16.3 DNA and Protein Synthesis
... make up the cell walls of plants? A. Other molecules such as mRNA hold the code for creating non-protein molecules within an organism. B. Carbohydrates are created during photosynthesis and do not require genetic information or proteins. C. Enzymes are are made made of of protein proteinand andcan c ...
... make up the cell walls of plants? A. Other molecules such as mRNA hold the code for creating non-protein molecules within an organism. B. Carbohydrates are created during photosynthesis and do not require genetic information or proteins. C. Enzymes are are made made of of protein proteinand andcan c ...
DNA
... Structure of DNA • Made of nucleotides – Each nucleotide: • Sugar (deoxyribose) • Phosphate group (negatively charged) • Nitrogen base adenine (A) guanine (G) cytosine (C) thymine (T) ...
... Structure of DNA • Made of nucleotides – Each nucleotide: • Sugar (deoxyribose) • Phosphate group (negatively charged) • Nitrogen base adenine (A) guanine (G) cytosine (C) thymine (T) ...
Name: Date: Chapter 3 Directed Reading (Section 1) Directions
... 3.The subunits that make up DNA are called a. phosphates. c. amino acids. b. nucleotides. d. bases. 4. What two things must DNA be able to do? ...
... 3.The subunits that make up DNA are called a. phosphates. c. amino acids. b. nucleotides. d. bases. 4. What two things must DNA be able to do? ...
Topic 2 – DNA structure According to Watson and Crick, DNA
... According to Watson and Crick, DNA consists of two strands of nucleotides A nucleotide consists of: o A Deoxyribose sugar (5 carbons) o A phosphate group o A nitrogenous base § The only thing different between nucleotides ...
... According to Watson and Crick, DNA consists of two strands of nucleotides A nucleotide consists of: o A Deoxyribose sugar (5 carbons) o A phosphate group o A nitrogenous base § The only thing different between nucleotides ...
11.1 Replication of DNA
... Describe the sequence of events in DNA replication Identify the enzymes and state the reactions they control in DNA replication. Explain the semi-conservative nature of DNA replication ...
... Describe the sequence of events in DNA replication Identify the enzymes and state the reactions they control in DNA replication. Explain the semi-conservative nature of DNA replication ...
DNA Replication and Protein Synthesis sharepoint
... • the transfer of genetic material to the ribosome but DNA stays in the nucleus! • Gene expression = use of DNA information to form proteins – 2 stages → – first is transcription = mRNA copy is made. – Second is translation = 3 different RNA’s (mRNA, tRNA, rRNA) work to assemble amino acids into pro ...
... • the transfer of genetic material to the ribosome but DNA stays in the nucleus! • Gene expression = use of DNA information to form proteins – 2 stages → – first is transcription = mRNA copy is made. – Second is translation = 3 different RNA’s (mRNA, tRNA, rRNA) work to assemble amino acids into pro ...
Unit 4 Review: Molecular Genetics
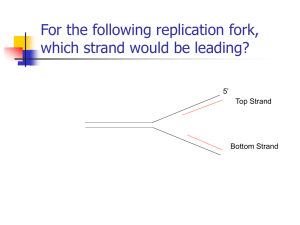
... 11) Sketch and label a 7 base-pair DNA segment starting from the skeleton provided. The first two basepairs of the parent strand are still hydrogen-bonded, but the remaining five base-pairs of this replication fork are separated and undergoing replication. The lines extending from the 2 parent stra ...
... 11) Sketch and label a 7 base-pair DNA segment starting from the skeleton provided. The first two basepairs of the parent strand are still hydrogen-bonded, but the remaining five base-pairs of this replication fork are separated and undergoing replication. The lines extending from the 2 parent stra ...
Molecular Genetics
... • Directionality of DNA: refers the end-to-end chemical orientation of a single strand of nucleic acid. • One strand runs in the 5’ to 3’ direction while the other strand runs in the 3’ to 5’. • The 3’ end terminates with the hydroxyl group of the deoxyribose sugar. • The 5’ end terminates with a ph ...
... • Directionality of DNA: refers the end-to-end chemical orientation of a single strand of nucleic acid. • One strand runs in the 5’ to 3’ direction while the other strand runs in the 3’ to 5’. • The 3’ end terminates with the hydroxyl group of the deoxyribose sugar. • The 5’ end terminates with a ph ...
Genes and DNA
... Watson and Crick • After looking at chargaff’s work and Franklin’s work. They came to the conclusion that “DNA must look like a long, twisted ladder. This lead to the explanation on how DNA is copied and how it functions in the cell. ...
... Watson and Crick • After looking at chargaff’s work and Franklin’s work. They came to the conclusion that “DNA must look like a long, twisted ladder. This lead to the explanation on how DNA is copied and how it functions in the cell. ...
DNA - Imagine School at Lakewood Ranch
... Cells use the genes they need to do their job and ignore the other genes Example: Cells in your stomach produce the proteins needed to digest your food while muscle cells produce proteins to make your muscles move. ...
... Cells use the genes they need to do their job and ignore the other genes Example: Cells in your stomach produce the proteins needed to digest your food while muscle cells produce proteins to make your muscles move. ...
DNA - Miss Gleason`s Science
... • Watson and Crick- working on a model of DNA – Saw Franklins x-ray- used her research to build model of DNA – Double Helix- 2 strands wound around each other ...
... • Watson and Crick- working on a model of DNA – Saw Franklins x-ray- used her research to build model of DNA – Double Helix- 2 strands wound around each other ...
Is an inducible operon normally off or on?
... Put the following enzymes in order for DNA replication ...
... Put the following enzymes in order for DNA replication ...
