* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SBI3U - misshoughton.net
Survey
Document related concepts
Eukaryotic DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
DNA repair protein XRCC4 wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
Homologous recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
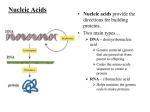
SBI3U DNA STRUCTURE DNA nucleotide monomer of DNA Composed of a phosphate, deoxyribose sugar, nitrogenous base (A,T,C,G) o Adenine always pairs with Thymine o Cytosine always pairs with Guanine called complementary base pairs Note: Two types of bases: 1. Purines – double ring structure (e.g. adenine, guanine) 2. Pyrimidines – single ring structure (e.g. cytosine, thymine) o A forms 2 hydrogen bonds with T o C forms 3 hydrogen bonds with G Double stranded structure forms a “Double Helix” The code of the DNA is in the sequence of bases o A sequence of 3 bases (called a codon) codes for an amino acid e.g. AAA codes for phenylalanine AGT codes for serine A gene is composed of a specific sequence of nucleotides (bases) that codes for a specific amino acid sequence specific protein A chromosome is composed of hundreds to thousands of genes Importance of the Double Helix Structure: Ensures no errors are made during replication o Having a complementary strand acts like a “spell check” o If an incorrect or damaged base is added, it will be replaced with a proper base DNA REPLICATION Process by which other copies of DNA is made Occurs in the nucleus, before cell division STEPS: 1. The original DNA molecule unzips with the help of an enzyme that breaks the bonds between the complementary base pairs 2. Free nucleotides bond to each of the unzipped parent chains (other enzymes help do this) each parent strand is used to build a complementary strand Recall: Adenine bonds to Thymine, Cytosine bonds to Guanine 3. Sugar and phosphate of the adjacent nucleotides bond to form the backbone of the new DNA strand 4. Two new copies of DNA are produced from the original DNA molecule. this is referred to as “Semi-Conservative” method