* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The glory that was Greece
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Legislative assemblies of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Roman architecture wikipedia , lookup
Conflict of the Orders wikipedia , lookup
Executive magistrates of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Slovakia in the Roman era wikipedia , lookup
Switzerland in the Roman era wikipedia , lookup
Roman Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Elections in the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Roman funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Romanization of Hispania wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republican governors of Gaul wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
First secessio plebis wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Constitution of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman technology wikipedia , lookup
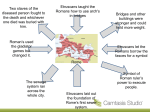
PAGES 128-131 THE ROMAN WORLD TAKES SHAPE SETTING THE SCENE Romans loved stories of heroes Horatius Single handedly held off Etruscan army while his fellow Romans tore down the bridge behind him He then dove into the river with the bridge and swam to safety on the other side This story tells us the virtues that Romans admired Courage Loyalty Devotion to duty Geography Rome began as a small city-state on the Italian peninsula which is centrally located on the Mediterranean Sea. Rome is the center of Italy Italy was much easier to unify than Greece Apennine Mountains are less rugged. Broad fertile plains in the north & in the west supported a growing population People 800BC Latins migrated into Italy Settled along the Tiber River in small villages over seven low-lying hills These Latins were the ancestors to the Romans Their villages grew into Rome, the city on 7 hills Etruscans Greek colonists shared Italian peninsula with Romans Etruscans even ruled over Rome for a time Romans adapted the alphabet, the use of the arch in building, and gods & goddesses from the Etruscans The Roman Republic 509BC Founding of the Roman state by driving out their Etruscan ruler Set up a republic to keep one person from too much power Senate was most powerful governing body 300 members were patricians, landholding upper class Made the laws & served for life 2 consuls Elected by the senators Supervised the business of the government Commanded the armies Rome had system of checks on the power of government During war senate could choose a dictator, but they could only rule for 6 months and then had to give up their power Plebeians Farmers, Merchants, Artisans, & Traders Made up most of population, but had no influence 450BC Government had laws of Rome inscribed on 12 tablets 1st breakthrough for Plebeians because they had protested that no one knew all of the laws because they were not written down Plebeians eventually gained right to elect their own officials called tribunes Tribunes could veto laws they felt were harmful to Plebeians Plebeians eventually were elected to consuls & other high offices, & then the Senate. 2,000 years later U.S. adapted a Senate, the Veto, & political checks on power Roman Society Family was the basic unit of Roman society Roman law stated the male was the head of household, & had absolute power His wife was subject to his authority, & was not allowed to take care of her own affairs Roman Women Played a larger role in society than Greek women Most worked at home raising their family, spinning, & weaving Women gained more freedom as the centuries passed on. They were eventually allowed to: Go to public baths Dine out Attend theater Have political influence Roman Education & Religion Girls & boys learned to read & write Children began learning about history later in the republic Roman gods & Greek gods shared similarities Jupiter is Zeus Juno is Hera Neptune is Poseidon Expansion Rome succeeded because of a loyal & well-trained army 5,000 men made up a legion Fought without pay & supplied their own weapons Rewards & harsh punishment Showing courage in battle would get you gifts, but if your unit fled from a battle….1 out of 10 men in the unit were put to death Defeated enemies had to acknowledge Roman leadership, pay taxes, & supply soldiers, & in return they got to keep their own customs & local government. Rome placed soldiers throughout the empire & built allweather military roads This began the unification of Italy under the Roman Empire