* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2.4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes
Nuclear fusion wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Fine chemical wikipedia , lookup
California Green Chemistry Initiative wikipedia , lookup
Water splitting wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
Al-Shifa pharmaceutical factory wikipedia , lookup
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Artificial photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon proliferation wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Supramolecular catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Chemical Corps wikipedia , lookup
Photoredox catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Chemical plant wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen-bond catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Chemical industry wikipedia , lookup
Process chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
VX (nerve agent) wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme catalysis wikipedia , lookup
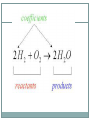
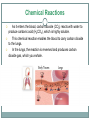
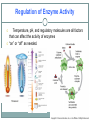
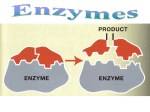
2.4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chemical Reactions A chemical reaction is a process that changes, or transforms, one set of chemicals into another by changing the chemical bonds that join atoms in compounds. @Mass and energy are conserved during chemical transformations.@ The elements or compounds that enter into a chemical reaction are known as reactants. The elements or compounds produced by a chemical reaction are known as products. Chemical Reactions As it enters the blood, carbon dioxide (CO2) reacts with water to produce carbonic acid (H2CO3), which is highly soluble. This chemical reaction enables the blood to carry carbon dioxide to the lungs. In the lungs, the reaction is reversed and produces carbon dioxide gas, which you exhale. What is released or absorbed whenever chemical bonds form or are broken? Energy Changes @Energy is released or absorbed whenever chemical bonds are formed or broken during chemical reactions.@ Chemical reactions that release energy often occur on their own, or spontaneously. Chemical reactions that absorb energy will not occur without a source of energy. Exothermic Reactions 7 @Reaction in which heat is given off is exothermic@(Ex. combustion of fuels) Endothermic Reactions 8 @Reaction in which heat is absorbed is endothermic@ (Ex. water is evaporated) Chemists call the energy needed to get a reaction started the . Activation Energy 10 Energy needed to get a reaction going is the activation energy. What is a catalyst? A catalyst is a substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction. @Catalysts work by lowering a reaction’s activation energy.@ The Enzyme-Substrate Complex The substrates bind to a site on the enzyme called the active site. The active site and the substrates have complementary shapes. The fit is so precise that the active site and substrates are often compared to a lock and key. Regulation of Enzyme Activity Temperature, pH, and regulatory molecules are all factors that can affect the activity of enzymes “on” or “off” as needed.