* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download energy - WordPress.com
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs free energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
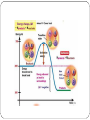
Metabolism • The sum of the processes within an organism • Living organisms are in a constant struggle to survive • All life processes require energy • Most commonly used for of energy is Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) • Most ATP in made in the mitochondria All biochemical pathways in your body Energy • Energy is used anytime work is performed • Climb a mountain • Car travels down the road • Link amino acids together • Pump sucrose across a membrane Many forms… • Chemical • Electrical • Mechanical • Light • Thermal Regardless of the form, energy exists in one of two states… • Kinetic Energy • Stored Energy Kinetic Energy • energy of motion • Performs work by making things move Potential Energy • stored energy • chemical potential/gravitational energy The First Law of Thermodynamics The total amount of energy in any closed system is constant. Energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only be converted from one form to another. If a physical system gains an amount of energy, another physical system must experience a loss of energy of the same amount. BOND ENERGY • A measure of the strength or stability of the covalent bond • Measured in KJ/mol (equal to amount of energy absorbed per mole when the bond between atoms is broken Important • Energy is absorbed when product bonds break and energy is released when product bonds form Question • How will this affect the net amount of energy absorbed or released in the overall reaction? Energy Diagrams… • the y-axis indicates the level of potential energy for the reactants before the reaction and the products after the reaction has occurred • If energy is released, the reaction is EXOTHERMIC • If energy is absorbed, the reaction is ENDOTHERMIC Bond energy and Potential energy have an inverse relationship • The weaker the bond, the higher the potential energy • The stronger the bond, the lower the potential energy Enthalpy (∆ H) This is calculated by using the following formula; ∆ H total = ∆ H final - ∆ H initial Exothermic Reaction have a - ∆ H Endothermic Reactions have a + ∆ H Hey, PROVE IT!!!