Cardiff International School Dhaka (CISD) Lost Class Make Up
... (b) Hydrogen bonding is a special type of bond. These hydrogen bonds are what allow for DNA to have their unique structure. Hydrogen bonds occur between base pairs which link complementary strands and enable replication. (c) Semiconservative replication would produce two copies that each contained o ...
... (b) Hydrogen bonding is a special type of bond. These hydrogen bonds are what allow for DNA to have their unique structure. Hydrogen bonds occur between base pairs which link complementary strands and enable replication. (c) Semiconservative replication would produce two copies that each contained o ...
Forensics_DNA Structure_2013
... Complimentary Base Pairing Bases held together with Hydrogen bonds- WEAK BONDS Guanine pairs with Cytosine ...
... Complimentary Base Pairing Bases held together with Hydrogen bonds- WEAK BONDS Guanine pairs with Cytosine ...
Nucleic Acid Worksheet Honors
... In what position(s) of the sugar does this occur? In what position(s) of the base does this occur? 11. Instead of the term “Formation of a nucleoside”, what could the name of the reaction be? What functional group is being formed? 12. What is the difference between “Uridine” and “Uridine 5’-monophos ...
... In what position(s) of the sugar does this occur? In what position(s) of the base does this occur? 11. Instead of the term “Formation of a nucleoside”, what could the name of the reaction be? What functional group is being formed? 12. What is the difference between “Uridine” and “Uridine 5’-monophos ...
Pl Path 111- Variability in Plant Pathogens
... result of recombination occurs during sexual processes. • When two haploid nuclei (1N) containing different gnentic maeterial unite to form diploid (2N) nucleus called a Zygote, when under go meiotic division produce new haploid . Recombination of gnentic factor occurs during meiotic division of zyg ...
... result of recombination occurs during sexual processes. • When two haploid nuclei (1N) containing different gnentic maeterial unite to form diploid (2N) nucleus called a Zygote, when under go meiotic division produce new haploid . Recombination of gnentic factor occurs during meiotic division of zyg ...
Slide ()
... PJ, Weil some P. Harper's Illustrated Biochemistry, 30e;transfer, 2015 Available similar. RNA Citation: is subjected to electrophoresis before blot transfer. This requires different steps from those of DNA primarilyat: to ensure that the http://mhmedical.com/ Accessed: August ...
... PJ, Weil some P. Harper's Illustrated Biochemistry, 30e;transfer, 2015 Available similar. RNA Citation: is subjected to electrophoresis before blot transfer. This requires different steps from those of DNA primarilyat: to ensure that the http://mhmedical.com/ Accessed: August ...
Nucleic Acids - Biology Junction
... 8. Number of origins of replication on the chromosomes of eukaryotes 9. DNA replication in which each new DNA has one parental and one newly made strand 12. Built the first model of DNA 14. Form the steps of a DNA molecule 17. Studied 2 strains of Pneumococcus bacteria and found living bacteria coul ...
... 8. Number of origins of replication on the chromosomes of eukaryotes 9. DNA replication in which each new DNA has one parental and one newly made strand 12. Built the first model of DNA 14. Form the steps of a DNA molecule 17. Studied 2 strains of Pneumococcus bacteria and found living bacteria coul ...
The structure of DNA
... Do you want to do the whole sequence???...1,600 bps!! Below is half of the partial genetic code for the hemoglobin protein, use your understanding of DNA to make a complete DNA model, add some twists to make the famous “double helix”…. ...
... Do you want to do the whole sequence???...1,600 bps!! Below is half of the partial genetic code for the hemoglobin protein, use your understanding of DNA to make a complete DNA model, add some twists to make the famous “double helix”…. ...
Coloring DNA
... 9. What sugar is found in DNA? _______________________ In RNA? ____________________ 10. How do the bases bond together? A bonds with _____ ...
... 9. What sugar is found in DNA? _______________________ In RNA? ____________________ 10. How do the bases bond together? A bonds with _____ ...
Homologous recombination
Homologous recombination is a type of genetic recombination in which nucleotide sequences are exchanged between two similar or identical molecules of DNA. It is most widely used by cells to accurately repair harmful breaks that occur on both strands of DNA, known as double-strand breaks. Homologous recombination also produces new combinations of DNA sequences during meiosis, the process by which eukaryotes make gamete cells, like sperm and egg cells in animals. These new combinations of DNA represent genetic variation in offspring, which in turn enables populations to adapt during the course of evolution. Homologous recombination is also used in horizontal gene transfer to exchange genetic material between different strains and species of bacteria and viruses.Although homologous recombination varies widely among different organisms and cell types, most forms involve the same basic steps. After a double-strand break occurs, sections of DNA around the 5' ends of the break are cut away in a process called resection. In the strand invasion step that follows, an overhanging 3' end of the broken DNA molecule then ""invades"" a similar or identical DNA molecule that is not broken. After strand invasion, the further sequence of events may follow either of two main pathways discussed below (see Models); the DSBR (double-strand break repair) pathway or the SDSA (synthesis-dependent strand annealing) pathway. Homologous recombination that occurs during DNA repair tends to result in non-crossover products, in effect restoring the damaged DNA molecule as it existed before the double-strand break.Homologous recombination is conserved across all three domains of life as well as viruses, suggesting that it is a nearly universal biological mechanism. The discovery of genes for homologous recombination in protists—a diverse group of eukaryotic microorganisms—has been interpreted as evidence that meiosis emerged early in the evolution of eukaryotes. Since their dysfunction has been strongly associated with increased susceptibility to several types of cancer, the proteins that facilitate homologous recombination are topics of active research. Homologous recombination is also used in gene targeting, a technique for introducing genetic changes into target organisms. For their development of this technique, Mario Capecchi, Martin Evans and Oliver Smithies were awarded the 2007 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine.