* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download (for quiz): Taxonomy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
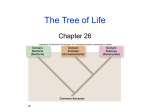
Chapter 18 The science of grouping organisms according to their presumed natural relationships. ARISTOTLE ◦ First to classify organisms more than 2000 years ago. ◦ Classified all organisms into TWO groups Plants Further classified by stem differences. Animals Further classified based on where animals were found. (air, land, water) Everyday names given to organisms. Common names may NOT accurately describe the organism. ◦ Examples: jellyfish, mountain lion Mean:Two Names CAROLUS LINNAEUS – Swedish naturalist (1707-1778) ◦ He broke organisms into hierarchical categories Categories (smallest to largest) Examples SPECIES Structurally similar organisms sapiens GENUS Similar species grouped Homo FAMILY Similar genera Hominidae ORDER Similar families Primates CLASS Similar orders Mammalia PHYLUM/DIVISION Similar classes Chordata KINGDOM Similar phyla/divisions Animalia Binomial name Includes Genus & species names Examples: ◦ Rana pipiensLeopard frog ◦ Homo sapiens – Human beings Subspecies: morphologically different & geographically separated. Varieties: Morphologically different & often not geographically separated. Strain: Biochemically dissimilar group within a species. ◦ Example: bacteria Phylogeny: Evolutionary history of a species. Taxonomic Identification: ◦ Dichotomous Key – A written set of choices that leads to the name of an organism. ◦ Phylogenetic Tree – A visual model of the inferred relationships among organisms. ◦ Biosystematics – A form of taxonomy that examines reproductive compatibility & gene flow. Studies speciation, or formation of a new species. KINGDOM CELL TYPE # OF CELLS NUTRITION Archaebacteria Prokaryotic Unicellular Autoheterotrophic Eubacteria Prokaryotic Unicellular Autoheterotrophic Protista Eukaryotic Uni & multicellular Autoheterotrophic Fungi Eukaryotic Uni & multicellular Heterotrophic Plantae Eukaryotic Multicellular Autotrophic (rarely hetero-) Animalia Eukaryotic Multicellular heterotrophic Methanogens “true bacteria” Amoebas Mushroom Mosses, ferns Mammals