* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Webquest - Nutley Public Schools
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
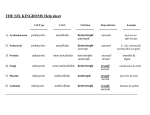
Name _____________________________ Chapter 4 Webquest How are living organisms and nonliving things similar? Everything on Earth is made up of matter (chemical elements) o What are the four states of matter? o How many elements (types of atoms) are on the periodic table of elements? o _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ What are the four most common elements in living organisms? (Give name and symbol) _______________________________________________________________ How are living organisms and nonliving things different? 1. Living organisms are made up of at least one cell o Although all living organisms are made up of cells, not all living organisms are made up of the same type of cells o Cells come in many sizes, but most are microscopic o What is the average size of plant and animal cells? ____________________________ What is the smallest type of cell? ________________________________________ What is the largest cell (can see without a microscope)? ________________________ What is the longest cell (but still microscopic)? ______________________________ Cells come in many different shapes How many different cell types are in the human body? _________________________ Each cell type has a different shape because each type of cell has a different job (Form Fits Function!). In multicellular organisms, all the cells contain the same DNA, but have become differentiated. Describe the shape and job of a human nerve cell. Draw a picture of a nerve cell. Describe the shape and job of a human skin cell. Draw a picture of a skin cell. Living organisms are made up of at least one cell (continued) o Bacteria come in three different shapes, what are they? Draw a picture of each shape. 2. Living organisms contain DNA o What does the abbreviation DNA stand for? ______________________________________ o DNA is sometimes referred to as a “chromosome”. How many chromosomes (strands of DNA) do humans have? _____________________ How many chromosomes does E. coli (a type of bacteria) have? ___________________ How many chromosomes does lettuce have? _________________________________ Pick two more living organisms. How many chromosomes does that species have? _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 3. Living organisms need energy to survive (needs a constant food source). o Some living organisms can produce their own food. These are known as autotrophs. o Give two examples of autotrophs. Give their common and scientific name. Where do they live? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ o Some living organisms need to eat other living organisms for a food source. These are known as heterotrophs. Give an example of an herbivore (common and scientific name, where does it live?) _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ Give an example of an omnivore (common and scientific name, where does it live?) _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ Give an example of a carnivore (common and scientific name, where does it live?) _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ Give an example of a decomposer (common and scientific name, where does it live?) _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 4. All living organisms grow (by cell enlargement and adding new cells through cell division) o What is the largest animal? (common and scientific name, where does it live?) __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ o What is the largest plant? (common and scientific name, where does it live?) __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 5. All living organisms have a metabolism o List three reactions in your body that require energy to occur __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 6. All living organisms maintain homeostasis o Homeostasis – stable, internal living conditions o What is the word origin of “homeostasis”? _______________________________________ 7. Respond to stimuli from the environment o What type of sensory organs do humans have? ____________________________________ o How do plants respond to stimuli (direction of sunlight)? ____________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ 8. Reproduce o Parents pass down DNA to offspring. Sometimes mutations can occur, changing the DNA. o What are two ways DNA mutations can occur? __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ Discovery of the Cell & The Cell Theory A cell is the smallest unit of matter that can carry on the process of life What are the three parts of the Cell Theory (proposed in 1800s)? 1. ____________________________________________________________________ 2. ____________________________________________________________________ 3. ____________________________________________________________________ Who is Robert Hooke (1635 – 1703) and how did he contribute to creation of the cell theory? o _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ Who was Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1632 – 1723) and how did he contribute to the cell theory? o _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 6 KINGDOMS CELL TYPE & NUMBER OF CELLS Prokaryote and/or Eukaryote Unicellular and/or Multicellular ArchaeBacteria (Domain Archae) Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Unicellular (Domain Bacteria) Autotroph and/or Heterotroph Autotroph Heterotroph Multicellular Prokaryotic Eubacteria TYPE OF NUTRITION Eukaryotic Unicellular Autotroph Heterotroph Multicellular Prokaryotic Protista Eukaryotic (Domain Eukarya) Unicellular Autotroph Heterotroph Multicellular Fungi (Domain Eukarya) Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Unicellular Autotroph Heterotroph Multicellular Plantae (Domain Eukarya) Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Unicellular Autotroph Heterotroph Multicellular Animalia (Domain Eukarya) Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Unicellular Multicellular Autotroph Heterotroph OTHER INFORMATION EXAMPLES Name ______________________________ Chapter 18 - Classification Grouping Things You Use Daily: Fill in the table going from most general to most specific. LEVEL I II 1. 2. A. Clothing 3. 4. 1. 2. B. School 3. 4. 1. 2. C. Hobbies 3. 4. III a. b. a. b. a. b. a. b. a. b. a. b. a. b. a. b. a. b. a. b. a. b. a. b. 1. Explain how you use a classification system to group some of your belongings. __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Explain how classification systems are used by businesses. __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________