* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download energy-and-entropy-introduction
Survey
Document related concepts
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
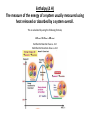
Metabolism is the sum of all chemical reactions in an organism. Energy is the ability to do work How do these work together? Metabolism in a nutshell WOW There is a lot going on! What is energy • • Energy Energy is used anytime work is performed • Climb a mountain • Car travels down the road • Link amino acids together • Pump sucrose across a membrane Many forms… • Chemical • Electrical • Mechanical • Light • Thermal Regardless of the form, energy exists in one of two states… • Kinetic Energy • Stored Energy- Potential energy Kinetic vs. Potential Energy Kinetic Energy • energy of motion • Performs work by making things move Potential Energy • stored energy • chemical potential/gravitational energy The First Law of Thermodynamics The total amount of energy in any closed system is constant. Energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only be converted from one form to another. If a physical system gains an amount of energy, another physical system must experience a loss of energy of the same amount. BOND ENERGY • A measure of the strength or stability of the covalent bond • Measured in KJ/mol (equal to amount of energy absorbed per mole when the bond between atoms is broken(energy is needed to be put into the breaking of the bonds)) Important • Energy is absorbed by the bonds as energy is put in to break them and energy is released Question • How will this affect the net amount of energy absorbed or released in the overall reaction? Endothermic vs. Exothermic Energy Diagrams… • the y-axis indicates the level of potential energy for the reactants before the reaction and the products after the reaction has occurred • If energy is released, the reaction is EXOTHERMIC • If energy is absorbed, the reaction is ENDOTHERMIC Bond energy and Potential energy have an inverse relationship • The weaker the bond, the higher the potential energy • The stronger the bond, the lower the potential energy Enthalpy (∆ H) The measure of the energy of a system usually measured using heat released or absorbed by a system overall. This is calculated by using the following formula; ∆ H total = ∆ H final - ∆ H initial Exothermic Reaction have a - ∆ H Endothermic Reactions have a + ∆ H The second Law of Thermodynamics In every energy transfer or conversion, some of the useful energy in the system becomes unusable and increases the entropy of the universe. So what is Entropy?? Entropy is a measurement of the disorder in a system. CHAOS….. In chemical reactions entropy actually increases when • Solids react to form liquids or gases • Liquids react to form gases • The total number of product molecules is greater than the total number of reactant molecules There is energy expended to maintain the living structures in all living things. This allows order to be established even when there is disorder (entropy). Spontaneous change is a change that will, once begun, continue on its own under a given set of conditions and it will not require a continuous supply of energy. So a non spontaneous reaction is one that needs continual energy input to continue. Gibbs Free Energy: What is this?? What is the equation? Define exergonic and endergonic reactions. P.137-138 Compare and contrast Kinetic and Potential energy Exothermic and Endothermic reactions