Problem Set 3A
... 1. (Read the first 3 questions before you do any of them.) Draw a section of the E. coli chromosome as replication is occurring through that region. Give yourself plenty of room and make the replication bubble stretch most of the way from one side of your paper to the other. Show both replication fo ...
... 1. (Read the first 3 questions before you do any of them.) Draw a section of the E. coli chromosome as replication is occurring through that region. Give yourself plenty of room and make the replication bubble stretch most of the way from one side of your paper to the other. Show both replication fo ...
Bio07_TR__U04_CH12.QXD
... Matching On the lines provided, match the letter of the scientist(s) with the description of his or their conclusions. a. Griffith b. Avery c. Hershey and Chase ______________ 1. ...
... Matching On the lines provided, match the letter of the scientist(s) with the description of his or their conclusions. a. Griffith b. Avery c. Hershey and Chase ______________ 1. ...
Ch. 16 Molecular Basis of Genetics
... helic - = a spiral (helicase: an enzyme that untwists the double helix of DNA at the replication forks) liga - = bound or tied (DNA ligase: a linking enzyme for DNA replication) -phage = to eat (bacteriophages: viruses that infect bacteria) semi - = half (semiconservative model: type of DNA replicat ...
... helic - = a spiral (helicase: an enzyme that untwists the double helix of DNA at the replication forks) liga - = bound or tied (DNA ligase: a linking enzyme for DNA replication) -phage = to eat (bacteriophages: viruses that infect bacteria) semi - = half (semiconservative model: type of DNA replicat ...
Glossary of Terms – DNA and the production of proteins
... Structures found in nucleus which carry genetic information Molecule, found in the nucleus which carries the genetic code Strand of DNA which codes for a protein Subunit of DNA molecule which consists of a phosphate group, deoxyribose sugar and a base Parts of the DNA structure which pair up with on ...
... Structures found in nucleus which carry genetic information Molecule, found in the nucleus which carries the genetic code Strand of DNA which codes for a protein Subunit of DNA molecule which consists of a phosphate group, deoxyribose sugar and a base Parts of the DNA structure which pair up with on ...
Chapter 12
... The Double___________: 1. The structure of DNA was discovered through the work of three people: A. _________________________ (1950s) - she used a technique called ______________________________ to show that DNA has two strands that form a ________. ...
... The Double___________: 1. The structure of DNA was discovered through the work of three people: A. _________________________ (1950s) - she used a technique called ______________________________ to show that DNA has two strands that form a ________. ...
Genetic Engineering Topic #0008D By: Tony Hoffman
... Can we change DNA? Yes we can…by a method called Gene Splicing - the process of cutting the DNA of a gene in order to add base pairs. 1. Chemicals called restriction enzymes act as the scissors to cut the DNA. Once it finds that sequence in a strand of DNA, it attacks it and splits the base pairs a ...
... Can we change DNA? Yes we can…by a method called Gene Splicing - the process of cutting the DNA of a gene in order to add base pairs. 1. Chemicals called restriction enzymes act as the scissors to cut the DNA. Once it finds that sequence in a strand of DNA, it attacks it and splits the base pairs a ...
Lecture 8
... 2. Efficiency: whenever sufficiently long homologous sequences are brought together in a single cell under appropriate conditions, the production of recombinant sequence is more of a rule than exception. 3. Complexity: Several proteins are required in base paring and strand exchange. It is a conserv ...
... 2. Efficiency: whenever sufficiently long homologous sequences are brought together in a single cell under appropriate conditions, the production of recombinant sequence is more of a rule than exception. 3. Complexity: Several proteins are required in base paring and strand exchange. It is a conserv ...
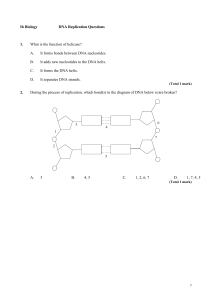
Ib Biology DNA Replication Questions 1. What is the function of
... [Freeman, Scott, Biological Science, 1st, 2002. Electronically reproduced by permission of Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, New Jersey] ...
... [Freeman, Scott, Biological Science, 1st, 2002. Electronically reproduced by permission of Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, New Jersey] ...
DNA Recombination Mechanisms
... Recombination occurs randomly between two homologous sequences and the frequency of recombination between two sites is proportional to the distance between the sites ...
... Recombination occurs randomly between two homologous sequences and the frequency of recombination between two sites is proportional to the distance between the sites ...
DNA Structure copy
... Sides of the ladder =“BACKBONE” and consist of alternating phosphate groups and sugars held together by covalent bonds The “RUNGS” = nitrogen bases ...
... Sides of the ladder =“BACKBONE” and consist of alternating phosphate groups and sugars held together by covalent bonds The “RUNGS” = nitrogen bases ...
The discovery:DNA
... The discovery:DNA .The Swiss biochemist Friedrich Miescher (18441895) discovered the nucleic acids in 1868. His experiment: ...
... The discovery:DNA .The Swiss biochemist Friedrich Miescher (18441895) discovered the nucleic acids in 1868. His experiment: ...
made of three parts sugar, phosphate, and base Scientist that
... Scientist who worked with pneumonia & mice & discovered transformation ...
... Scientist who worked with pneumonia & mice & discovered transformation ...
