* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DNA Structure
Eukaryotic DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
DNA repair protein XRCC4 wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Homologous recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
DNA nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
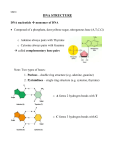
DNA Structure Section 11.2 Nucleic Acids (2 groups) DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid Stores genetic info Nucleic Acid made of nucleotides ONLY 4 types of nucleotides make up DNA RNA Ribonucleic acid Plays key role in cells (Details to come…) Nucleotides Each nucleotide has 3 parts 1. ring-shaped sugar called deoxyribose 2. A phosphate group (phosphorous surrounded by 4 oxygens) 3. Nitrogen base: single or double ring of carbon & nitrogen atoms w/ functional groups Nitrogen Bases Pyrimidines Single ringed Thymine (T) Cytosine (C) Purines Double ringed Adenine (A) Guanine (G) DNA Strands To make a strand of DNA: The nucleotides are joined together w/ a covalent bond connecting the sugar of one nucleotide to the phosphate group of the next This makes up the “Backbone” of DNA (sides of the ladder) DNA’s Structure Rosalind Franklin & Maurice Wilkins produced photos of DNA using Xray crystallography Gives clues to shapes & dimensions Showed DNA to be a helix The Double Helix James Watson & Francis Crick created a model w/ the assistance of Franklin’s photos: 2 strands of nucleotides wound around each other forming a DOUBLE HELIX Hypothesized the nitrogen bases across from each other formed hydrogen bonds Complementary Base Pairs The structure of the nitrogen bases determine specific pairings b/w the nucleotides sizes & ability to form H-bonds A always pairs w/ T (complementary bases) G always pairs w/ C (complementary bases) The sequence on one strand can vary: the sequence of the bases on the 2nd strand are determined by the first. http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/units/ba sics/builddna/ Concept Check 11.2 1. What are the three parts of a nucleotide? Which parts make up the backbone of a DNA strand? 2. List the two base pairs found in DNA. 3. If six bases on one strand of a DNA double helix are AGTCGG, what are the six bases on the complementary section of the other strand of DNA?