* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Respiration Scrambled Steps
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium in biology wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Specialized pro-resolving mediators wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
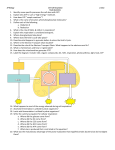
Scrambled Steps of Cellular Respiration Cut the following steps into strips. Put the following Steps to Cellular Respiration in Order. Somewhere in the list is the purpose of cellular respiration. Be sure to identify it and put it at the top of your list next to the hand-written words “Purpose of cellular respiration.” Glycolysis breaks a 6-carbon molecule in half. During this process of fermentation, plants produce alcohol, while animals produce lactic acid. This process only produces 2 ATP. Two things can happen: If oxygen is present, pyruvic acid enters the mitochondria to enter the Kreb’s Cycle. As H+ ions pass back across the mitochondrial membrane through ATP Synthase, molecules of ATP are made. From the Kreb’s cycle, NADH and FADHS enter the electron transport chain. The products are 2 molecules of pyruvic acid (each has 3-carbons). The process that releases energy by breaking down food in the presence of oxygen. Each protein in the electron transport chain passes an electron to the next protein and pumps an H+ ion into the intermembrane space. If no oxygen is present (anaerobic), pyruvic acid goes through “fermentation.” In the cytoplasm of a cell, cellular respiration begins. The final end products of cellular respiration are energy (ATP), H2O, and CO2. Here in the Krebs’ cycle, pyruvic acid (pyruvate) is converted into CO2, H2O, and 2 ATP. The electron transport chain takes electrons from NADH and FADH2 and moves them down the series of proteins. Label all parts and indicate where each process occurs: