* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
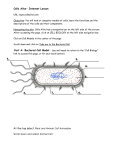
Cells Alive- Internet Lesson Name ______________________ URL: www.cellsalive.com Date ______________Block__________ Objective: You will look at computer models of cells; learn the functions and the descriptions of the cells and their components. Navigating the site: Cells alive has a navigation bar at the top, after accessing the page, click on CELL BIOLOGY under contents. From here, you will access the links: PART A: "How Big is a.." PART B-F Cell Models which will have Cell Models The bacterial cell model. The animal cell model, and The plant cell model. Part A. "HOW BIG IS A...." Here you will look at objects found on the head of a pin. Your job is to rank them in order of size on the chart below and estimate the length of each (in nanometers, micrometers, or millimeters). The line in the bottom right corner of the screen is used to help you estimate. Sketch each of the objects. (Click START THE ANIMATION to get started) *Change the magnification to utilize the length scale. Object Human hair Dust Mite Red Blood Cells E. coli Staphylococcus Ebola virus Rhinovirus Sketch Size in nanometers, micrometers or millilmeters Part B: Cell Models:(you will need to return to the “cell biology” link to access this page under contents) 1. What two general classes are cells divided into and what is the classification based upon? 2. Give a brief description of eukaryotic cells 3. Give a brief description of prokaryotic cells Part C: Prokaryotic Cell Model - (you will need to return to the "Cell Models" link to access this page, it is on the top) Click the START THE ANIMATION button to get started Label the following Diagram: Briefly describe the function of each organelle in the diagram: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Part D: Animal Cell Model - (you will need to return to the "Cell Models" link to access this page, it is on the top) *Click the Eukaryotic Cell to get to the animal and plant cells models. For this model, you will need to click on the various parts of the cell to go to a screen that tells you about the parts. Answers to the following questions are found there. 1. What do mitochondria do? Sketch each of the following. Mitochondria 2. How big are mitochondria? 3. What does the Golgi Apparatus do? 4. What is the difference between smooth and rough ER? Lysosome 5. What does the nucleus look like? 6. What does the nucleus store and what else does it do? Golgi Apparatus 7. What does the cytoskeleton do? 8. Cytosol goes by what other name? Rough ER 9. What is the function of the cytosol? 10. What is the function of the lysosome? Part E: Plant Cell Model - (you will need to return to the "Cell Models" link to access this page) 1. What other type of cell has a cell wall? Sketch the following Chloroplast 2. What is the function of the Chloroplast? 3. In plant cells, what does the vacuole do? Vacuole Part F: Overview For the chart below, place a check in the box if the cell has that component. Plant Chloroplast Vacuole Ribosome Mitochondria DNA Endoplasmic Reticulum Cell Wall Golgi Apparatus Centrioles Animal Bacteria Name _____KEY_________________ Date ______________Block__________ Cells Alive- Internet Lesson URL: www.cellsalive.com Objective: You will look at computer models of cells; learn the functions and the descriptions of the cells and their components. Navigating the site: Cells alive has a navigation bar at the left, after accessing the page, click on CELL BIOLOGY on the left side navigation bar. From here, you will access the links: 1) "How Big is a..", 2) the bacterial cell model. 3)the animal cell model, and 4)the plant cell model. Part A. "HOW BIG IS A...." Here you will look at objects found on the head of a pin. Your job is to rank them in order of size on the chart below and estimate the length of each (in nanometers, micrometers, or millimeters). The line in the bottom right corner of the screen is used to help you estimate. Sketch each of the objects. Object Sketch Size in nanometers, micrometers or millilmeters 2pts Human hair 125-150 micrometers 2pts 2pts Dust Mite 225-250 micrometers 2pts 2pts Red Blood Cells 5-10 micrometers 2pts 2pts E. coli 2 micrometers 2pts 2pts Staphylococcus 0.5-1.0 micrometers 2pts Ebola virus 2pts 100 nanometers wide 1000 nanometers long 2pts 2pts Rhinovirus 25-30 nanometers 2pts Part B: Cell Models:You will need to return to the “cell biology” link to access this page, or hit your back button 4. What two general classes are cells divided into and what is the classification based upon? 2pts Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic 5. Give a brief description of eukaryotic cell. 2pts They are highly structural and has a nucleus 6. Give a brief description of prokaryotic cells They are simply structural and do not has a nucleus Part C: Bacterial Cell Model – On the top of the Cell Models page Label the following Diagram: Briefly describe the function of each organelle in the diagram: 1. Flagellum – long appendages which rotate throughout the cell 2. Pilus – hair-like structures that allow the bacteria to attach to other cells for protein 3. Nucleoid – the DNA in the bacteria cells. It is confined in the central region. 4. Plasma membrane – Lipid bilayer much like the plasma membrane of other cells 5. ribosomes – Gives the cytoplasm of bacteria an appearance 6. Cell wall – maintains the overall shape of a bacteria cell 7. Capsule – the layer that protects the bacterial cell Part D: Animal Cell Model - (you will need to return to the "Cell Biology" link to access this page, or hit your back button) For this model, you will need to click on the various parts of the cell to go to a screen that tells you about the parts. Answers to the following questions are found there. 1. What do mitochondria do? Sketch each of the following. Provides the energy a cell needs to do things Mitochondria 2. How big are mitochondria? About the size of a bacteria 3. What does the Golgi Apparatus do? Stack of membrane bound vesicles that are important to package micromolecules throughout the cell Lysosome 4. What is the difference between smooth and rough ER? Smooth controls various functions and Rough collects and transfers ribosomes throughout the cell 5. Where is the nucleolus found? 6. What does the nucleolus do? Golgi Apparatus 7. What does the cytoskeleton do? Helps maintain the cells shape 8. Cytosol goes by what other name? cytoplasm 9. What is the function of the cytosol? Fluid that controls the cells metabolism 10. What is the function of the lysosome? Kill&digest Rough ER Part E: Plant Cell Model - (you will need to return to the "Cell Biology" link to access this page, or hit your back button) 1. What other type of cell has a cell wall? Sketch the following Bacteria Chloroplast 2. What makes the plant cells green? Chloroplast 3. In plant cells, what does the vacuole do? Stores nutrients and releases the cells waste products Vacuole Part F: Overview For the chart below, place a check in the box if the cell has that component. Plant Animal Chloroplast X Vacuole X X Ribosome X X Mitochondria X X DNA X X Endoplasmic Reticulum X X Cell Wall X Golgi Apparatus X Centrioles Bacteria X X X X X