* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name date ______ score
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
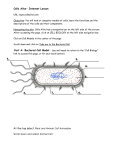
Name ____________________________________________________ Block - _____ Date ___________________ Webquest: Cells Objective: You will look at computer models of cells, learn the functions and the descriptions of the cells and their components. Part A. "HOW BIG IS A...." The following website will allow you to see the relative size of various cells (prokaryotic and eukaryotic) as well as the organelles that are found inside of these cells. Also included on the list are some commonly discussed viruses. Since most people are familiar with how little a grain of salt is, it has been included on the list to give you relative size. Go to the following Using FireFox, URL: http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/cells/scale/ When you are ready to begin, use the slide bar found below the picture on your screen. As you slide it to the right, it will zoom in on the images. WARNING! DO NOT VENTURE FROM THIS INTERNET SITE!! Doing so will earn you a zero and lead to disciplinary action for insubordination and after school detention Place the list of the following items in order from largest to smallest; include the size of each one to its right (and be sure to include units): Structure E. coli bacteria HIV Size Structure glucose Size Structure Grain of Salt Human Egg mitochondria Rhinovirus Ribosome Size (causes AIDS) Red Blood Cell (also known as the cold virus) Skin Cell Sperm Water molecule __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ __________________________ _________________________ mm = 0.001 m μm = 0.000001m nm = 0.000000001 m pm = 0.000000000001 m For the next part of the webquest, you will be navigating the site: Cells.alive. Or type in the URL: www.cellsalive.com; select the "Cell Biology" link to access this page. On the left side of the page is a navigation bar. From here, you will access the links for the rest of the lab. Plant, Animal and Bacteria Cell Models Living cells are divided into two types - ________________________ and ________________________ (use our spelling with a ‘k’). This division is based on internal complexity. The following pages can provide graphic roadmaps to the organization of both of these cell types. ________________________: These cells are simple in structure, with no recognizable organelles. They have an outer cell wall that gives them shape. Just under the rigid cell wall is the more fluid cell membrane. The cytoplasm enclosed within the cell membrane does not exhibit much structure when viewed by electron microscopy. Part B: Bacterial Cell Model – to complete this part you will need to scroll down the page to the part about bacteria. Part C: Animal Cell Model - (you will need to return to the "Cell Biology" link to access this page, or hit your back button) ________________________: The cells of protozoa, higher plants and animals are highly structured. These cells tend to be larger than the cells of bacteria, and have developed specialized packaging and transport mechanisms that may be necessary to support their larger size. Use the Interactive animation of plant and animal cells to learn about their respective organelles. For the animal cell model, you will need to click on the various parts of the cell to go to a screen that tells you about the parts. Answers to the following questions are found there. Sketch each of the following. 1. What do mitochondria do? Mitochondria 2. What does the Golgi Apparatus do? 3. What is the function of the lysosome? Golgi Apparatus 4. What is a vacuole? 5. What is the difference between smooth and rough ER? Rough ER 6. What does a ribosome do? 7. Where is the nucleolus found? Ribosome 8. What does the nucleolus do? 9. What does the cytoskeleton do? 10. Cytosol goes by what other name? Nucleus & Nucleolus 11. What is the function of the cytosol? Part D: Plant Cell Model - (you will need to return to the "Cell Biology" link to access this page, or hit your back button) 1. What other type of cell has a cell wall? Sketch the following Chloroplast 2. What makes the plant cells green? 3. In plant cells, what does the vacuole do? PROCEED TO CELL QUIZ at http://www.biologycorner.com/bio1/cellquiz.html