* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Republic - s3.amazonaws.com
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Berber kings of Roman-era Tunisia wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Roman Senate wikipedia , lookup
Leges regiae wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Legislative assemblies of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Senatus consultum ultimum wikipedia , lookup
Executive magistrates of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Augustus wikipedia , lookup
Conflict of the Orders wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
First secessio plebis wikipedia , lookup
History of the Constitution of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Treaties between Rome and Carthage wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
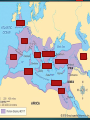
The Roman Republic RISE OF AN EMPIRE The Republic Geography: Peninsula –on the Mediterranean Sea Rome is located halfway between Alps and Sicily Tiber River –the legend of Romulus and Remus Fewer mountains & less rugged than Greece Fertile land The Republic First Settlers 1. Etruscans - Native to northern Italy 2. Greeks - Colonized southern Italy and Sicily 3. Latins - Built the original settlement at Rome The Republic republic: officials chosen by the people (citizens) Patricians: wealthy landowners who held most power Plebeians: most people farmers, merchants, traders, artisans had little influence The Twelve Tables A written law code that was carved on 12 tablets. The Twelve Tables established the idea that all free citizens had a right to protection of the law. The Republic senate: 300 patricians (landholding upper class) consuls: two patrician executives elected by senate, must consult them dictator: elected during a crisis to rule for six months Plebeians Rising Assembly: representative group of plebians tribunes: elected to protect plebeian interests, had veto power Laws of the Twelve Tables written laws plebeians appeal decisions by patrician judges Legacy Plebeians gain access to high offices and senate Did not have to use war or revolution to gain power U.S. adopts senate, veto, checks on power Roman Legacy Aqueducts Sanitation Roads Irrigation Education Medicine Roman Legions all male citizens who owned land required to serve in army legion: group of 6000 men well-trained, disciplined treated conquered people pretty well The Punic Wars st 1 Punic War Carthage – competing with Rome for trade, control Carthage has strong navy, Rome builds one to fight it Rome wins, gains Sicily nd 2 Punic War Hannibal General from Carthage attacked Rome by land (with elephants!) defeated by Scipio rd 3 Punic War Romans still not satisfied after 50 years of peace “Carthago delenda est” Carthage must be destroyed! Romans attack AND burn Carthage enslave people Rome now controls the Mediterranean Problems in the Republic Provinces complain of corrupt officials Wealthy Romans take land from small farmers Slaves are used on big farms (latifundia). This pushes small farmers and workers into cities Problems in the Republic The Gap between rich and poor widens The poor revolt Slaves revolt too Spartacus slaves led 70,000 Reform Attempts 2 Brothers try to help Tiberius Gracchus Wanted to redistribute (give back) land to the poor BUT, he was killed by senate Gaius Gracchus Same reforms, same fate The Army Changes This is the beginning of a professional fighting force Soldiers become more loyal to generals than republic!!!! paid, equipped soldiers (mercenaries) gave land to veterans Closer look at the 12 Tables Read the 12 tables Reword each in words that your little brothers or sisters could understand Then, tell me some similarities you see with Hammurabi’s Code (I have class sets if you need it) and the laws here in America