Ch. 16 Stem Notes
... a. Leading strand b. Lagging strand c. Okazaki fragments d. DNA ligase e. Primer 15. Label the diagram below: ...
... a. Leading strand b. Lagging strand c. Okazaki fragments d. DNA ligase e. Primer 15. Label the diagram below: ...
Honors DNA Study Guide
... _____ Studied a substance found only in the nucleus; named it “nuclein” _____ Tested all macromolecules to see which one transforms bacteria. Found only nucleic acid transforms _____ Worked with radioactive viruses and showed that the only inject DNA into the cells they infect _____ Combined data fr ...
... _____ Studied a substance found only in the nucleus; named it “nuclein” _____ Tested all macromolecules to see which one transforms bacteria. Found only nucleic acid transforms _____ Worked with radioactive viruses and showed that the only inject DNA into the cells they infect _____ Combined data fr ...
DNA, Protein Synthesis, and Gene Expression Review Historical
... 3. What are the three parts of a DNA nucleotide (be specific)? 4. Which bases are purine, and which are pyrimidine? What is the basic structure of each (single ring or double ring)? 5. Why is DNA called a double helix? 6. What is in the DNA backbone, and why are they considered antiparallel? 7. What ...
... 3. What are the three parts of a DNA nucleotide (be specific)? 4. Which bases are purine, and which are pyrimidine? What is the basic structure of each (single ring or double ring)? 5. Why is DNA called a double helix? 6. What is in the DNA backbone, and why are they considered antiparallel? 7. What ...
DNA & Protein Synthesis Jeopardy - Warren Hills Regional School
... The major portion of the translation process in which the chain of amino acids grows as the ribosome moves along the mRNA. ...
... The major portion of the translation process in which the chain of amino acids grows as the ribosome moves along the mRNA. ...
Study Guide: Chapter 2
... 12. Compare and contrast genetic information in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. 13. Where is DNA found in eukaryotes? 14. Study Figure 12-10. Write a description of how DNA is packaged in the cell start with the double helix and describe how DNA is eventually packaged into a chromosome. 15. Define chrom ...
... 12. Compare and contrast genetic information in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. 13. Where is DNA found in eukaryotes? 14. Study Figure 12-10. Write a description of how DNA is packaged in the cell start with the double helix and describe how DNA is eventually packaged into a chromosome. 15. Define chrom ...
Study guide for Ch 13-16,18 Test AP Biology 2014
... how much adenine there is and then calculate cytosine and guanine. (Chargaff’s Rule) What type of mutation occurs in sickle cell so that glutamic acid then becomes valine? If given a DNA base sequence, be able to give the complementary strand or the mRNA strand that would be opposite it. Know what a ...
... how much adenine there is and then calculate cytosine and guanine. (Chargaff’s Rule) What type of mutation occurs in sickle cell so that glutamic acid then becomes valine? If given a DNA base sequence, be able to give the complementary strand or the mRNA strand that would be opposite it. Know what a ...
MCB 421-2006: Homologous Recombination
... RecA-RecBC pathway catalyzes exchanges between two DNAs if at least one of them has free ends (like during conjugation), while the RecA-RecFOR pathway catalyzes exchanges between chromosomes without ends, for example, between two circular plasmids. We can also say that both RecG and Ruv functions he ...
... RecA-RecBC pathway catalyzes exchanges between two DNAs if at least one of them has free ends (like during conjugation), while the RecA-RecFOR pathway catalyzes exchanges between chromosomes without ends, for example, between two circular plasmids. We can also say that both RecG and Ruv functions he ...
DNA Review
... An abnormality or deformation of an organism due to pollutants in the environment that affect the organism’s DNA. ...
... An abnormality or deformation of an organism due to pollutants in the environment that affect the organism’s DNA. ...
Unit 8 Test Review Answers do not have to be in complete
... 11. What did Rosalind Franklin do that led to the discovery of the shape of DNA? 12. What did Watson and Crick do that led to the discovery of the shape of DNA? 13. What name is give to the shape of DNA? 14. How is DNA different in prokaryotes and eukaryotes? 15. What role do histones play in the st ...
... 11. What did Rosalind Franklin do that led to the discovery of the shape of DNA? 12. What did Watson and Crick do that led to the discovery of the shape of DNA? 13. What name is give to the shape of DNA? 14. How is DNA different in prokaryotes and eukaryotes? 15. What role do histones play in the st ...
