* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Honors DNA Study Guide
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Homologous recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA repair protein XRCC4 wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
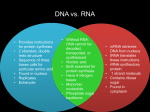
Name __________________________________________ Date ________________________________ Period _________ STUDY GUIDE: DNA (structure & function) 1. Label the diagram of DNA using the word/terms in the word-bank. Each will be used only once. Word-Bank: Base pair Deoxyribose Hydrogen bond Nitrogen base Nucleotide Phosphate 2. What is a “nucleotide”? 3. Place a check mark in the correct column(s) for each statement. Some answers may have multiple checks. CHARACTERISTIC DNA mRNA tRNA rRNA Contains ribose Contains deoxyribose Double-stranded Single-stranded Involved in translation Involved in transcription Contains uracil Contains thymine Can be found in the nucleus; never leave it Found in the nucleus & sometimes leaves it to go to ribosomes with a copy of DNA’s master strand Made of nucleotides Forms ribosomes 4. Match the scientist to their contribution to the discovery of DNA: a. Fred Griffith b. Rosalind Franklin & Maurice Wilkins c. Hershey and Chase e. Oswald Avery f. Chargaff g. Friedrich Miescher d. Watson and Crick _____ Showed transformation of bacteria in mice; 1 st to show that protein was not the genetic material _____ Concluded that A binds with T and G binds with C _____ X-ray crystallography pictures of DNA showed it was a helical structure _____ Studied a substance found only in the nucleus; named it “nuclein” _____ Tested all macromolecules to see which one transforms bacteria. Found only nucleic acid transforms _____ Worked with radioactive viruses and showed that the only inject DNA into the cells they infect _____ Combined data from other scientists to show the 3-d structure of DNA 5. Summarize the processes of: a. Replication: (include the enzymes involved) b. Transcription: c. Translation: 6. To illustrate your knowledge of the protein synthesis process, starting with the DNA, create a chart like the following and complete (CAREFUL…AA chains are found using a CODON chart…not and anti-codon chart) DNA TAC AAA CCA TTG CGA AAT AGA ATT TGA mRNA (codon) tRNA (anticodon) Amino acid (hint: use the codon) (Abbreviate them) 7. a) Define a mutagen: b) Give an example of a positive and a negative effect of a mutagen: 8. Describe each of the following types of mutations: a. insertions: b. deletions: c. substitutions: 9. Which of the mutations above are considered a: a. point mutation? __________________________ b. frameshift mutation? ____________________________ 10. Protein Synthesis: Use the figure below to answer the following questions. Fill your answers into the blanks. Use letters A-E to answer questions 1-5: _____ 1. Which letter points to a cell nucleus? _____ 2. Which letter points to a tRNA? _____ 3. Which letter points to an anticodon? _____ 4. Which letter points to a mRNA leaving the nucleus? _____ 5. Which letter shows translation occurring at the ribosome? 11. What is letter “F” pointing to? 12. What is letter “G” pointing to?