* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download dr._mather-brown_presentation
Duffy antigen system wikipedia , lookup
Inflammation wikipedia , lookup
Gluten immunochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Herd immunity wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Major histocompatibility complex wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Social immunity wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
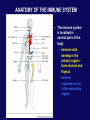
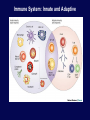
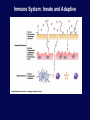
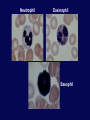
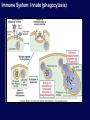
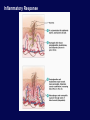
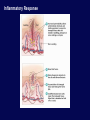
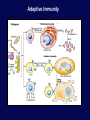
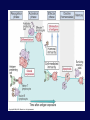
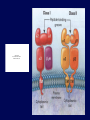
Immune System Overview GOT DEFENSE? ANATOMY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM • The immune system is localized in several parts of the body – immune cells develop in the primary organs bone marrow and thymus – immune responses occur in the secondary organs IMMUNITY Adaptive Innate Players Humoral •Macrophages •Granulocytes •Natural killer cells •Complement •Other chemicals Characteristics •Action is immediate; minutes to hours •Response is nonspecific •First line of defense against invading pathogens •Response is not enhanced on repeated exposure to pathogen Cell-Mediated Players •Antigen Presenting Cells •T cells •B cells •Antibodies Characteristics •Action requires days to develop •Response is specific •Prevents progression to disease •Response is enhanced on repeated exposure to pathogen Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Cytokines • Soluble protein molecules used by cells of the immune system to communicate. • Functions include: – Mediation of natural immunity – Regulation of lymphocyte activation, growth, and differentiation – Regulation of immune-mediated inflammation – Stimulation of immature leukocyte growth and differentiation • Interleukins (IL-2 & IL-4), interferons ( ), tumor necrosis factors ( and ), and transforming growth factor Immune System: Innate and Adaptive 2. The immune system consists of: Innate (non-specific) immunity •Anatomic barriers (Skin,mucous membranes) •Physiological barriers (temperature, pH) •Phagocytic Barriers (cells that eat invaders) •Inflammatory barriers (redness, swelling, heat and pain) Adaptive (specific) immunity Neutrophil Eosinophil Basophil Monocytes Dendritic cell Immune System: Innate (phagocytosis) 1. Phagocytic cells: Macrophage, Neutrophil, and Dendritic cells. 2. Phagocytosis serves two key functions: • Killing microbes • Antigen (Ag) Presentation QuickTime™ and a Photo - JPEG decompressor are needed to see this picture. GOT DEFENSE? QuickTime™ and a GIF decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a Cinepak decompressor are needed to s ee this pic ture. Immune System: Innate (phagocytosis) Opsonization Immune System: Innate Inflammation • A hallmark of innate immunity • Local accumulation of immune cells and molecules against • microbes Function to eliminate infections but often cause tissue damage & diseases Inflammatory Response Inflammation Inflammatory Response The immune system consists of: Innate (non-specific) immunity Adaptive (specific) immunity •Anatomic barriers (Skin,mucous membranes) •Antigen specificity •Physological barriers (temperature, pH) •Phagocytic Barriers (cells that eat invaders) •Inflammatory barriers (redness, swelling, heat and pain) •Diversity •Immunological memory •Self/nonself recognition Adaptive Immunity Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) • • • • • Also known as Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) Membrane bound, not soluble “Present” processed protein antigens (peptides) to naïve T cells MHC I -> produced by almost all nucleated cells, present antigen to CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) MHC II -> produced by “professional” antigen presenting cells, present antigen to CD4+ lymphocytes (T helper cells) QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. T Cell Receptors (TCRs) • • • • • • Produced by T lymphocytes Are surface bound, not secreted Recognize “processed” peptide antigens presented on MHC molecules Heterodimer of or chains Like antibodies, each chain has a variable and constant region Also undergo gene rearrangement prior to expression The immune system has evolved to: •Protect against invading pathogens or foreign substances. •Maintain tissue homeostasis. • Meanwhile, microbes have evolved to survive in the host.