* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Communication
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
Nerve growth factor wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Index of biochemistry articles wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Ultrasensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
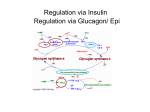
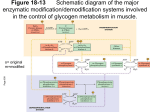
Cell communication 1: cell signaling and signal transduction. 3-7-2016 Can single cell live alone without any kind of communication with others or environment? For bacteria, • Communicate with environment – Chemotaxis: to detect nutrients and avoid toxicic substance • Communicate with other bacteria – Quorum sensing (來偷聽細菌們的對話吧!) For multicellular organism, • Communicate with environment – Sensory system: see, smell, hearing, taste, touch etc. • Communicate with others – Chemical , visual , language and words. • Communicate within – – – – – – Development : from single fertilized egg to adult body. Transport system: circulation, digestion, secretion. Neural system: fast communication, learning and memory. Endocrine system: homeostasis, growth and reproduction. Immune system: defense against non-self. Failure of communication: cancer and aging. Elements of Communication • Signal – What it is? who send? how to produce? and when to send? • Receiver – Receptor: specificity and sensitivity – Localization – Control: amount and sensitivity • Signal interpretation – Signal transduction: amplify, diversify and integration • Responses – Cell contend dependent Cell: integration of various signals and to make proper response 16_06_extracellular_sig.jpg Cell communication within our body 16_03_signal_various.jpg Generation of body pattern 16_04_Contact_depend.jpg Path of signal transduction discovery 16_07_change_behavior.jpg Biochemical study of hormonal action: how hormone activates liver/muscle phosphorylase to break down glycogen? Glc-1-P → Glc-6-P → Glycolysis Glycogen P Glycogen phosphorylase a* ATP Phosphatase n P Glycogen phosphorylase b (inactive) n-1 How hormone (glucogon or epinephrine) activate hepatic enzyme to degrade glycogen? Liver Glycogen Pancreas Low blood sugar Glucagon or Epinephrine stress Glycogen synthase Glucose Glycogen phosphorylase Effect of epinephrine on phosphorylase activity in dog liver slices. Sutherland EW et al J. Biol. Chem. (1956) EFFECT OF EPINEPHRINE AND GLUCAGON ON THE REACTIVATION OF PHOSPHORYLASE IN LIVER HOMOGENATES J. Biol. Chem. 224: 463 – 475; 1957 Effect of boiled E/G treated membrane extract on activation of phosphorylase in the test tube cAMP is converted from ATP by membrane bound enzyme Adenylate Cyclase (AC) AC in different tissues can only be activated by specific hormone (liver/glucagon; ACTH/ adrenal gland). Hormone may need interact with its specific receptor first! ? ? The second messengers concept Sutherland, E. W. Pharmac. Rev., 18, 145 (1966). How cAMP activates glycogen phosphorylase through phosphorylaion? Isolation of phosphorylase kinase; Is phosphorylase kinase a direct targert of cAMP? NO! its activation also need to be phosphorylated – another kinase? EG Krebs isolated phosphorylase kinase kinase and demonstrated that is the direct target of cAMP! EH Fisher isolated protein phosphatase which reverse the phosphorylation reaction. Krebs and Fisher establish that protein phosphorylation is a reversible control mechanism of many enzymes and proteins! p.428 O Protein Kinase OH + ATP Protein Protein O P O + ADP O Pi H2O Protein Phosphatase A protein kinase transfers the terminal phosphate of ATP to a hydroxyl group on a protein. A protein phosphatase catalyzes removal of the Pi by hydrolysis. Epinephrine cascade. Epinephrine triggers a series of reactions in hepatocytes in which catalysts activate catalysts, resulting in great amplification of the signal. Binding of a small number of molecules of epinephrine to specific βadrenergic receptors on the cell surface activates adenylyl cyclase. The numbers of molecules shown are simply to illustrate amplification and are probably gross underestimates. ? ? How adenyl cyclase is activated? By hormone receptor directly? Or Need some other activators? GTP dependent transmembrane signaling?! GORDON M. TOMKINS found the cytocidal effect of cyclic AMP on clonal S49 lymphoma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 70, 76-79 (1973) Add Epinephrine Beta adrenergic receptor Activation of AC Increase cAMP Activate PKA Cell die! What’s wrong about this cAMP resistant cells? Defect in regulatory subunit? Defect in catalytic subunit? Defect in down stream targets of kinase? What else? Gillman et al were able to select another S49 cell variant (cyc-) that appeared to have normal receptors and adenylyl cyclase but that failed to generate a cyclic AMP signal in response to appropriate hormones (b-adrenergic agonists or prostaglandins). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 2016 – 2020 (1977) Solubilize membrane from wild type cells hormone adenylyl cyclase unc unc hormone Hormone No cAMP cAMP G protein coupled receptor: 7 trans-membrane protein G proteins dissociate into two signaling proteins when activated 16_20_second_messeng.jpg Adenylyl cyclase ATP Cyclic AMP If cAMP can play as an important intracellular second messager, how about other nucleotide? In 1975, FERID MURAD identified guanylate cyclase catalyzes the formation of guanosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate (cyclic GMP) from GTP. Guanylate cyclase is activated by various agents including sodium azide, hydroxylamine, nitroglycerin, sodium nitrite etc. None of them physiological relevant! The obligatory role of endothelial cells in the relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by acetylcholine Furchgott RF, Zawadzki JF Nature 288, 373 – 376; 1980 Ignarro LJ, Byrns RE, Buga GM, Wood KS. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor from pulmonary artery and vein possesses pharmacologic and chemical properties identical to those of nitric oxide. Circ Res. 1987;61:866–879. How is the receptor mediated signaling desensitized? How the signal is turned off ? Hormone association 41 • Arachidonic acid present in membrane lipids are released for eicosanoid synthesis in the cell interior by phospholipase A2 Discovery of growth factor and its signal transduction pathway 46 47 8-day chick embryo sensory ganglia cultured in the presence of fragments of mouse control or sarcoma 180 cells for 24 hrs. Rita Levi-Montalcini Cancer Research 14: 49-54 (1954) 48 A soluble factors secreted from mouse sarcoma 180 cells which can promote nerve growth from sensory ganglia (Nerve Growth Factor, NGF) What is biochemical nature of NGF? Protein or Nucleic Acid? To remove nucleic acid by digesting with snake venom. Snake venom itself contains NGF activity! 49 Mouse salivary gland extract (NGF) were injected into newborn mice. Some unexpected; non-NGF related phenomenon were observed! Cohen S. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 46: 302-311 (1960) 50 J. Biol. Chem. 1962 51 Cohen S. J. Biol. Chem. (1973) 52 Characterization of growth factor receptors • Label ligand with radioactive isotope • Binding assay • Determining specificity of the ligand binding • Scatcard analysis – Km verse total receptor number • How signal of the growth factor receptor transduced? 53 Epidermal growth factor stimulates phosphorylation in membrane preparations in vitro Nature 276, 409 - 410 (23 November 1978) 54 EGF stimulates protein phosphorylation in the membrane fraction of target cells (PNAS 1978) 55 56 57 58 59 60 Extrinic signals 62 How the signal is turned off ? a-subunit of G protein has GTPase activity. Cholera toxin blocks a-subunit’s GTPase activity through ADP-ribosylation of a-subunit. Then ? 63