* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Deoxyribonucleic Acids DNA
DNA repair protein XRCC4 wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Homologous recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
DNA nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
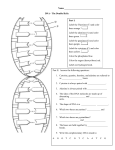
Chapter 12 Deoxyribonucleic Acids 2 Cornell Questions Chromosomes- A threadlike linear strand of DNA and associated proteins in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells that carries the genes and functions in the transmission of hereditary information. In prokaryotes (bacteria) it is a circular strand of DNA in that contains the hereditary information necessary for cell life. DNA is made up of 2 strands of the bases guanine, adenine, thymine, and cytosine, covalently bonded. The 2 strands are complementary, (side-by-side in opposite directions). The four nitrogen-containing bases found in DNA are divided into two groups: purines and pyrimidines. Stopped here 1st per Adenine and guanine are two-ringed bases called purines. Thymine and cytosine are One-ringed bases called pyrimidines. Each strands forms helix, and the two helices are held together through hydrogen bonds, ionic forces, forming a double helix. The Structure of DNA Cornell Style Notes with 3 Questions DNA is a long molecule made up of units called nucleotides. Nucleotides are made up of three basic components: a 5- carbon sugar called deoxyribose, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base, (nitrogencontaining base). There are four kinds of nitrogenous bases in DNA, two are purines adenine and guanine, and two are pyrimidines, thymine and cytosine. The back bone of a DNA chain is formed by sugar and phosphate groups of each nucleotide. Transparency #173 nucleotide pairing draw below.