* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Processes vocabulary 11/1/16
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
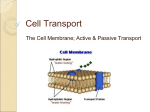
Vocabulary Cell Processes WORD DEFINITION Mixture Combination of substances in which the individual substances do not change or combine chemically, but instead retain their own individual properties Compounds that always contain hydrogen and carbon Organic compound Enzyme Inorganic compound Osmosis Endocytosis Excoytosis A type of protein that regulates nearly all chemical reactions in cells Compound, such as , H÷O that is made from elements other than carbon and whose atoms usually can be arranged only in one structure Type of passive transport that occurs when water diffuses through a cell membrane Process by which a cell takes in a substance by surrounding it with the cell membrane Process by which vesicles release their contents outside the cell ESSENTIAL CHARACTERISTICS EXAMPLES Can be gases, solids, liquids, or any combination of them; living things contain mixtures called suspensions blood Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids are organic compounds found in living things Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins proteins Contain fewer atoms than organic compounds; contain elements needed by living things Water Calcium phosphate salts Cells contain water and are surrounded by water Diffusion Passive transport Molecules and particles too large to move by diffusion use transport proteins engulfed in a vesicle Vesicle fuses to the cell membrane Cells in the stomach Metabolism Passive transport Active transport Diffusion Equilibrium Photosynthesis Respiration Fermentation The total of all chemical reactions in an organism Movement of substances through a cell membrane without the use of cellular energy Energy-requiring process in which transport proteins bind with particles and move them through a cell membrane A type of passive transport in cells in which molecules move from areas where there are more of them to areas where there are fewer of them Occurs when molecules of one substance are spread equally throughout another substance Food-making process by which plants and many other producers use light energy to produce glucose and oxygen from carbon dioxide and water Series of chemical reactions used to release stored energy in food molecules Process by which oxygen-lacking cells and some one-celled organisms release small amounts of energy from glucose molecules Chemical reactions of metabolism need enzymes Includes diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion; depends on the size of the molecule Active transport involves transport proteins; cellular energy is used to move particles through the cell membrane Cellular passive transport diffusion stops when equilibrium is reached After equilibrium is reached, it is maintained because the molecules continue to move Organisms that make their own food are called producers; must have chlorophyll to capture sunlight Enzymes are needed for the chemical reactions of respiration Produces wastes such alcohol, carbon dioxide, and lactic acid Diffusion Osmosis Facilitated diffusion Nutrients in the soil through the roots of a plant Oxygen in the blood Plants Producers Breaking down carbohydrates Yeasts`