* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download RG 5 - Membrane Transport
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
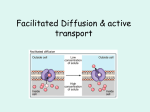
AP Biology Reading Guide Chapter 5 – Cell Transport and Communication Chapters 37.1 and 5.1- 4 – Membrane Structure and Function; Transport Across Membranes* *Adapted and modified from Robbyn Tuinstra’s work __________________________________________________________________________________ QUESTIONS – Membrane Structure 1. Describe the fluid-mosaic membrane model proposed by Singer and Nicolson. 2. Sketch a generic phospholipid. Identify the position of the hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions. 3. Match the structure with the correct letter from the diagram. __________ Cholesterol __________ Hydrophobic end of phospholipids __________ Cytoskeleton __________ Integral protein __________ Glycolipid __________ Lipid bilayer __________ Glycoprotein __________ Oligosaccharides __________ Peripheral protein __________ Hydrophilic end of phospholipids 4. What components of the cell membrane contribute to the fluid quality of the cell membrane? 5. Explain how composition of the membrane may affect fluidity of the membrane. 6. How are integral proteins different from peripheral proteins? __________________________________________________________________________________________ Page 1 of 5 AP Biology Reading Guide Chapter 5 – Cell Transport and Communication Integral Proteins Peripheral Proteins 7. What types of amino acid side chains would you predict interface with the fatty acid core of the membrane vs. the extracellular and intracellular regions? 8. Define each of the following terms: Term Definition Glycoprotein Glycolipid 9. What are some possible roles of carbohydrates on the surface of the cell membrane? QUESTIONS – Cell Transport 10. Why is the plasma membrane described as selectively permeable? 11. Identify the molecules can passively cross a membrane and those that are excluded. Freely permeable Impermeable 12. Describe the process of diffusion. What drives the diffusion process? Why is it spontaneous? 13. Name a physiologically relevant process that occurs by simple diffusion. 14. Write the equation for Fick’s Law below. Define all terms of the equation. __________________________________________________________________________________________ Page 2 of 5 AP Biology Reading Guide Chapter 5 – Cell Transport and Communication 15. Describe how each of the following affects the rate of diffusion. MOLECULAR SIZE TEMPERATURE CONCENTRATION GRADIENT 16. Define osmosis and osmotic pressure. 17. Examine the diagrams below. The arrows indicate the direction of net water movement. Answer the following questions. a. Which panel shows a hypertonic environment? A B C _____________________________ b. Which panel shows a cell hypertonic to its environment? _______________________ c. Which panel shows an isotonic environment? _____________________________ d. Describe what is happening to the plant and animal cells in Panel B (use the terms crenation and plasmolysis). e. Explain why this is happening. f. Describe what is happening to the plant and animal cells in Panel C (use the terms cytolysis and turgor pressure). 18. Define facilitated diffusion. 19. Compare and contrast a channel protein and a carrier protein. Why can the rate of facilitated diffusion using a carrier protein become saturated as concentration of solute increases? __________________________________________________________________________________________ Page 3 of 5 AP Biology Reading Guide Chapter 5 – Cell Transport and Communication 20. What is a gated channel? Distinguish between a ligand-gated and voltage-gated channel. 21. Is there a specific water channel protein? Explain why the discovery of this channel does not discount the generally observation that transport of water is a passive process. 22. Contrast movement by facilitated diffusion with movement by active transport. 23. Why is active transport directional, whereas simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion bidirectional processes? 24. Describe what is occurring during the functioning of the Na-K pump (pictured at right). 25. Why does the action of the Na-K pump result in the formation of an electric gradient? 26. Distinguish between primary active transport and secondary active transport? Give an example of each. Then discuss how primary active transport provides the energy required for secondary active transporter. Describe and Contrast the Three Methods of Endocytosis Phagocytosis Pinocytosis ReceptorMediated Endocytosis 27. Explain how selectivity can be achieved by receptor-mediated endocytosis. Give a physiologically relevant example of this process. __________________________________________________________________________________________ Page 4 of 5 AP Biology Reading Guide Chapter 5 – Cell Transport and Communication 28. Distinguish between various transport processes in a cell by completing the following chart: Type of transport Energy Required? Direction Requirements Examples Diffusion Osmosis Facilitated transport Active transport Exocytosis Endocytosis __________________________________________________________________________________________ Page 5 of 5