Prentice hall Biology Worksheets
... Matching On the lines provided, match the letter of the scientist(s) with the description of his or their conclusions. a. Griffith b. Avery c. Hershey and Chase 1. concluded that the genetic material of a bacteriophage is DNA 2. concluded that DNA was the factor that transmits genetic information fr ...
... Matching On the lines provided, match the letter of the scientist(s) with the description of his or their conclusions. a. Griffith b. Avery c. Hershey and Chase 1. concluded that the genetic material of a bacteriophage is DNA 2. concluded that DNA was the factor that transmits genetic information fr ...
Across
... 2. the two sides of DNA held together by weak ____ bonds 5. always pairs with cytosine 6. where protein is assembled from the message on the RNA 7. the shape of DNA, double ____ 9. process of copying DNA 13. composed of a sugar, a base, and a phosphate 14. sections of DNA that code for a trait 15. r ...
... 2. the two sides of DNA held together by weak ____ bonds 5. always pairs with cytosine 6. where protein is assembled from the message on the RNA 7. the shape of DNA, double ____ 9. process of copying DNA 13. composed of a sugar, a base, and a phosphate 14. sections of DNA that code for a trait 15. r ...
Name Bozeman – What is DNA? http://backpack.tv/video/biology
... 2. Complete the following chart: ...
... 2. Complete the following chart: ...
Chapter 8—Microbial Genetics Study Guide NOTE: I will not test you
... 5. Compare and contrast prokaryotic genetics with eukaryotic genetics (introns and exons with respect to RNA processing). 6. What is the lac operon? a. Describe its parts and their functions. b. Is it an inducible or repressible operon? i. What is the inducer? 7. What is a mutation? a. What is a bas ...
... 5. Compare and contrast prokaryotic genetics with eukaryotic genetics (introns and exons with respect to RNA processing). 6. What is the lac operon? a. Describe its parts and their functions. b. Is it an inducible or repressible operon? i. What is the inducer? 7. What is a mutation? a. What is a bas ...
DNA RNA Test Review Guide
... Name the monomer of DNA and its 3 parts. Describe the bonds holding the monomers of DNA together. Explain the discovery of Watson and Crick. What was Rosalind Franklin’s contribution? Maurice Wilkins? What was known before Franklin’s work? Who received the Nobel prize? Explain the importance of DNA, ...
... Name the monomer of DNA and its 3 parts. Describe the bonds holding the monomers of DNA together. Explain the discovery of Watson and Crick. What was Rosalind Franklin’s contribution? Maurice Wilkins? What was known before Franklin’s work? Who received the Nobel prize? Explain the importance of DNA, ...
Ch - TeacherWeb
... C. tRNA- the supplier. Transfers rna delivers amino acids to ribosomes to be assembled. ...
... C. tRNA- the supplier. Transfers rna delivers amino acids to ribosomes to be assembled. ...
homologous recombination
... of interest. By mechanisms that are poorly understood but are similar to what occurrs during meiosis and mitosis when homolgous chromosomes align along the metaphase plane, the engineered construct finds the targeted gene and recombination takes place within the homolgous (meaning identical in this ...
... of interest. By mechanisms that are poorly understood but are similar to what occurrs during meiosis and mitosis when homolgous chromosomes align along the metaphase plane, the engineered construct finds the targeted gene and recombination takes place within the homolgous (meaning identical in this ...
Homologous recombination
Homologous recombination is a type of genetic recombination in which nucleotide sequences are exchanged between two similar or identical molecules of DNA. It is most widely used by cells to accurately repair harmful breaks that occur on both strands of DNA, known as double-strand breaks. Homologous recombination also produces new combinations of DNA sequences during meiosis, the process by which eukaryotes make gamete cells, like sperm and egg cells in animals. These new combinations of DNA represent genetic variation in offspring, which in turn enables populations to adapt during the course of evolution. Homologous recombination is also used in horizontal gene transfer to exchange genetic material between different strains and species of bacteria and viruses.Although homologous recombination varies widely among different organisms and cell types, most forms involve the same basic steps. After a double-strand break occurs, sections of DNA around the 5' ends of the break are cut away in a process called resection. In the strand invasion step that follows, an overhanging 3' end of the broken DNA molecule then ""invades"" a similar or identical DNA molecule that is not broken. After strand invasion, the further sequence of events may follow either of two main pathways discussed below (see Models); the DSBR (double-strand break repair) pathway or the SDSA (synthesis-dependent strand annealing) pathway. Homologous recombination that occurs during DNA repair tends to result in non-crossover products, in effect restoring the damaged DNA molecule as it existed before the double-strand break.Homologous recombination is conserved across all three domains of life as well as viruses, suggesting that it is a nearly universal biological mechanism. The discovery of genes for homologous recombination in protists—a diverse group of eukaryotic microorganisms—has been interpreted as evidence that meiosis emerged early in the evolution of eukaryotes. Since their dysfunction has been strongly associated with increased susceptibility to several types of cancer, the proteins that facilitate homologous recombination are topics of active research. Homologous recombination is also used in gene targeting, a technique for introducing genetic changes into target organisms. For their development of this technique, Mario Capecchi, Martin Evans and Oliver Smithies were awarded the 2007 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine.