15.3 µL? 4. What is the purpose of the “first stop” on the micropipettor? 5. What is the purpose of the “second sto ...
... 1. What the window look like on a P-20 if you dialed in 6.3 µL? 2. What the window look like on a P-20 if you dialed in 11.7 µL? 3. What the window look like on a P-20 if you dialed in 15.3 µL? 4. What is the purpose of the “first stop” on the micropipettor? 5. What is the purpose of the “second sto ...
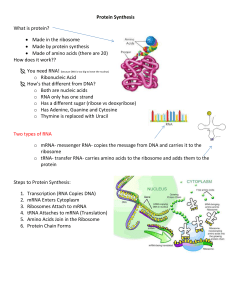
Protein Synthesis - Madison County Schools
... Protein Synthesis What is protein? Made in the ribosome Made by protein synthesis Made of amino acids (there are 20) How does it work?? You need RNA! (because DNA is too big to leave the nucleus) o Ribonucleic Acid How’s that different from DNA? o Both are nucleic acids o RNA only has one ...
... Protein Synthesis What is protein? Made in the ribosome Made by protein synthesis Made of amino acids (there are 20) How does it work?? You need RNA! (because DNA is too big to leave the nucleus) o Ribonucleic Acid How’s that different from DNA? o Both are nucleic acids o RNA only has one ...
1.The general formula for amino acids, explain it term by
... 6.Give a list from the smallest to biggest common terms in molecular biology. Nucleotide
... 6.Give a list from the smallest to biggest common terms in molecular biology. Nucleotide
File
... Polymerase III covalently bonds the sugar-phosphate backbones of the newly hydrogen bonded nucleotides for each of the ...
... Polymerase III covalently bonds the sugar-phosphate backbones of the newly hydrogen bonded nucleotides for each of the ...
Prezentace aplikace PowerPoint
... DNA is a nucleic acid. Within cells, DNA is organized into long structures called chromosomes. • Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a family of large biological molecules that perform vital roles in the coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. Together with DNA, RNA comprises the nucleic acids, ...
... DNA is a nucleic acid. Within cells, DNA is organized into long structures called chromosomes. • Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a family of large biological molecules that perform vital roles in the coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. Together with DNA, RNA comprises the nucleic acids, ...
Genetics
... What's the center of heredity in a cell? In eukaryotic organisms it is the nucleus, in prokaryotes it is the nucleoid region. What is the genetic material? In eukaryotes & prokaryotes it is DNA, in viruses it can be either DNA or RNA. What do DNA & RNA stand for? DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid / RNA: ri ...
... What's the center of heredity in a cell? In eukaryotic organisms it is the nucleus, in prokaryotes it is the nucleoid region. What is the genetic material? In eukaryotes & prokaryotes it is DNA, in viruses it can be either DNA or RNA. What do DNA & RNA stand for? DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid / RNA: ri ...
biology quiz chapter 12
... Answer the following questions on a separate sheet of paper. 1. What are the three types of RNA? 2. What are the three differences between DNA and RNA 3. What is a Codon? 4. If there are 64 possible codons and only 20 amino acids what has to be true? 5. Why does mRNA have to carry DNA’s message to t ...
... Answer the following questions on a separate sheet of paper. 1. What are the three types of RNA? 2. What are the three differences between DNA and RNA 3. What is a Codon? 4. If there are 64 possible codons and only 20 amino acids what has to be true? 5. Why does mRNA have to carry DNA’s message to t ...
DON`T PANIC! THIS SECTION OF SLIDES IS AVAILABLE AT
... part of one strand of the DNA becomes the template for the RNA (a process called “transcription”) feeds selected instructions to ribosomes (molecule factories) about what amino acids must be located and carried to the ribosome to make proteins. “worker”- build structure, function as enzymes to catal ...
... part of one strand of the DNA becomes the template for the RNA (a process called “transcription”) feeds selected instructions to ribosomes (molecule factories) about what amino acids must be located and carried to the ribosome to make proteins. “worker”- build structure, function as enzymes to catal ...
Study Guide to Chapter 5 Ð DNA
... template to make a strand of ___________________ a) mRNA b) tRNA. This occurs in __________ a) the nucleus b) the ribosome). Once the strand is complete it detaches from DNA. The second step in making a protein is called __________________ a) transcription b) translation. The molecule of ___________ ...
... template to make a strand of ___________________ a) mRNA b) tRNA. This occurs in __________ a) the nucleus b) the ribosome). Once the strand is complete it detaches from DNA. The second step in making a protein is called __________________ a) transcription b) translation. The molecule of ___________ ...
ANSWER KEY Nucleic Acid and DNA Replication Outline Notes
... During MITOSIS- chromosomes (DNA) are copied (replicated) ...
... During MITOSIS- chromosomes (DNA) are copied (replicated) ...
Biotech
... PCR • This is the polymerase chain reaction. It is a technique to multiply a sample of DNA many times in a short period of time. It supplies the scientist with sufficient DNA for further testing. http://www.dnalc.org/resources/animations/pcr.html ...
... PCR • This is the polymerase chain reaction. It is a technique to multiply a sample of DNA many times in a short period of time. It supplies the scientist with sufficient DNA for further testing. http://www.dnalc.org/resources/animations/pcr.html ...
22. Recombinant DNA Technology
... 1. Heat shock: CaCl2 at 0oC then heat to 37-42oC 2. Electroporation – apply high voltage BAC – 5,000 to 400,000 bp insert ...
... 1. Heat shock: CaCl2 at 0oC then heat to 37-42oC 2. Electroporation – apply high voltage BAC – 5,000 to 400,000 bp insert ...
Deoxyribozyme
_DNAzyme.png?width=300)
Deoxyribozymes, also called DNA enzymes, DNAzymes, or catalytic DNA, are DNA oligonucleotides that are capable of catalyzing specific chemical reactions, similar to the action of other biological enzymes, such as proteins or ribozymes (enzymes composed of RNA).However, in contrast to the abundance of protein enzymes in biological systems and the discovery of biological ribozymes in the 1980s,there are no known naturally occurring deoxyribozymes.Deoxyribozymes should not be confused with DNA aptamers which are oligonucleotides that selectively bind a target ligand, but do not catalyze a subsequent chemical reaction.With the exception of ribozymes, nucleic acid molecules within cells primarily serve as storage of genetic information due to its ability to form complementary base pairs, which allows for high-fidelity copying and transfer of genetic information. In contrast, nucleic acid molecules are more limited in their catalytic ability, in comparison to protein enzymes, to just three types of interactions: hydrogen bonding, pi stacking, and metal-ion coordination. This is due to the limited number of functional groups of the nucleic acid monomers: while proteins are built from up to twenty different amino acids with various functional groups, nucleic acids are built from just four chemically similar nucleobases. In addition, DNA lacks the 2'-hydroxyl group found in RNA which limits the catalytic competency of deoxyribozymes even in comparison to ribozymes.In addition to the inherent inferiority of DNA catalytic activity, the apparent lack of naturally occurring deoxyribozymes may also be due to the primarily double-stranded conformation of DNA in biological systems which would limit its physical flexibility and ability to form tertiary structures, and so would drastically limit the ability of double-stranded DNA to act as a catalyst; though there are a few known instances of biological single-stranded DNA such as multicopy single-stranded DNA (msDNA), certain viral genomes, and the replication fork formed during DNA replication. Further structural differences between DNA and RNA may also play a role in the lack of biological deoxyribozymes, such as the additional methyl group of the DNA base thymidine compared to the RNA base uracil or the tendency of DNA to adopt the B-form helix while RNA tends to adopt the A-form helix. However, it has also been shown that DNA can form structures that RNA cannot, which suggests that, though there are differences in structures that each can form, neither is inherently more or less catalytic due to their possible structural motifs.