* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Dna Mutations
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
DNA repair protein XRCC4 wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Transformation (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
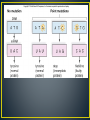
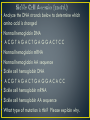
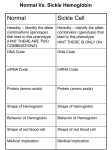
• Point mutations (only affect one base in a codon) • Frameshift mutations—alter the way the codons are read • Substitution: a mutation that exchanges one base for another • Causes: • change to a codon to one that encodes a different amino acid and cause a small change in the protein produced • change a codon to one that encodes the same amino acid and causes no change in the protein produced. These are called silent mutations. • change an amino-acid-coding codon to a single "stop" codon and cause an incomplete protein. This can have serious effects since the incomplete protein probably won't function. • Frameshift mutation: changes that can alter a gene so that its message is no longer correctly expressed •Insertions: mutations in which extra bases are inserted into a new place in the DNA • Example: •Deletions: mutations in which a section of DNA is lost, or deleted. • Example: • Sickle cell anemia is the result of a type of mutation in the gene that codes for part of the hemoglobin molecule. Recall that hemoglobin carries oxygen in your red bloods cells. The mutation causes these red blood cells to become stiff & sickle-shaped when they release their oxygen. The sickled cells tend to get stuck in blood vessels, causing pain and increased risk of stroke, blindness, damage to the heart & lungs, and other conditions. • Analyze the DNA strands below to determine which amino acid is changed • Normal hemoglobin DNA • ACGTAGACTGAGGACTCC • Normal hemoglobin mRNA • Normal hemoglobin AA sequence • Sickle cell hemoglobin DNA • ACGTAGACTGAGGACACC • Sickle cell hemoglobin mRNA • Sickle cell hemoglobin AA sequence • What type of mutation is this? Please explain why.