* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BASE PAIR RULE or
DNA repair protein XRCC4 wikipedia , lookup
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Homologous recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
DNA nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
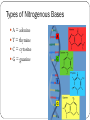
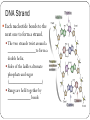
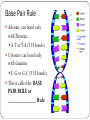
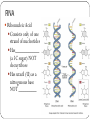
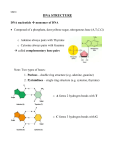
DNA & RNA The Vocabulary of DNA Genetics—The study of genes & _________ _______-- inherited characteristic determined by the presence and expression of dominant and/or recessive alleles. ________-- a segment of DNA that codes for a protein, which in turn codes for a trait (skin tone, eye color, etc.) Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins took DNA X-ray photos that were essential to the discovery of the __________________of DNA by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953. When Watson, Crick and Wilkins got their Nobel prize awards in 1962, Rosalind Franklin was cheated of deserved recognition in part by her early death from cancer in 1958. Why is the Study of DNA Important? It’s essential to all life on earth Medical Benefits—disease detection, treatment, prevention Development of ________ Forensics Nucleotides Consists of… ___________ Carbon sugar (deoxyribose) ___________ base Types of Nitrogenous Bases A = adenine T = thymine C = cytosine G = guanine DNA Strand Each nucleotide bonds to the next one to form a strand. The two strands twist around a ________________to form a double helix. Sides of the ladder alternate phosphate and sugar (___________________) Rungs are held together by _____________ bonds Base Pair Rule Adenine can bond only with Thymine A-T or T-A (2 H bonds) Cytosine can bond only with Guanine C-G or G-C (3 H bonds) This is called the BASE PAIR RULE or ______________ Rule RNA Ribonucleic Acid Consists only of one strand of nucleotides Has____________ (a 5C sugar) NOT deoxyribose Has uracil (U) as a nitrogenous base NOT _________