* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sickle Cell Mutation WS - Lincoln Park High School
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
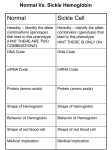
Name _______________________________________________________________ Date _____________Period ______ Sickle Cell Allele Mutation WS Sickle cell disease is a disorder that gets its name from the sickle shape of red blood cells (RBCs) which normally have a round, disk-like shape. The sickle-shaped RBCs are caused by a faulty hemoglobin resulting from a point mutation in which just one nucleotide base is changed in the gene that codes for the alpha subunit polypeptide of hemoglobin. When oxygen levels in the red blood cells are low, the hemoglobin molecules clump together within red blood cells, causing them to acquire a sickle shape. This is dangerous because these cells can block blood flow in narrow capillaries that lead to vital organs, cutting off the oxygen supply and leading to cell death. Use your knowledge of base-pairing and the mRNA genetic code chart at the bottom of the page to complete the table below. Segment of normal hemoglobin allele DNA template (gene) mRNA codons tRNA anticodons Amino acids ATGCTCGCA Same segment of sickle cell hemoglobin allele ATGCACGCA 1. How many CODONS are there in this portion of the gene? _____ 2. How many NUCLEOTIDES code for one amino acid? _____ 3. Is the point mutation in the sickle cell allele a substitution, insertion, or deletion of a nucleotide? _________________ 4. The gene coding for the alpha-subunit polypeptide of hemoglobin is actually 423 nucleotides long. How many amino acids long is the alpha-subunit? _______ 5. A silent mutation is one that does not affect the amino acid sequence of the gene’s protein product. Create a substitution mutation in the normal hemoglobin DNA sequence provided in the chart so that the final protein is unaffected (i.e., the amino acid sequence does not change). Point out the altered mRNA codon that codes for the same amino acid as the original codon.