* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 10chap19guidedreadingVideo
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Histone acetylation and deacetylation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
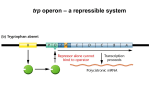
AP Biology Name _________________________ Chapter 18.3+ Guided Reading Assignment 1. What is the main component of most bacterial genomes? 2. How is the DNA arranged in the nucleoid region of the bacterial genome? 3. What is a plasmid? 4. What are the two ways that metabolic control can occur within bacteria? 5. What is the key advantage of grouping genes of related function in to one transcription unit? 6. Where is an operator positioned? 7. What does the operator control? 8. What is the name for the operator, promoter, and the genes they control? 9. What can happen if the trp operan is turned “on”? 10. How does a repressor work? 11. What gene controls the making of the trp repressor protein? 12. What are the two states that the operator vacillates (switches between)? 13. How is the trp repressor protein an allosteric protein? 14. What are the two methods of negative gene regulation? 15. Why is the trp operan considered repressible? 16. What is the definition of an inducible operan? Page 1 of 4 17. Why are repressible enzymes generally associated with anabolic pathways and how is this an advantage to the organism? 18. How does positive gene regulation work? Chapter 19 Guided Reading Assignment 1. Define the following terms: a. Chromatin b. Nucleosome 2. Outline the levels of DNA packing in the eukaryotic nucleus below next to the diagram provided. 3. What is the difference between heterochromatin and euchromatin? Which is transcribed? 4. What is cell differentiation? 5. IF cells carry all of the genetic differences, why then are cells so unique – what is responsible for this? 6. In the diagram below – highlight all of the potential locations for gene expression regulation in eukaryotic cells. How does this compare with prokaryotic cells? Page 2 of 4 7. What effect do the following have on gene expression? a. Histone acetylation b. Histone deacteylation c. DNA methylation 8. How does methylation relate to genomic imprinting? 9. Define epigenetic inheritance. 10. How do the following control elements assist in regulation? a. Transcription factors b. Enhancers c. Activators d. Repressors 11. Use the diagram to the right to explain the interactions of enhancers and transcription activators. 12. Explain how RNA processing is a mechanism of post-transcriptional regulation. 13. What role do microRNA’s play in post-transcriptional regulation 14. What is RNA interference? 15. How does translation provide another opportunity for control? 16. What is the difference between oncogenes,proto-oncogenes and tumor-suppressor genes? 17. What is the p53 gene? 18. Why is said that people inherit predispositions to cancer not cancer itself? Page 3 of 4 Video Review Bozeman Science: (you can also do a video search for “Bozeman Gene Regulation”) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3S3ZOmleAj0 1. How do bacteria use the lac operon? 2. What are the genes within the lac operon? 3. What is the promoter used for? 4. What is the role of the Operator? How does the repressor work with the operator? 5. What type of macromolecule is the repressor? 6. How is the trp operon different from the lac operon? 7. What are transcription factors? SciShow: (you can also do a video search for “SciShow Epigenetics”) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kp1bZEUgqVI 1. How can clones be different from one another if they have the same DNA? 2. How do Methyl Groups control gene expression? 3. What are histones? 4. How are genes and epigenetics like a computer? 5. Is epigenetic information permanent? Explain. 6. How can mom pass epigenetic information to her unborn child? Page 4 of 4