* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lac Operon
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Histone acetylation and deacetylation wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
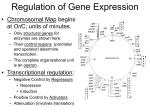
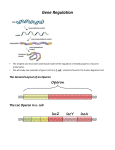
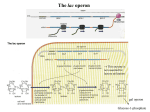
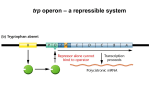
Genetics - Ch 10 Molecular Mechanisms of Gene Regulation Control of Gene Expression DNA -------------> transcriptional control RNA ------------> protein translational control Operon: (prokaryotes) several adjacent genes regulated together and coding for proteins involved in a common process repressor gene promoter operator gene A gene B gene C Operator: Repressor binding site Promoter: transcriptional activation site Repressible Vs. Inducible Operons Repressible System: in biosynthetic (anabolic) pathways repressible system substrate present -> operon turned off Trp Operon Inducible System: in degradative (catabolic) pathways substrate present -> operon turned on Lac Operon Inducible system Lac Operon to metabolize (break down) lactose constitutive inducible Z protein= ß-galactosidase a) cleaves lactose --> glu + gal b) shifts bonds in lactose --> allolactose Lac Operon: Inducer always some repressors in cell allolactose is an inducer: •makes repressor fall off operator •transcription occurs Lac Operon: Enhancer CRP protein: cAMP receptor protein CRP/cAMP: enhancer •binds to activator site upstream from Promoter •helps RNA pol to attach to Promoter low glucose --> high cAMP high glucose --> low cAMP cAMP: cyclic adenosine monophosphate Lac Operon under Different Cell Conditions what if…? no glu, high lac high cAMP, high allolac high transcription high glu, no lac low cAMP, low allolac no transcription no glu, no lac high cAMP, no allolac no transcription some glu & lac low cAMP, some allolac not enhanced, induced low transcription Mutated Lac Operon & Areas what if …? I- no repressor Lac operon turned on Oc repressor can’t bind to operator Lac operon turned on I-d repressor can’t bind to operator Lac operon turned on Is allolactose can’t bind to repressor Lac operon turned off Trp Operon for production of tryptophan a.a. Trp Operon: Repressible System [Trp] --> Trp operon turned off trpR aporepessor (always present) combines with co-repressor (tryptophan) to form functional repressor negative feedback loop trpR Trp Operon Controlled by Attenuation trpR P O 1 2 3 4 Leader trpE trpD trp C trp B trpA attenuator •attenuation can form under certain conditions •base-pairing can occur between 1-2 2-3 3-4 Attenuation High levels of Tryptophan in Cell •transcription & translation occur simultaneously in Prokaryotes •leader transcript (1) has 2 trp codons (UGGUGG) •ribosomes moves fast along transcript •stem-loop 3 - 4 fprms, poly Us after •early termination of transcription, translation stops (only leader peptide forms - has no function) Low Levels of Tryptophan in Cell •ribosome stalls at UGGUGG in leader transcript (1) •stem-loop 2 - 3 forms, no poly U after •transcription continues Low Levels of other Amino Acids •ribosome stalls way early •stem-loops 1-2 & 3-4 form, poly U after •early termination of transcription