* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman Senate wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Leges regiae wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Centuriate Assembly wikipedia , lookup
Conflict of the Orders wikipedia , lookup
Switzerland in the Roman era wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Roman Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Senatus consultum ultimum wikipedia , lookup
Executive magistrates of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Demography of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republican governors of Gaul wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Legislative assemblies of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
History of the Constitution of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
History of the Constitution of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Augustus wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
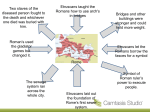
The Roman Empire 500 B.C.E. to 500 C.E. Geography of Italy • Peninsula • 3 main islands: Corsica, Sardinia & Sicily • Alps mountain range to the North • Rome near dormant volcano People of Italy • 2000 BCE – the Italic tribes settled in the central part of Italy • Latins were the most important of the Italic tribes. • Mainly good farmers who knew little about civilization. • Fights for the land between the Greeks, Etruscans and Latins Etruscans • 1000 B.C.E. – Etruscans came to Italy. • Were highly civilized – good craftsmen, traders, sailors, and shipbuilders • Knew how to write • Taught Italians what they knew Etruscan Art Etruscan influence • • • • • Rome became civilized Wall around the city 1st sewer system Arches in architecture Ruled as kings Founding of Rome • 1400 BCE Latins moved near the Tiber river. • City of Rome was founded – Surrounded by 7 hills – 1st settlement was a village of huts on the Palatine hill Legend of Romulus & Remus • Rome founded in 753 B.C.E. • Founder was Romulus, who was raised with his twin brother, Remus, by a she-wolf Roman Religion • Influenced by both Etruscans and Greeks • Personalities and legends of Greek gods and goddesses with different names • Rituals of Etruscans to win favor of the gods Roman Republic 509 B.C.E to 27 B.C.E • 509 B.C.E. – last Etruscan king forced out by the Latins & Republic started • Republic: form of government in which power rests with citizens who have a right to vote to select their leaders. Social Classes • Patricians: aristocratic landowners who held most of the power. Only ones who be elected to public office. • Plebeians: common farmers, artisans and merchants who were the majority of the population. • Citizens: free born Latin males 3 Branches of Government 1. Legislative (Senate/Assemblies) 2. Judicial (Praetors) 3. Executive (Consuls) Twelve Tables 1. Idea that all free citizens – both patricians and plebeians - had the right to protection of the law. (Rule of Law) 2. Written in 451 BC to prevent patricians from abusing law 3. Influenced all European law, even US law: -innocent until proven guilty - right to face your accuser Consuls • Consuls: 2 officials that commanded the army and directed the government. – 1 year term – 10 years between terms – Could veto the other consul Senate • Aristocratic branch of the government with legislative and administrative functions • 300 members of Patrician class – Plebeians later allowed into senate – Position for life – Controlled foreign & economic policy – Advised the consuls Assemblies • Assembly of Centuries (aka Centuriate Assembly) was made up of all citizen-soldiers – Patrician controlled – Less power than senate – Appointed consuls • Assembly of Tribes (aka Tribal Assembly) was made up of plebeians – Elected tribunes – Made laws for common people (eventually everyone) Dictator • In times of crisis – republic could appoint a dictator – Absolute power to make laws and command army – Power lasted for 6 months – Chosen by consul and elected by senate • 1st dictator was Sulla Punic Wars 264 to 146 BCE • • • • Rome vs. Carthage 3 different wars Hannibal & Scipio Rome becomes the dominant force in the Mediterranean Collapse of the Republic 1. Wide gap between rich & poor (majority) 2. Slaves (POWs) worked on huge Roman farms called latifunidas 3. Small farmers and returning soldiers became homeless 4. Civil War First Triumvirate • Triumvirate: group of 3 rulers • Julius Caesar, Crassus & Pompey • Caesar wins a civil war and was named dictator for life – absolute ruler • Adored by people Caesar’s Reforms • Expanded the Senate to 900 members, most loyal to him •Gave land to the poor •Used public works to create jobs •Raised pay for soldiers •Expanded Roman citizenship to people from the provinces Beware the Ides of March March 15, 44 BCE Second Triumvirate • Octavian – Caesar’s nephew & heir • Mark Antony – Caesar’s second-in-command • Lepidus – commander of Caesar’s cavalry • Doesn’t last long! Lepidus forced into exile… • Mark Antony & Octavian divide the Empire in half: Octavian takes the West, Antony the East Roman Empire 27 BCE to 476 CE • Octavian Augustus becomes 1st Roman Emperor – rules for 45 years • Keeps the Senate under control, but the army is the real basis of his power •Expands the Roman Empire •Gives land to his soldiers •Reforms Roman tax system •Build extensive road system to protect & control the provinces •Began the PAX ROMANA “Roman Peace” – 100 years of peace & prosperity Rome’s Expansion • Spread around Mediterranean, Europe and into parts of Africa and Asia • Success due to – Well-trained professional army – Extensive road system – Treated conquered people well (international law) – Extensive bureaucracy The Five “Good” Emperors Nerva Hadrian Trajan -Vast building projects (bridges, roads, aqueducts -Reorganized bureaucracy -Defended against invaders -Maintained peace & prosperity Antonius Pius Marcus Aurelius Fall of the Roman Empire • Economy declines as trade was disrupted, inflation occurred, and harvests failed • Barbarian invasions led to use of mercenaries • Loss of patriotism and corruption of politicians Legacy of Rome • Arts & Literature – Sculptures, Mosaics – Virgil, Ovid and Tacitus • Language: – Latin – Basis for French, Spanish, English, etc. • System of law: – All person had the right to equal treatment under the law – Innocent until proven guilty – Burden of proof on accuser – Punished for actions, not thoughts – A grossly unfair law could be set aside.