1 - EPHSLinnBiology
... The nucleus of the cell contains a “blueprint” (instructions) for the structure of a cell and cell activity. These instructions are found within structures called ___29___. A normal person has ___30___ (a number) of these structures in every nucleus of every cell. The structures inside the nucleus a ...
... The nucleus of the cell contains a “blueprint” (instructions) for the structure of a cell and cell activity. These instructions are found within structures called ___29___. A normal person has ___30___ (a number) of these structures in every nucleus of every cell. The structures inside the nucleus a ...
Genetic Engineering Paper Exercise
... Which of these 3 recognition sequences are present in the human DNA? Explain which restriction enzyme you would choose to isolate this gene. Use scissors (restriction enzymes) to isolate the gene, making sure you make your cut exactly as shown above. Step 2 Insertion of gene into bacterial plasmid U ...
... Which of these 3 recognition sequences are present in the human DNA? Explain which restriction enzyme you would choose to isolate this gene. Use scissors (restriction enzymes) to isolate the gene, making sure you make your cut exactly as shown above. Step 2 Insertion of gene into bacterial plasmid U ...
Topic 12 DNA - Ms. Mogck`s Classroom
... • she also discovered the phosphate group was on the outside (backbone) • Maurice Wilkins showed her work to Watson and Crick without her knowledge ...
... • she also discovered the phosphate group was on the outside (backbone) • Maurice Wilkins showed her work to Watson and Crick without her knowledge ...
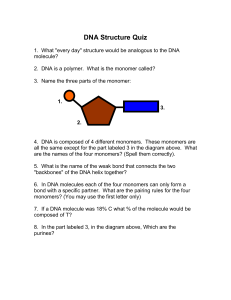
DNA Structure quick review/quiz
... DNA Structure Quiz 1. What "every day" structure would be analogous to the DNA molecule? 2. DNA is a polymer. What is the monomer called? 3. Name the three parts of the monomer: ...
... DNA Structure Quiz 1. What "every day" structure would be analogous to the DNA molecule? 2. DNA is a polymer. What is the monomer called? 3. Name the three parts of the monomer: ...
Mitosis and DNA worksheet
... 15. What is the disorder that occurs when the cells are unable control the cell cycle? _____________________ 16. List the causes of this disorder __________________________________________ 17. List the treatments of this disorder _______________________________________ ...
... 15. What is the disorder that occurs when the cells are unable control the cell cycle? _____________________ 16. List the causes of this disorder __________________________________________ 17. List the treatments of this disorder _______________________________________ ...
DNA and DNA Replication Guided Notes
... The number of ___________________and mutations are reduced by “proofreading enzymes” ...
... The number of ___________________and mutations are reduced by “proofreading enzymes” ...
11.3 and 11.4 Notes - West Branch Schools
... During DNA replication, the two strands of the original parent DNA molecule, shown in blue, each serve as a template for making a new strand, shown in yellow. Replication results in two daughter DNA molecules, each consisting of one original strand and one new strand. ...
... During DNA replication, the two strands of the original parent DNA molecule, shown in blue, each serve as a template for making a new strand, shown in yellow. Replication results in two daughter DNA molecules, each consisting of one original strand and one new strand. ...
Document
... 6. Scientists were surprised about how much the DNA molecule could do, because they thought only ____________________ molecules could give instructions and be copied during cell division. ...
... 6. Scientists were surprised about how much the DNA molecule could do, because they thought only ____________________ molecules could give instructions and be copied during cell division. ...
Title - Iowa State University
... Semi-conservative- The mechanism which DNA replicate, where the parent strands separate and serve as a template for the daughter strands, etc. Complementary- Opposites that combine to form the whole. Replication fork- Where the unwinding of the helices and new strands are synthesized occurs. Telomer ...
... Semi-conservative- The mechanism which DNA replicate, where the parent strands separate and serve as a template for the daughter strands, etc. Complementary- Opposites that combine to form the whole. Replication fork- Where the unwinding of the helices and new strands are synthesized occurs. Telomer ...
DNA Modeling Lab Report - the Biology Scholars Program Wiki
... 15. After reading Watson and Crick’s original paper, write a short essay (1-2 paragraphs) as a group, describing: A. The technique used to determine the structure (feel free to do a quick online search) B. What you consider to be the important findings that they describe. C. Use the paper provided a ...
... 15. After reading Watson and Crick’s original paper, write a short essay (1-2 paragraphs) as a group, describing: A. The technique used to determine the structure (feel free to do a quick online search) B. What you consider to be the important findings that they describe. C. Use the paper provided a ...
DNA Replication Amoeba Sisters Video
... DNA Replication Amoeba Sisters Video As you watch the animation on DNA Replication, answer the following questions. ...
... DNA Replication Amoeba Sisters Video As you watch the animation on DNA Replication, answer the following questions. ...
Bioinformatics programming exercise II
... The special structure of the DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) allows stored information to be preserved and passed from one cell to another (cell division). The strands of DNA’s famous double helix structure are held together by nucleotide bonds, where A (Adenine) only binds with T (Thymine) and G (Guani ...
... The special structure of the DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) allows stored information to be preserved and passed from one cell to another (cell division). The strands of DNA’s famous double helix structure are held together by nucleotide bonds, where A (Adenine) only binds with T (Thymine) and G (Guani ...
Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis Review Guide
... What are purines? How many rings do they have? What are pyrimidines? How many rings do they have? The double helix structure of DNA was discovered by what FOUR scientists (last names only are okay) and in what year? Be able to label the structures of a DNA molecule (refer to notes): a. What is the b ...
... What are purines? How many rings do they have? What are pyrimidines? How many rings do they have? The double helix structure of DNA was discovered by what FOUR scientists (last names only are okay) and in what year? Be able to label the structures of a DNA molecule (refer to notes): a. What is the b ...
2054, Chap. 13, page 1 I. Microbial Recombination and Plasmids
... A. recombination = process of combining genetic material from 2 organisms to produce a genotype different from either parent (exchange of DNA between different genes) 1. occurs during meiosis as crossing over between homologous chromosomes 2. genetic recombination (homologous recombination) is the m ...
... A. recombination = process of combining genetic material from 2 organisms to produce a genotype different from either parent (exchange of DNA between different genes) 1. occurs during meiosis as crossing over between homologous chromosomes 2. genetic recombination (homologous recombination) is the m ...
DNA - Midway ISD
... protein. Each unique gene has a unique sequence of bases. This unique sequence of bases will code for the ...
... protein. Each unique gene has a unique sequence of bases. This unique sequence of bases will code for the ...
The Structure of DNA DNA Has the Structure of a Winding Staircase
... • Early 1950’s, James Watson and Francis Crick determined that DNA is a molecule that is a double helix. • A double helix is two strands twisted around each other. ...
... • Early 1950’s, James Watson and Francis Crick determined that DNA is a molecule that is a double helix. • A double helix is two strands twisted around each other. ...
Homologous recombination
Homologous recombination is a type of genetic recombination in which nucleotide sequences are exchanged between two similar or identical molecules of DNA. It is most widely used by cells to accurately repair harmful breaks that occur on both strands of DNA, known as double-strand breaks. Homologous recombination also produces new combinations of DNA sequences during meiosis, the process by which eukaryotes make gamete cells, like sperm and egg cells in animals. These new combinations of DNA represent genetic variation in offspring, which in turn enables populations to adapt during the course of evolution. Homologous recombination is also used in horizontal gene transfer to exchange genetic material between different strains and species of bacteria and viruses.Although homologous recombination varies widely among different organisms and cell types, most forms involve the same basic steps. After a double-strand break occurs, sections of DNA around the 5' ends of the break are cut away in a process called resection. In the strand invasion step that follows, an overhanging 3' end of the broken DNA molecule then ""invades"" a similar or identical DNA molecule that is not broken. After strand invasion, the further sequence of events may follow either of two main pathways discussed below (see Models); the DSBR (double-strand break repair) pathway or the SDSA (synthesis-dependent strand annealing) pathway. Homologous recombination that occurs during DNA repair tends to result in non-crossover products, in effect restoring the damaged DNA molecule as it existed before the double-strand break.Homologous recombination is conserved across all three domains of life as well as viruses, suggesting that it is a nearly universal biological mechanism. The discovery of genes for homologous recombination in protists—a diverse group of eukaryotic microorganisms—has been interpreted as evidence that meiosis emerged early in the evolution of eukaryotes. Since their dysfunction has been strongly associated with increased susceptibility to several types of cancer, the proteins that facilitate homologous recombination are topics of active research. Homologous recombination is also used in gene targeting, a technique for introducing genetic changes into target organisms. For their development of this technique, Mario Capecchi, Martin Evans and Oliver Smithies were awarded the 2007 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine.