* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 8
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Urban heat island wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the Arctic wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
North Report wikipedia , lookup
Future sea level wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Saskatchewan wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Years of Living Dangerously wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
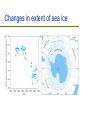
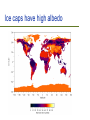
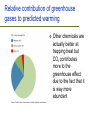
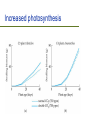
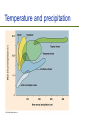
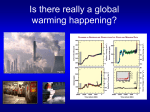
Current Climate Change Ch. 17, Bush Outline Evidence Are for recent climate change humans the cause? Potential change ecological effects of climate Outline Evidence Are for recent climate change humans the cause? Potential effects of climate change Evidence of Temperature Changes Three main sources of data: – Direct measurements of temperature – Location of ice caps and tropical glaciers – Thickness of ice caps Temperature records We have accurate records only for the past 120 years Most temperature readings taken at cities which are “heat islands” Whaling and Polar Ice caps Changes in extent of sea ice Thickness of Ice Caps Submarines make careful measurements of the distance between the ice and the bottom of the sea Have estimated that the thickness of the ice caps have decreased from 3.1m to 1.8m Tropical Glaciers are melting Kilimanjaro All tropical glaciers are above 4800 m At the current rate of temperature change, it is estimated that all will be gone in 50 years The effect of melting ice caps There is not enough water trapped in the ice caps to create “Waterworld” The biggest effect of ice caps melting comes from the decrease in ALBEDO Albedo = brightness Ice caps have high albedo Outline Evidence Are for recent climate change humans the cause? Potential effects of climate change Last glacial period ended 11,000 years ago 90% of last 2 million years has been glacial For the last 10,000 years, plants and animals have been living in an unusually warm environment Temperature changes over the years The rate of climate change we are currently experiencing is only matched by the rapid warming at the end of the last ice age Temperature changes in history Between 1400-1700 the earth was a few degrees colder Called “The Little Ice Age” Influenced history: – Outcome of battles – Crops failing causing famine Greenhouse effect Light energy enters the atmosphere Changes to heat energy Light energy exits atmosphere but heat energy is trapped The Greenhouse effect The greenhouse effect is not all bad Without the greenhouse effect, the earth would be, on average, -18 C Creation of greenhouse gases The burning of fossil fuels is increasing the greenhouse effect Important greenhouse gases: – – – – HCF’s, CFC’s Methane CO2 Water vapour Relative contribution of greenhouse gases to predicted warming Other chemicals are actually better at trapping heat but CO2 contributes more to the greenhouse effect due to the fact that it is way more abundant CO2 and water vapour CO2 causes minor increase in temperature Increase in temperature causes more water vapour via evaporation Water vapour leads to further greenhouse effect and higher temperature Carbon cycle In the natural carbon cycle, respiration and decomposition increase CO2 Photosynthesis decreases CO2 Burning fossil fuels now contributes to CO2 gain Fossil fuels Fossil fuels are ancient organisms that did not decompose The major culprits… Carbon sinks Each year humanity dumps roughly 8 billion metric tons of carbon into the atmosphere – 6.5 billion tons from fossil fuels and 1.5 billion from deforestation But less than half that total, 3.2 billion tons, remains in the atmosphere to warm the planet Forests, grasslands, and the waters of the oceans are acting as carbon sinks Outline Evidence Are for recent climate change humans the cause? Potential effects of climate change Potential effects of CO2 increase Predicted changes in temperature Changes to the natural world Changes to human life Recent increases in CO2 Jagged line is caused by seasonal changes in photosynthesis; in summer N. Hemisphere plants use up more CO2 Pollution can mitigate increases in temperature Pollutants such as those from car exhaust are causing increases in cloud cover Cloud cover increases albedo Air pollution increases albedo CO2 and temperature changes Simulations of temperature changes are becoming increasingly accurate Predicted temperature change Five principal research groups all produce climate models Differences arise in the predictions made about social and political change Medium estimate is that the average temperature on Earth will rise ~3.5 C Increased photosynthesis Planting trees to decrease temp Deforestation causes decreases in CO2 absorption Planting trees will have the opposite effect ->decreases CO2 C4 evolution changing atmospheres C4 photosynthesis appears to have evolved at a time when O2 was high and CO2 was low and temperatures were high The global distribution of C4 plants in today's world C4 grasslands (orange) have evolved in the tropics and warm temperate regions where C3 forests (green) are excluded by seasonal drought and fire. C3 grasses (yellow) remain dominant in cool temperate grasslands because C4 grasses are less productive at low temperatures. Temperature and precipitation Climate affects ecology Deserts will spread N. Hemi. plants will migrate north Predicted migration of beech and maple trees Migration of species Industrialization may impede the migration of many species Temperate species (and island species) may have nowhere to migrate to If migration can not occur then extinction will likely take place Cold-adapted species Implications to Conservation Extinction and global warming One study indicated that, by 2050, current warming trends could bring about extinction of 15 to 37 percent of the 1,103 species they studied A mere 6 degrees of global warming was enough to wipe out up to 95 per cent of the species which were alive on earth at the end of the Permian period, 250 million years ago Arable land will have new locations Best conditions for farming will move towards poles Will be at the latitude of the Canadian Shield More irrigation needed as crop land will be drier Expected 20% decrease in cultivatable land Other reasons why global warming a threat to life on Earth? Incidences of heat attacks, respiratory disease and stroke will increase Disease and pests are more likely to spread Tropical storms, tornadoes, landslides, heatwaves and droughts will both increase in number and intensity Air quality will become poorer coastal cities like Miami, New Orleans, Los Angeles and Bangkok will be flooded as ocean level rises due to melting glaciers ocean levels rise, some inland drinking water sources will become contaminated by saltwater Summary The Earth is becoming increasingly warm Recently, humans have contributed to this phenomenon Temperature increases will have severe effects to the natural world